Difference Between Acute and Subacute Endocarditis
Key Difference – Acute vs Subacute Endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is a microbial infection of the heart valves or the mural endocardium that leads to the formation of vegetations composed of thrombotic debris and organisms often associated with the destruction of underlying cardiac tissues. Depending on the time taken for the development of symptoms, infective endocarditis is further divided into two subcategories as acute endocarditis and subacute endocarditis. The key difference between these two forms is, there is a sudden onset of symptoms in acute endocarditis whereas in subacute endocarditis the symptoms develop over a prolonged period of time.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Infective Endocarditis
3. What is Acute Endocarditis
4. What is Subacute Endocarditis
5. Similarities Between Acute and Subacute Endocarditis
6. Side by Side Comparison – Acute vs Subacute Endocarditis in Tabular Form
7. Summary
What is Infective Endocarditis?
Infective endocarditis is a microbial infection of the heart valves or the mural endocardium that leads to the formation of vegetations composed of thrombotic debris and organisms often associated with the destruction of underlying cardiac tissues. Bacteria are the commonest causative agents of infective endocarditis though it is possible to be due to the infections by other categories of organisms also. There are main two varieties of infective endocarditis as acute and subacute endocarditis. This classification is made based on the speed with which the clinical features develop.
Risk Factors
- Intravenous drug abuse
- Poor dental hygiene
- Intravascular cannulae
- Soft tissue infections
- Cardiac surgery and permanent pacemakers
Clinical Features Consistent With Both Forms of Infective Endocarditis
- New valve lesion/ regurgitant murmur
- Embolic events of unknown origin
- Sepsis of unknown origin
- Hematuria, glomerulonephritis and renal infarctions
- Fever
- Peripheral abscesses of unknown origin
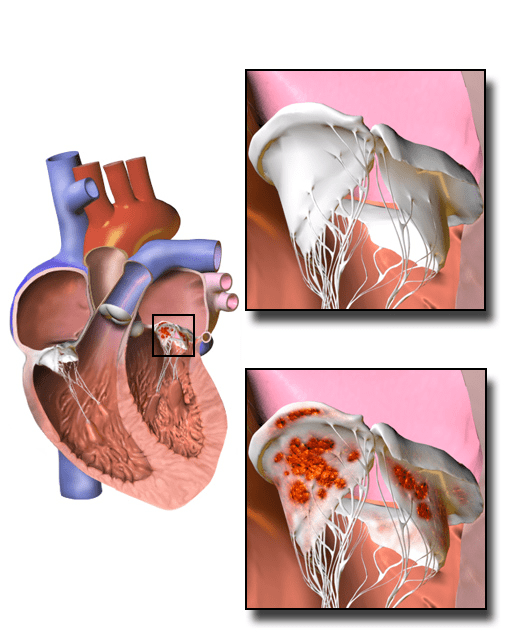
Fig 01: Infective Endocarditis
Modified Duke’s Criteria for the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis
Major Criteria
- Blood culture/s positive for a characteristic organism or persistently positive for an unusual organism
- Echocardiographic evidence confirming the valvular lesions
- New valvular regurgitation
Minor Criteria
- Predisposing heart lesions or intravenous drug use
- Fever
- Vascular lesions such as Janeway lesions and splinter hemorrhages
- Microbiologic evidence including a single culture positive for an unusual organism
Investigations
- Blood cultures
- Echocardiogram
Management
Antibiotic treatment has to be commenced as soon as possible. For starting the empirical antibiotic therapy blood samples should be taken to be sent to cultures. Antibiotic therapy has to be continued for 4-6 weeks. The patient should respond to the antibiotics within the first 48 hours of their administration. The effectiveness of the therapy will be shown by the resolution of fever, decline in the level of serum markers of infection and relief of systemic symptoms. Surgical intervention is necessary when the patient does not respond to the antibiotic therapy.
What is Acute Endocarditis?
Acute endocarditis is typically caused by a highly virulent organism that infects a previously normal heart valve resulting in the rapid development of necrotizing and destructive lesions. The commonest causative agent isolated from heart valves that are affected by acute endocarditis is Staphylococcus aureus. Acute endocarditis is difficult to be cured with antibiotics alone and require surgical removal of the vegetations most of the time. Acute endocarditis is characterized by the sudden onset of fever, malaise, chills, and lastitude.
