Difference Between Autoimmune Disease and Immune Deficiency
Key Difference – Autoimmune Disease vs Immune Deficiency
Let us first briefly regard what is immune system before looking at the difference between autoimmune disease and immune deficiency. The immune system is the defense system of the body which helps to protect self-tissues from harmful external agents. Autoimmune diseases are caused by overactive immune system leading to damage of self-tissues and organs in the absence of a harmful stimulus. Immune deficiency is a disease where the immune system is not capable of mounting an immune response against foreign material, organisms due to a single or multiple defects in the immune system. This is the key difference between autoimmune disease and immune deficiency.
What is Autoimmune Disease?
Autoimmune diseases are caused by inappropriate activation of the immune system causing damage to self-tissues. The immune system develops antibodies or cell mediated immunity against our own tissues in the absence of a harmful stimulus. This leads to the damage of self-tissues causing vital organ failures. Although the etiology is not clear, genetic susceptibility and environmental agents such as ultraviolet rays, drugs (e.g. hydralazine) are known to induce autoimmunity. These diseases can occur as systemic or local. Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE), Systemic Sclerosis (SS), and Rheumatoid Arthritis diseases are some examples of systemic diseases where multiple organs are affected. Examples of local diseases where only a single organ is affected are Grave’s disease, Myasthenia gravis, etc. In these conditions, specific antibodies against various cell or nuclear receptors can be detected in the patient’s serum, which are helpful as biomarkers in the diagnosis. Autoimmune diseases are treated with immune suppressants such as steroids, methotrexate, and azathioprine. These conditions occur more commonly among middle age females but not necessarily. The autoimmune disease usually has a remitting and relapsing course. Prognosis vary depending on the extent of the organs affected.
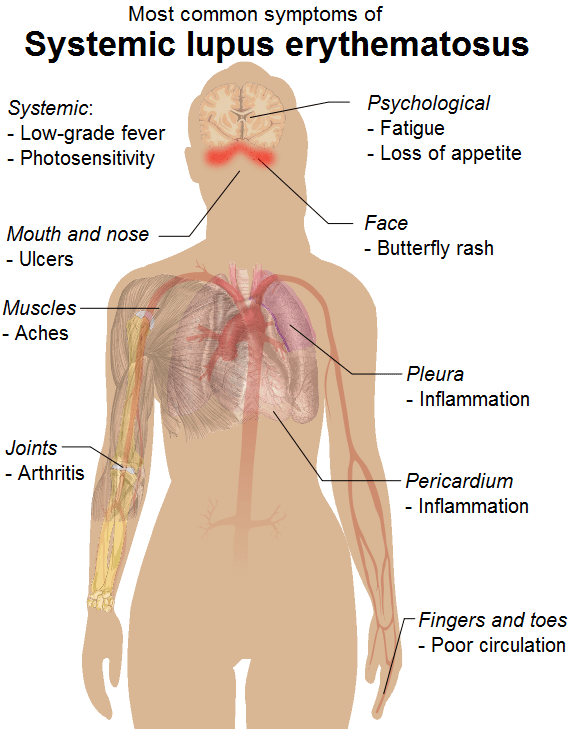
Systemic Lupus Erythematous is an example of autoimmune disease
What is Immune Deficiency?
Immune deficiency is the lack of single or multiple components of the immune system. Therefore, these patients are not capable of mounting an effective immune response against certain pathogens depending on the missing component. For example, these defects can be in cellular immunity, humoral immunity or in the complement system. Immune deficiency can be inherited or acquired immunity. This can occur due to some disease like diabetes, HIV or drugs such as immune suppressants. Typically, these patients suffer from recurrent or atypical infections. Diagnosis is based on the detection of the missing component of the immune system by laboratory assays. Treatment is mainly by prevention of infections by immunization, prophylactic antibiotics as well as by replacement of the missing component of the immune system in certain cases. These patients will have poor quality lifestyle due to recurrent infections. A permanent cure is not usually possible, and some cases can be treated with stem cell transplantation. These patients need lifelong follow-up and care.
