Difference Between Anterograde and Retrograde Amnesia
The key difference between anterograde and retrograde amnesia is that anterograde amnesia refers to the inability to create new memories while retrograde amnesia refers to the inability to recall past memories.
Amnesia is a form of memory loss caused by brain damage or diseases. It can also happen due to various sedatives and hypnotic drugs. The memory can be completely lost or partially lost. Amnesia is associated mainly with the damage to the medial temporal lobe. There are three major types of causes as head trauma, traumatic events and physical deficiencies. Anterograde amnesia and retrograde amnesia are the two main types of amnesia. Those suffering from anterograde amnesia cannot create new memories, while those suffering from retrograde amnesia cannot recall facts or past experiences.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Anterograde Amnesia
3. What is Retrograde Amnesia
4. Similarities Between Anterograde and Retrograde Amnesia
5. Side by Side Comparison – Anterograde vs Retrograde Amnesia in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Anterograde Amnesia?
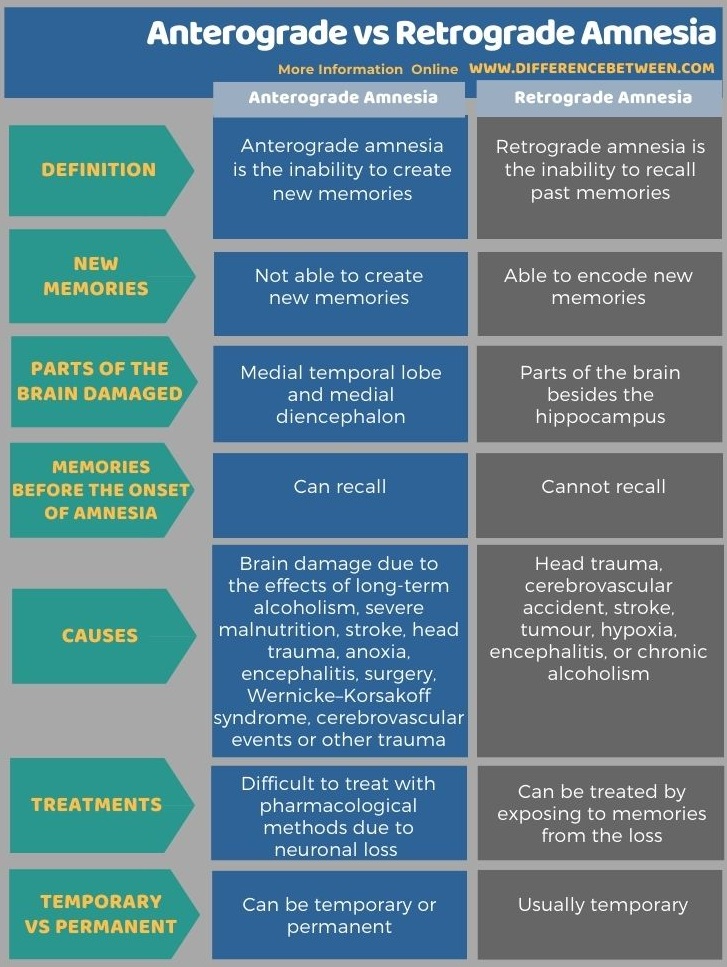
Anterograde amnesia is the inability to form new memories due to brain damage. Patients cannot transfer new information from short term store to long term store. Hence, they cannot remember things for a long period of time. But long-term memories from before the event remain intact.

Anterograde amnesia condition can be temporary or permanent. It can happen due to the effects of long-term alcoholism, stroke, head trauma, severe malnutrition, encephalitis, surgery, cerebrovascular events, Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome, anoxia or other trauma. Medial temporal lobe and medial diencephalon are the two major regions associated with this condition.
What is Retrograde Amnesia?
Retrograde amnesia is the inability to recall past memories. These patients are unable to retrieve information that was acquired before the onset of the amnesia condition. They lose existing and previously made memories. Some people lose memory extending to a long time ago, while others may lose only a few months of memory. Most importantly, they can make new memories after the incident.
Retrograde amnesia is mainly caused due to the head trauma or brain damage to parts of the brain besides the hippocampus. Besides, stroke, tumour, hypoxia, encephalitis, or chronic alcoholism can also cause this condition. Retrograde amnesia is usually temporary. Hence, they can be treated by exposing them to memories from the loss.
What are the Similarities Between Anterograde and Retrograde Amnesia?
- In both types of amnesia, memory loss takes place due to brain damage.
- They are not mutually exclusive, and they can occur simultaneously.
- The severity of anterograde amnesia is usually correlated with the severity of retrograde amnesia.
- They tend to occur together in the same patients.
- Moreover, anterograde amnesia can sometimes occur in the absence of retrograde amnesia.
What is the Difference Between Anterograde and Retrograde Amnesia?
Anterograde amnesia is the inability to create new memories while retrograde amnesia is the inability to recall past memories. So, this is the key difference between anterograde and retrograde amnesia. Anterograde amnesia patients can remember past memories while retrograde amnesia patients can form new memories. Anterograde amnesia is difficult to treat with pharmacological methods due to neuronal loss while retrograde amnesia can be treated by exposing the patient to past memories.
Moreover, anterograde amnesia can be temporary or permanent while retrograde amnesia is usually temporary.
Below infographic shows more details of the difference between anterograde and retrograde amnesia.
Summary – Anterograde vs Retrograde Amnesia
Anterograde amnesia and retrograde amnesia are two major types of amnesia. Anterograde amnesia refers to the incapability of forming new memories due to brain damage while retrograde amnesia refers to the incapability of recalling past memories due to brain damage. Thus, this is the key difference between anterograde and retrograde amnesia.
Reference:
1. Barclay, Rachel. “Amnesia: Types, Symptoms, and Causes.” Healthline, Healthline Media, 8 Oct. 2013, Available here.
2. “Amnesia”. En.Wikipedia.Org, 2020, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “4894438” (CC0) via Pixabay
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26tza2cq6eXp66lsYyapZ1loprBs7vGq5idnV2Wuq%2Bx0qKYaA%3D%3D