Difference Between Antigenic and Phase Variation
The key difference between antigenic and phase variation is that antigenic variation is the mechanism that refers to the expression of antigenically distinct proteins, carbohydrate or lipids on their surfaces while phase variation is the high frequency reversible on and off switching of phenotype expression.
Antigenic and phase variation are two types of molecular mechanisms used by pathogens in order to avoid host immune responses. They are related to each other. These mechanisms allow microbes, especially bacteria, to adapt to more than one environment. As a result of phase and antigenic variation, a heterogenic phenotype of a clonal bacterial population is formed. In this population, individual cells express phase variable proteins or one of the multiple antigenic forms of the protein. These variations are mainly virulence strategies executed by pathogens.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Antigenic Variation
3. What is Phase Variation
4. Similarities Between Antigenic and Phase Variation
5. Side by Side Comparison – Antigenic vs Phase Variation in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Antigenic Variation?
Antigenic variation is a molecular mechanism that refers to the expression of functionally conserved and antigenically distinct moieties within a clonal population. Using this mechanism, infectious agents alter their proteins, carbohydrates or lipids, which are antigens present on their surfaces. Thus, due to antigenic variation, pathogens can periodically change or switch the molecular composition of their surface antigens. By altering those structures, they avoid host immune responses. There is a wide variety of surface structures in animal pathogens due to antigenic variation as well as phase variation. Pathogens temporarily camouflage themselves and prevent elimination of the entire population by the host’s immune system. Best examples for bacteria that show antigenic variation are genera Neisseria and Streptococci. Neisseria species vary their pili as a result of antigenic variation. It helps these species in adhesion. In contrast, Streptococci alter their M protein.
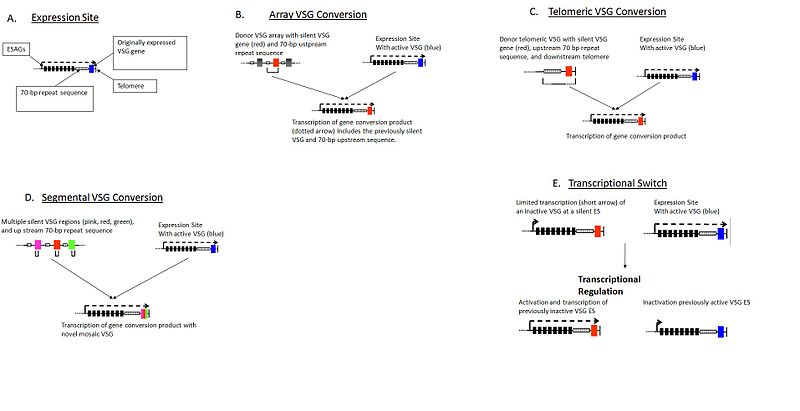
Figure 01: Antigenic Variation
Viruses are able to alter their genomes very fast and trick the immune system into not recognizing them. This is due to the antigenic variation seen in viruses. There are six different forms of antigenic variation as antigenic drift, shift, rift, lift, sift, and gift.
What is Phase Variation?
Phase variation is a molecular mechanism which allows bacteria and other microbes to avoid host immune responses. Moreover, it allows bacteria to deal with varying environments. Phenotypic variation can be defined as the switching of protein expression from an ON to an OFF phase. In other words, phase variation refers to the high frequency on and off switching of phenotype expression. As a result of phase variation, the level of expression of protein varies between individual cells of a population. These variations usually occur randomly at high frequency. However, they can be modulated by environmental conditions. In the end, phase variation results in a phenotypically heterogeneous population.
