Difference Between Agaricus and Polyporus
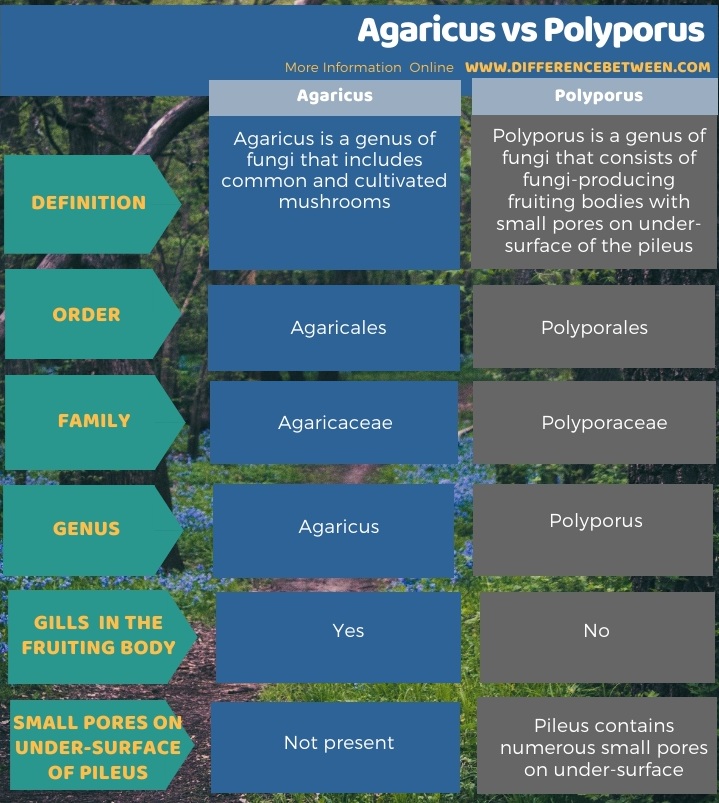
The key difference between Agaricus and Polyporus is that Agaricus is a genus of fungi that produces edible as well as poisonous fruiting bodies called mushrooms, while Polyporus is a genus of poroid fungi that forms large fruiting bodies with pores or tubes on the underside.
Fungi are eukaryotic microorganisms that have chitin in their cell walls. They belong to a separate kingdom called kingdom fungi. Yeast, mushrooms and molds are several familiar types of fungi. Many fungi are multicellular while few are unicellular. Ascomycota and Basidiomycota are two major phyla of kingdom Fungi. Basidiomycota is a large division of fungi that consists of mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, polypores, jelly fungi and other several groups. Agaricus and Polyporus are two genera of Basidiomycota.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Agaricus
3. What is Polyporus
4. Similarities Between Agaricus and Polyporus
5. Side by Side Comparison – Agaricus vs Polyporus in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Agaricus?
Agaricus is a genus of fungi that includes best known and most widely consumed mushrooms. This genus consists of more than 300 species, including edible and poisonous species. This genus is characterized by the production of fleshy and light-coloured cap and stem that raises the mushroom above the substrate it grows. Agaricus fungal species are mainly saprophytic. They grow on soil, decaying litter, manure piles, forest floor and wood logs, etc. Generally, they grow best on moist and shady places. Especially in the rainy season, Agaricus fungi are seen everywhere.
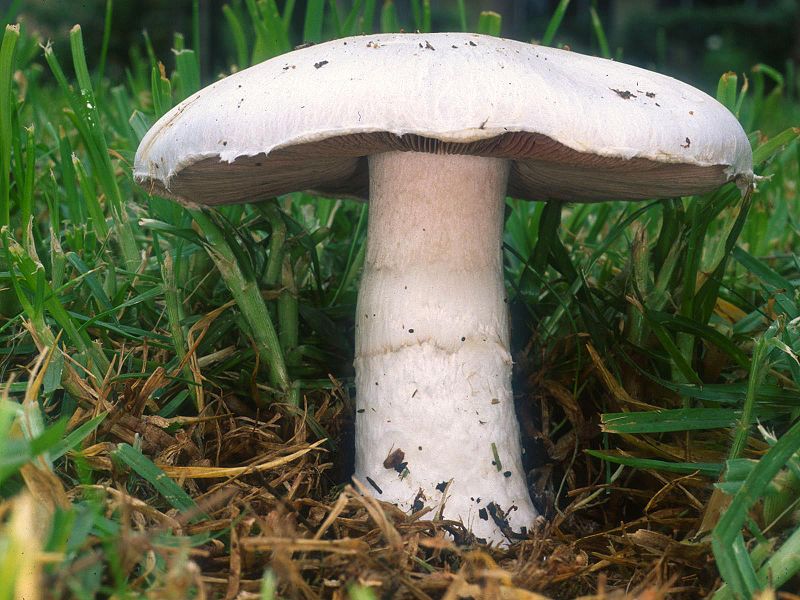

Figure 01: Agaricus
Agaricus fungi have two main structural parts: vegetative mycelium and fruiting body or the basidiocarp. Basidiocarp has three main parts: stipe, pileus and annulus. Stipe is the basal part of the fruiting body while pileus is the umbrella-shaped cap. Mycelia of Agaricus fungi are multicellular and filamentous. In addition, Agaricus fungi reproduce via sexual as well as asexual reproduction.