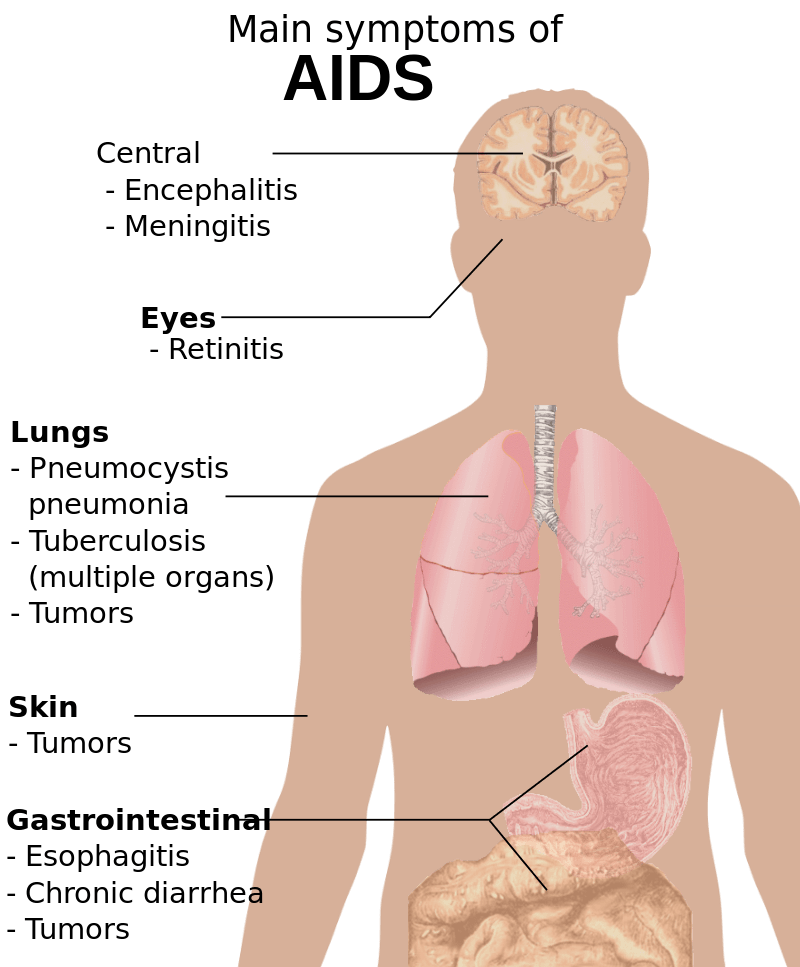
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
What is the difference between Autoimmune Disease and Immune Deficiency?
Definitions of Autoimmune Disease and Immune Deficiency:
Autoimmune Disease: Autoimmunity is caused by an overactive immune system in the absence of a pathogen.
Immune Deficiency: Immune deficiency is caused by an insufficient immune response in the presence of a pathogen or opportunistic organism.
Characteristics of Autoimmune Disease and Immune Deficiency:
Age
Autoimmune Disease: Autoimmune disease is common in middle age people.
Immune Deficiency: In immune deficiency, age distribution varies depending on the underlying cause.
Sex
Autoimmune Disease: Autoimmune disease is common among females.
Immune Deficiency: No specific sex distribution for immune deficiency.
Course
Autoimmune Disease: Autoimmune disease has a remitting and relapsing course.
Immune Deficiency: Immune deficiency is static and may increase in severity with time.
Etiology
Autoimmune Disease: Autoimmune disease is multifactorial
Immune Deficiency: Immune deficiency is caused by a specific genetic defect or environmental cause leading to suppression of single or multiple components of the immune system.
Diagnosis
Autoimmune Disease: Immune biomarkers are helpful in the diagnosis with the typical associations of symptoms and signs for autoimmune diseases.
Immune Deficiency: Immune deficiency is diagnosed by detecting the missing component of the immune system by specific laboratory assays.
Treatment
Autoimmune Disease: Autoimmune disease is treated with immune suppressants.
Immune Deficiency: Immune deficiency is treated by replacing the missing component with transfusions, prevention of infections with immunization and prophylaxis or in selected cases with stem cell transplantation.
Image Courtesy: “Symptoms of SLEH” äggström, Mikael. “Medical gallery of Mikael Häggström 2014“. Wikiversity Journal of Medicine 1 (2). (CC0) via Commons “Symptoms of AIDS” by Häggström, Mikael. “Medical gallery of Mikael Häggström 2014”. Wikiversity Journal of Medicine 1 (2). (CC0) via CommonsncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26t1K2moqWdqrumecOiqp6Zo5p6orrDZq2sZZmiura6xGabnp6ZmLamusKyZg%3D%3D