Difference Between Centriole and Centrosome
Key Difference – Centriole vs Centrosome
Centriole and centrosome are both components of Eukaryotic cells, which are adapted to carry many different cellular functions though there are exists a difference between them based on their structure and functional capabilities. The structural units of these two components are microtubules. Microtubules are composed of protein subunits known as tubulin, which is acidic in nature. They are essential components of the cytoskeleton and are involved in intracellular transport of organelles, cell migration, and segregation of chromosomes during the mitosis. The key difference between Centriole and centrosome is, the centrosome is considered as an organelle while centriole is not considered as an organelle. This article discusses the difference between centriole and centrosome in more detail.
What is Centriole?
Centriole is a key feature of eukaryotic cells and also found in most protists. However, plant and fungi cells lack centrioles. A centriole is made up of 9 triplets of microtubules arranging to form a cylindrical structure. A centriole is about 500 nm long and 200 nm in diameter. Centrioles are replicated during the S phase of cell cycle. Moreover, they form the basal body of flagella and cilia, which are important for the locomotion of cells. However, the structure of the centriole which makes the basal body is quite different; the wall is formed from nine sets microtubules with each set containing 2 microtubules, and two microtubules in the middle (9+2 arrangement).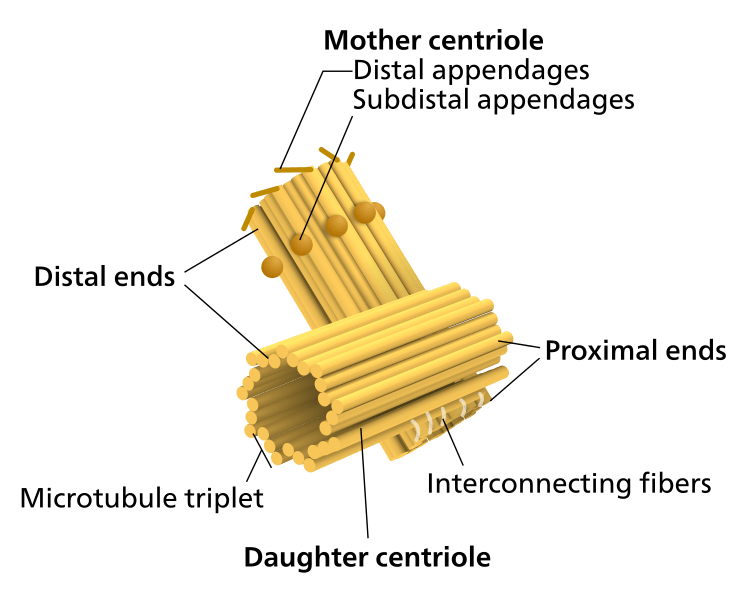
What is Centrosome?
Centrosome is an organelle found in the cytoplasm and located usually close to the nucleus. An amorphous mass of protein called pericentriolar material (PCM) is found around the centrosomes and is responsible for the nucleation of microtubule and anchoring. It is made up of two centrioles oriented at right angles to each other. The centrioles are replicated during the S phase of the cell cycle. During the onset of mitosis, two daughter centrioles start to move apart while forming the filaments of microtubules called mitotic spindle, which segregates the chromosomes into two sets. Surprisingly, recent studies found that centrosomes are not required for the progression of mitosis. The other important roles of centrosome include the formation of the cytoskeleton and releasing the signals to initiate the cytokinesis and cell cycle. It is found that cancer cells often have more than a normal number of centrosomes.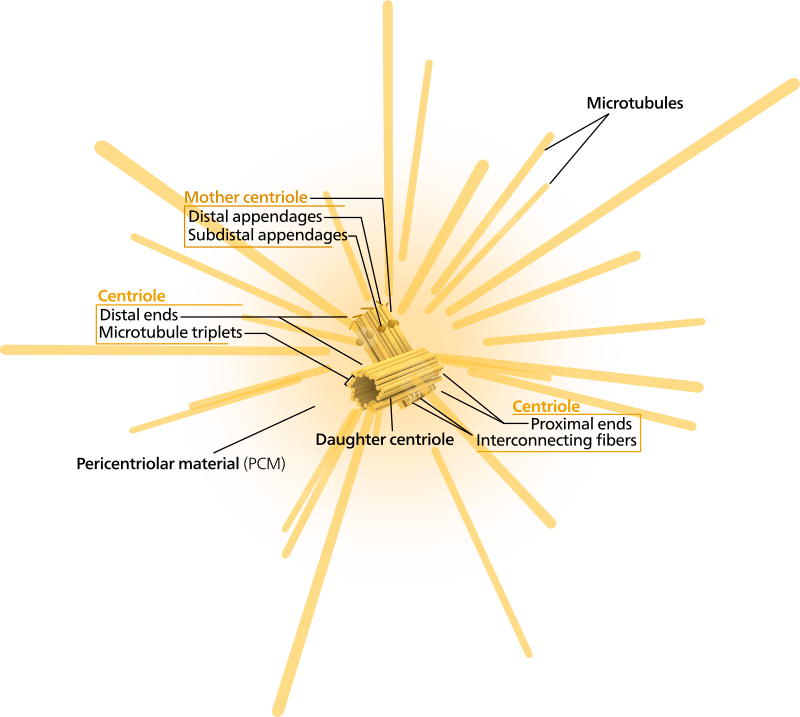
What is the difference Centriole and Centrosome?
Definition Centriole and Centrosome
Centriole: Centriole can be defined as each of a pair of minute cylindrical organelles near the nucleus in animal cells, involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
Centrosome: Centrosome can be defined as an organelle near the nucleus of a cell which contains the centrioles (in animal cells).
Characteristics of Centriole and Centrosome
Structure
Centriole: Centriole is made up of 9 triplets of microtubules arranging to form a cylindrical structure.
Centrosome: Centrosome is made up of two centrioles oriented at right angles to each other.
Functions
Centriole: Functions include the formation of the basal body of flagella and cilia, and also the centrosomes.
Centrosome: Functions include the formation of the spindle during the mitosis, the formation of the cytoskeleton and releasing the signals to initiate the cytokinesis and cell cycle.
Unlike centriole, the centrosome is considered as an organelle.
Image Courtesy: “Centriole-en” by Kelvinsong – Own work. (CC BY 3.0) via Wikimedia Commons “Centrosome (borderless version)-en” by Kelvinsong – Own work. (CC BY 3.0) via CommonsncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vxKerq6GfobJurc2dZK%2BrXZiyr8DRqKqopZVk