What is Subacute Endocarditis?
Subacute endocarditis is due to the infection of previously damaged cardiac valves by low virulent bacteria such as Viridans streptococci. There is only a minimal destruction of the cardiac valves.
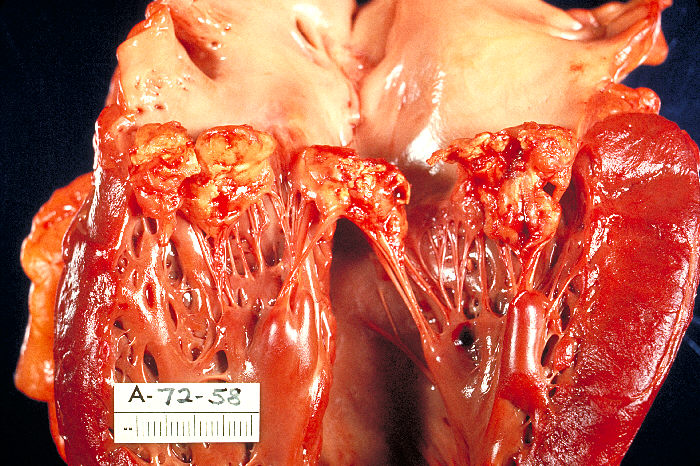
Figure 02: Valvular Changes in Endocarditis
The appearance of symptoms mentioned above usually happens few weeks after the initial infection. Subacute endocarditis can be treated only with antibiotics.
What is the Similarity Between Acute and Subacute Endocarditis?
- Valves of the heart are affected in both forms of endocarditis
What is the Difference Between Acute and Subacute Endocarditis?
Acute Endocarditis vs Subacute Endocarditis | |
| Acute endocarditis is typically caused by a highly virulent organism that infects a previously normal heart valve resulting in the rapid development of necrotizing and destructive lesions. | Subacute endocarditis is due to the infection of previously damaged cardiac valves by low virulent bacteria such as Viridans streptococci. |
| Cause | |
| Acute endocarditis is caused by organisms with a high virulence. | Subacute endocarditis is caused by organisms with a low virulence. |
| Affected Valves | |
| Previously normal cardiac valves are also affected. | Subacute endocarditis affects previously damaged cardiac valves only. |
| Therapy | |
| Antibiotic therapy alone is not sufficient to cure acute endocarditis. Surgical removal of the vegetation is necessary to have a successful outcome. | Antibiotic therapy can cure subacute endocarditis completely. |
| Symptoms | |
| There is a rapid onset of symptoms. | Symptoms develop over a protracted period of time. |
Summary – Acute vs Subacute Endocarditis
Acute endocarditis is typically caused by a highly virulent organism that infects a previously normal heart valve resulting in the rapid development of necrotizing and destructive lesions. On the other hand, subacute endocarditis is due to the infection of previously damaged cardiac valves by low virulent bacteria such as Viridans streptococci. In acute endocarditis, there is a sudden onset of symptoms unlike in subacute form of the disease in which case the development of symptoms takes at least few weeks.
Download the PDF Version of Acute vs Subacute Endocarditis
You can download PDF version of this article and use it for offline purposes as per citation note. Please download PDF version here Difference Between Acute and Subacute Endocarditis
Reference:
1.Kumar, Parveen J., and Michael L. Clark. Kumar & Clark clinical medicine. Edinburgh: W.B. Saunders, 2009.
2.Kumar, Vinay, Stanley Leonard Robbins, Ramzi S. Cotran, Abul K. Abbas, and Nelson Fausto. Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. 9th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Elsevier Saunders, 2010.
Image Courtesy:
1.’Endocarditis’By BruceBlaus – Own work, (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.’Haemophilus parainfluenzae Endocarditis PHIL 851 lores’ By Public Health Image Library (PHIL), (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26twq6rnmWRo7FuwtJmqq6akZjCtbGMnqWdp5OWv6W106KqaA%3D%3D