What is Polyporus?
Polyporus is a genus of fungi belonging to order Polyporales and family Polyporaceae. All Polyporus species are poroid fungi characterized by having fruiting bodies with centrally-placed stipes and pores on the underside of the cap.
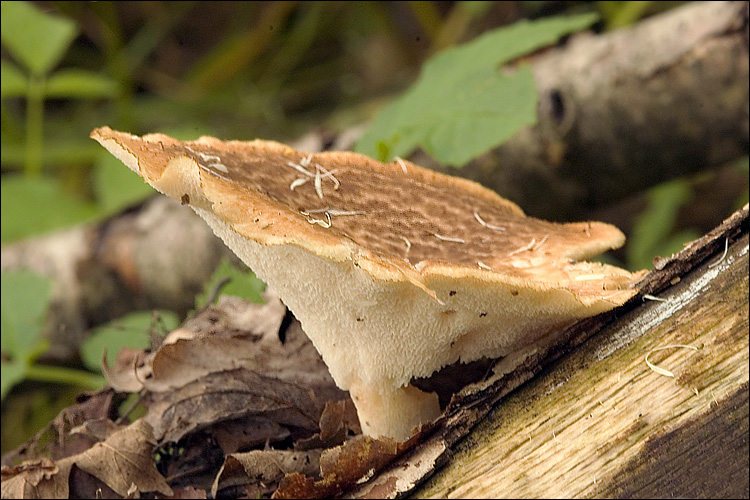

Figure 02: Polyporus
There are about 50 different species included in this genus. They are popular as wood-rotting fungi. Similar to Agaricus fungi, Polyporus fungi have two structural parts as vegetative mycelium and basidiocarp. The special feature of the basidiocarp of Polyporus fungi is that pileus does not have any gills in the underside. However, it contains numerous small pores on under-surface.
What are the Similarities Between Agaricus and Polyporus?
- Agaricus and polyporus are two fungi belonging to Kingdom Fungi and phylum Basidiomycota.
- They belong to class Agaricomycetes.
- Both fungi produce fruiting bodies.
- Moreover, they are saprophytes.
- They produce umbrella-shaped cap or pileus.
- In both genera, there are species that produce edible fruiting bodies.
What is the Difference Between Agaricus and Polyporus?
Agaricus is a genus of fungi that includes common and cultivated mushrooms. On the other hand, Polyporus is a genus of fungi that consists of fungi producing fruiting bodies with small pores on under-surface of the pileus. So, this is the key difference between Agaricus and Polyporus. Agaricus is a genus that belongs to Agaricales while Polyporus is a genus that belongs to Polyporales. Therefore, this is also a difference between Agaricus and Polyporus.
The structural difference between Agaricus and Polyporus is that fruiting bodies of Agaricus fungi have gills in the under the surface while fruiting bodies of Polyporus fungi do not have gills.
Summary – Agaricus vs Polyporus
In summarizing the difference between Agaricus and Polyporus, Agaricus and Polyporus are two genera of fungi belonging to Basidiomycota. Agaricus is a genus that consists of fungi that are known as common mushrooms. In contrast, Polyporus is a genus that consists of pore fungi. Pore fungi are characterized by having fruiting bodies with numerous fine pores on the under-surface. Moreover, fruiting bodies of Polyporus fungi do not have gills, unlike the fruiting bodies produced by Agaricus fungi. Both Agaricus and Polyporus fungi are saprophytes.
Reference:
1. “Agaricus: Habitat, Structure and Reproduction.” Biology Discussion, 3 Mar. 2016, Available here.
2. “Polyporus: Habitat, Vegetative Mycellium and Reproduction.” Biology Discussion, 3 Mar. 2016, Available here.
Reference:
1. “Agaricus campestris” (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “2009-05-12 Polyporus tuberaster (Jacq.) Fr 43277” By user amadej trnkoczy (amadej) at Mushroom Observer, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26txpqpopulqHqiusNmp6ikqaW8s8HSaA%3D%3D