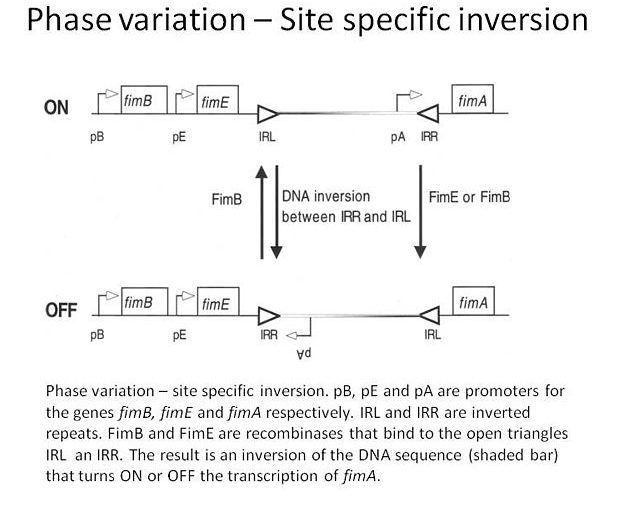
Figure 02: Phase Variation
Phase variation takes place in a range of organisms, including bacteria and nonbacterial forms such as protozoans and viruses, etc. One example of phase variation in gram-negative bacteria is the changes in observable phenotypes seen in surface structures such as fimbria, flagella, outer membrane proteins and lipopolysaccharides.
What are the Similarities Between Antigenic and Phase Variation?
- Phase and antigenic variation result in a heterogenic phenotype of a clonal bacterial population.
- Antigenic and phase variation contribute to bacterial virulence and help the bacterium evade the host immune system
- As a result of these mechanisms, pathogens have a wide variety of surface structures.
What is the Difference Between Antigenic and Phase Variation?
Antigenic variation refers to the expression of functionally conserved and antigenically distinct moieties within a clonal population. On the other hand, phase variation is the switching of protein expression from an ON to an OFF phase. So, this is the key difference between antigenic and phase variation. Also, as a result of antigenic variation, pathogens alter their proteins, carbohydrates or lipids, which are antigens present on their surfaces. In contrast, as the result of phase variation, pathogens vary the level of expression of proteins between individual cells of a population.
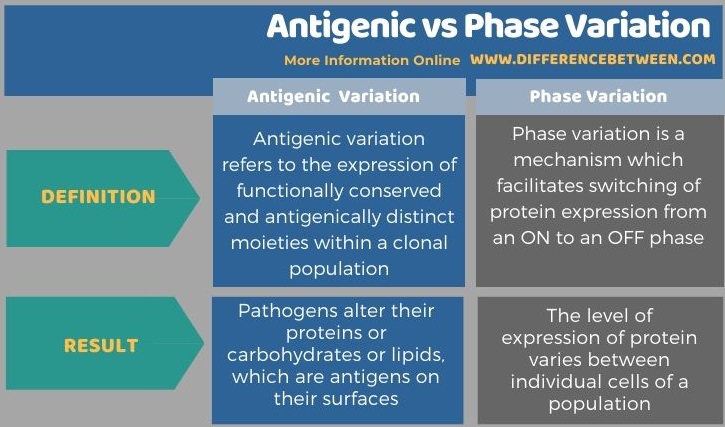
Summary – Antigenic vs Phase Variation
Antigenic and phase variation are two molecular mechanisms that aid infectious agents to avoid host immune responses. Antigenic variation results in alteration of surface antigens (proteins, carbohydrates and lipids) in order to trick the host antibodies not to recognize them. On the other hand, phase variation varies the level of expression of proteins between individual cells of a population. It is done by the high frequency on and off switching of phenotype expression. Thus, this summarizes the difference between antigenic and phase variation.
Reference:
1. Henderson, Ian R. et al. “Molecular Switches – The ON And OFF Of Bacterial Phase Variation”. Molecular Microbiology, vol 33, no. 5, 1999, pp. 919-932. Wiley, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01555.x. Accessed 28 Apr 2020.
2. “Antigenic Variation – An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics”. Sciencedirect.Com, 2020, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Mechanisms of antigenic variation” By Chris Stockdale, Michal R. Swiderski, J. David Barry, Richard McCulloch – PLoS Biology (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Mechanisms of antigenic variation” By Marjan W. van der Woude and Andreas J. Baumler – Clinical Microbiology Reviews (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26tza2goJ2enrBurc2dZKmgkaiybsLAq6CarJmku3A%3D