Difference Between Carboxylic Acid and Ester
Carboxylic Acid vs Ester
Carboxylic acids and esters are organic molecules with the group –COO. One oxygen atom is bonded to carbon with a double bond, and the other oxygen is bonded with a single bond. Since only three atoms are connected to the carbon atom, it has a trigonal planar geometry around it. Further, the carbon atom is sp2 hybridized. Carboxyl group is a widely occurring functional group in chemistry and bio chemistry. This group is the parent of related family of compounds known as acyl compounds. Acyl compounds are also known as carboxylic acid derivatives. Ester is a carboxylic acid derivative like that.
Carboxylic Acid
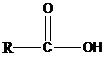
Carboxylic acids are the organic compounds having the functional group –COOH. This group is known as the carboxyl group. Carboxylic acid has a general formula as follows.
In the simplest type of carboxylic acid, R group equals to H. This carboxylic acid is known as formic acid. Despite formic acid, there are many other types of carboxylic acids with various R groups. The R group can be a straight carbon chain, branched chain, aromatic group, etc. Acetic acid, hexanoic acid, and benzoic acid are some of the examples for carboxylic acids. In the IUPAC nomenclature, carboxylic acids are named by dropping the final –e of the name of the alkane corresponding to the longest chain in the acid and by adding –oic acid. Always, the carboxyl carbon is assigned number 1. According to this, the IUPAC name for acetic acid is ethanoic acid. Other than the IUPAC names, many of the carboxylic acids have common names.
Carboxylic acids are polar molecules. Because of the –OH group, they can form strong hydrogen bonds with each other, and with water. As a result, carboxylic acids have high boiling points. Further, carboxylic acids with lower molecular weights easily dissolve in water. However, as the length of the carbon chain increases, the solubility decreases. Carboxylic acids have an acidity ranging from pKa 4-5. Since they are acidic, they react readily with NaOH and NaHCO3 solutions to form soluble sodium salts. Carboxylic acids like acetic acid are weak acids, and they exist in equilibrium with its conjugate base in aqueous media. However, if the carboxylic acids have electron withdrawing groups like Cl, F, they are acidic than the unsubstituted acid.
Ester
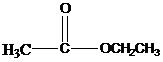
Esters have a general formula of RCOOR’. Esters are made by the reaction between a carboxylic acid with an alcohol. Esters are named by writing the names of the alcohol derived part first. Then the name derived from the acid part is written with the ending –ate or –oate. For example, ethyl acetate is the name of the following ester.
Esters are polar compounds. But they don’t have the capability to form strong hydrogen bonds to each other due to the lack of hydrogen bounded to oxygen. As a result, esters have lower boiling points compared to acids or alcohols with similar molecular weights. Often esters have a pleasant smell, which is responsible for producing the characteristic smells of fruits, flowers, etc.
What is the difference between Carboxylic Acid and Ester? • Esters are carboxylic acid derivatives. • Carboxylic acids have a general formula of RCOOH. Esters have a general formula of RCOOR’. • Carboxylic acids can make strong hydrogen bonds, but esters cannot. • Boiling points of esters are lower than that of carboxylic acids. • Compared to lower molecular weight acids, esters often have pleasant odors. |
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vwKuZqLCpobakecCcoJ1lkaOxbsLSZpysrJWnfA%3D%3D