Difference Between Carbonate and Bicarbonate
The key difference between carbonate and bicarbonate is that the carbonate ion has -2 electrical charge whereas, the bicarbonate has -1 electrical charge.
The human body produces carbon dioxide as a by-product of metabolism. Most of this carbon dioxide dissolves in blood plasma and present in the form of bicarbonate. Carbonate and bicarbonate system is mainly responsible for maintaining our blood pH value, and they act as a buffer in our blood. When carbon dioxide dissolves in water, bicarbonate and carbonic acid forms, and there is an equilibrium between these species.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Carbonate
3. What is Bicarbonate
4. Side by Side Comparison – Carbonate vs Bicarbonate in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Carbonate?
Carbonate is an inorganic ion containing a carbon atom and three oxygen atoms. It has a negative divalent charge (-2 electrical charge). Carbonate ion has a trigonal planar geometry, and its molecular weight is 60 g mol-1.
Although the Lewis structure of carbonate ion has one carbon-oxygen double bond and two carbon-oxygen single bonds, it is not the actual structure. Carbonate ion shows resonance stabilization. Hence, it has a hybrid structure of all resonance structures. Therefore, all the carbon-oxygen bonds have a similar length, and the oxygen atoms have a partial negative charge (hence, all the oxygen atoms are similar.).
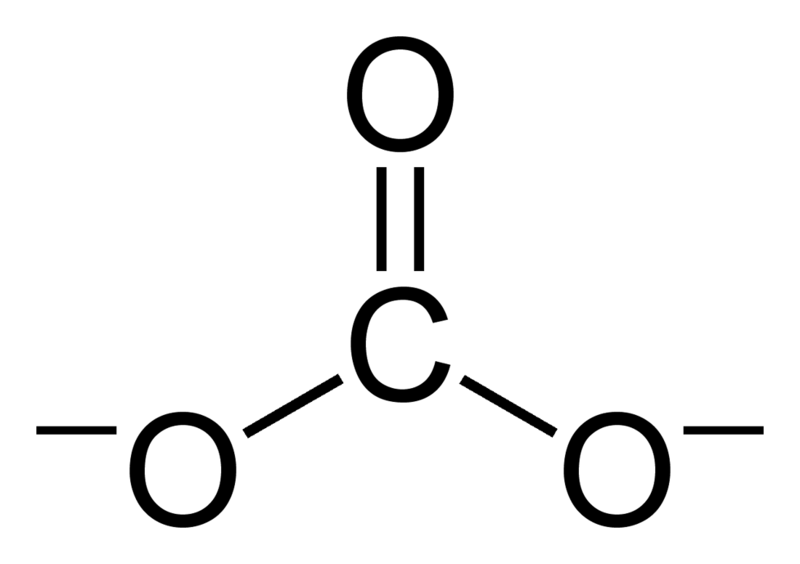
Figure 01: Chemical Structure of Carbonate Ion
When carbon dioxide or bicarbonate dissolves in water, carbonate ions form. And, this ion is in equilibrium with bicarbonate ions. Naturally, it combines with another metal ion or another positive ion to make compounds. There are various types of carbonate rocks, such as limestone (calcium carbonate), Dolomite (calcium- magnesium carbonate), potash (potassium carbonate) etc.
Furthermore, carbonate compounds play a crucial role in the carbon cycle. With time, the compounds containing carbon converts into sedimentary rocks when they deposit for a long time. Then, when these rocks are weathering, carbon dioxide is released back to the atmosphere. Likewise, when heating these compounds, they release carbon dioxide easily. Further, carbonate compounds are ionic, and they are insoluble in water.
What is Bicarbonate?
Bicarbonate is a monovalent anion having one hydrogen, one carbon and three oxygen atoms. It forms from deprotonation of carbonic acid. It has trigonal planar geometry around the central carbon atom. Bicarbonate ion has a molecular weight of 61 g mol-1.
