Difference Between Bohr and Rutherford Model
Key Difference – Bohr vs Rutherford Model
The concept of atoms and their structure was first introduced by John Dolton in 1808. He explained the laws of the chemical combination by considering atoms as invisible particles without a structure. Then in 1911, the New Zealand physicist Ernest Rutherford proposed that atoms consist of two components: a positively charged nucleus in the center of the atom and negatively charged electrons in the extranuclear part of the atom. Certain theories such as electromagnetic theory presented by Maxwell could not be explained with Rutherford’s model. Because of such limitations in Rutherford’s model, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr proposed a new model in 1913 based on the quantum theory of radiations. Bohr’s model was largely accepted and he was awarded the Nobel Prize for his work. Even though it was largely accepted, it still carries certain drawbacks and limitations. The main difference between Bohr model and Rutherford model is that in Rutherford model, electrons can revolve in any orbit around the nucleus, whereas in Bohr model, electrons can revolve in a definite shell.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Bohr Model
3. What is Rutherford Model
4. Side by Side Comparison – Bohr vs Rutherford Model in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Bohr Model?
Bohr’s model was proposed by Niels Bohr in 1922 to explain the structure of the atom. In this model, Bohr mentioned that the most of the atomic mass lies in the central nucleus that contains protons and electrons are arranged in definite energy levels and revolve around the nucleus. The model also proposed electronic configuration, which explains the arrangement of electrons in circular orbits designated as K, L, M, N, etc. Atoms with complete electron configurations are not active. Electron configuration determines the reactivity of the atom.
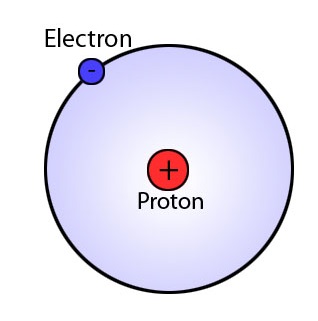
Bohr’s model is able to explain the spectrum of the hydrogen atom, but it cannot fully explain the reactivity of multielectron atoms. Moreover, it does not explain the Zeeman Effect, where each spectral line split up into more lines in the presence of an external magnetic field. In this model, an electron is considered only as a particle. However, a French physicist, de Broglie discovered that electrons have both wave and particle properties. Later on, a physicist put forth another principle called Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, which explains the impossibility of the simultaneous determination of exact position and momentum of small moving particles such as electrons. With this invention, Bohr’s model faced a serious setback.
What is Rutherford Model?
In 1911, Ernest Rutherford proposed Rutherford’s model. It states that the atom (the volume) consists mainly of space and the mass of the atom is centered in the nucleus, which is the core of the atom. The nucleus is positively charged and the electron orbit around the nucleus. The orbits have no definite paths. Moreover, since atoms are neutral, they have equal positive (in the nucleus) and negative charges (electrons).
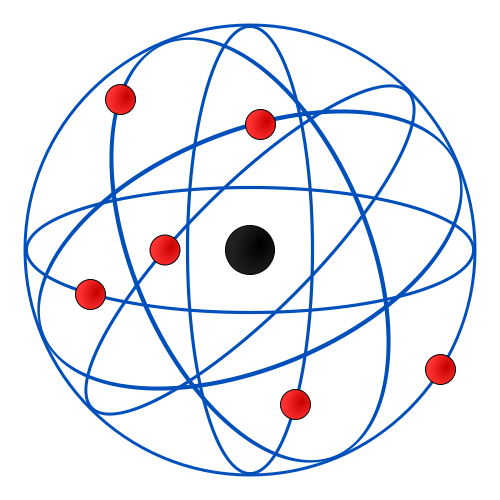
Rutherford’s model failed to explain the electromagnetic theory, the stability of atom and the existence of definite lines in the hydrogen spectrum.
What is the Difference Between Bohr and Rutherford Model?
Bohr vs Rutherford Model | |
| Bohr model was proposed by Niels Bohr in 1922. | Rutherford model was proposed by Ernest Rutherford in 1911. |
| Theory | |
| Most of the atomic mass lies in the central nucleus, which contains protons, and the electrons are arranged in definite energy levels or shells. | Most of the atom consists of empty space. The center of the atom contains a positively charged nucleus and its negatively charged electrons are present in the space surrounding the nucleus. |
| Emission of Radiation of Electrons | |
| Electrons only emit waves of definite frequencies. | Electrons emit waves of all frequencies. |
| Electron Emission Spectrum | |
| Electron emission spectrum is a line spectrum. | Electron emission spectrum is a continuous spectrum. |
Summary – Bohr vs Rutherford Model
Both Bohr and Rutherford models are planetary models that explain the atomic structure up to a certain extent. These models have limitations and do not explain some modern principles of physics. However, these models greatly contribute towards modern advanced models that explain the atomic structure. Bohr model states that most of the atomic mass is in the central nucleus, which contains protons and, that electrons are arranged in definite energy levels or shells, resulting in electron line spectrum. Rutherford’s model states that most of the atom consists of an empty space and the center of the atom contains a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons, resulting in continuous electron spectrum. This is the difference between Bohr and Rutherford Model.
Download PDF Version of Bohr vs Rutherford Model
You can download PDF version of this article and use it for offline purposes as per citation notes. Please download PDF version here Difference Between Bohr and Rutherford Model.
References:
1. Tarendash, A. S. Let’s review: chemistry, the physical setting. Barron’s Educational Series, 2006. Print.
2. Warren, D. Chemists in a social and historical context: chemists are real people, living in the real world. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2001. Print.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Bohr model” By Jia.liu – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Rutherford atom” By Own work (CreateJODER Xd Xd) (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26uzqGpZpmemXq3v4yrrK2glaezsL7DZqSonJWhfA%3D%3D