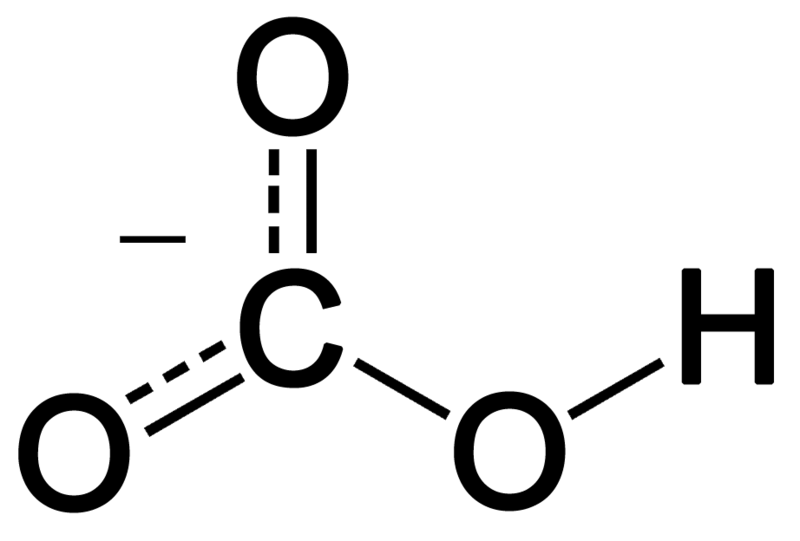
Figure 02: Resonance Structure of Bicarbonate Ion
Moreover, this ion shows resonance stabilization between the two oxygen atoms, which are not connected to hydrogen. In nature, bicarbonate is alkaline, and it is the conjugate acid of the carbonate ion and the conjugate base of the carbonic acid. Furthermore, the positively charged ions can combine with the negatively charged oxygen in this ion and form ionic salts. The most common salt of bicarbonate is sodium bicarbonate, which we name as baking powder in everyday use. Moreover, bicarbonate compounds release carbon dioxide when reacting with acids.
What is the Difference Between Carbonate and Bicarbonate?
Carbonate and bicarbonate are inorganic anions. The key difference between carbonate and bicarbonate is that the carbonate ion has -2 electrical charge whereas, the bicarbonate has -1 electrical charge. Moreover, due to the presence of the hydrogen atom, the molar mass of carbonate ion is 60 g/mol while the molar mass of bicarbonate ion is 61 g/mol.
Another significant difference between carbonate and bicarbonate is that, in strongly basic conditions, there will be more carbonate ions, whereas, bicarbonate ions will be more in weak basic solution. Furthermore, the ability to dissolve in water also contributes to a difference between carbonate and bicarbonate. That is; the compounds with carbonate ions are not soluble in water at the room temperature and atmospheric pressure. However, many bicarbonate salts are soluble in water at room temperature.
Below is a summary of the difference between carbonate and bicarbonate in tabular form.
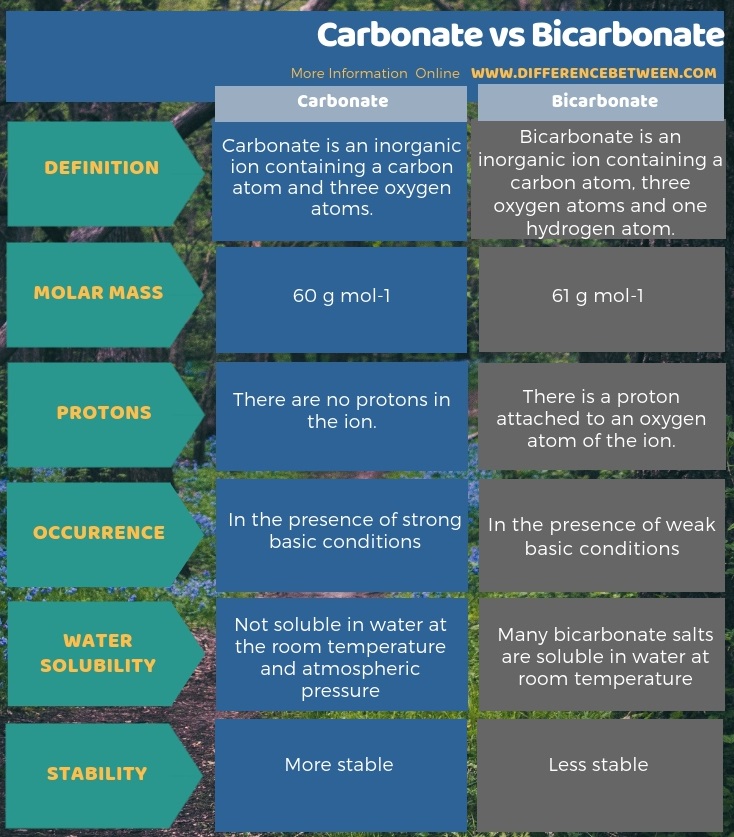
Summary – Carbonate vs Bicarbonate
Both carbonate and bicarbonate are ions containing carbon and oxygen atoms. However, bicarbonate ion has a hydrogen atom as well. Therefore, this hydrogen atom causes the ion to become monovalent anions while the carbonate is a divalent anion. In summary, the key difference between carbonate and bicarbonate is that the carbonate ion has -2 electrical charge whereas, the bicarbonate has -1 electrical charge.
Reference:
1. Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. “Carbonate.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 20 July 1998. Available here
2. “Bicarbonate Ion.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Carbonate-ion-localised-2D”By Ben Mills – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”Bicarbonate-resonance”By Hellbus – Own work, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vwKuZqKaRqbJurc2dZK%2BrXZe2pK3Rm6anmaSafA%3D%3D