Difference Between Directional and Disruptive Selection
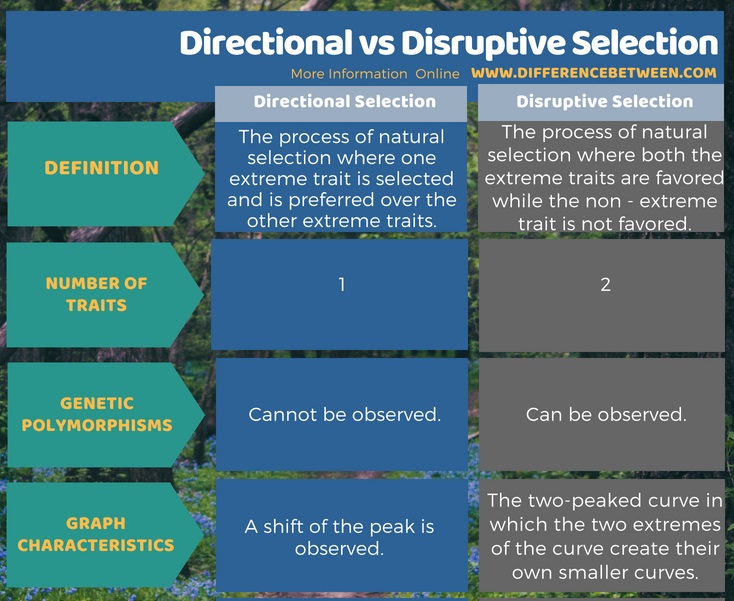
The key difference between directional and disruptive selection is that the directional selection prefers and selects only one extreme trait among the two extreme traits whereas the disruptive selection favours both extreme traits together.
The theories of directional and disruptive selection came into limelight with the introduction of the theory of Natural Selection by Charles Darwin, that explained the concept of evolution of many species. Therefore, directional and Disruptive selection are two types of natural selection which differ based upon the trait that favors during the process of evolution.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Directional Selection
3. What is Disruptive Selection
4. Similarities Between Directional and Disruptive Selection
5. Side by Side Comparison – Directional vs Disruptive Selection in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Directional Selection?
Directional selection is one way of natural selection. One extreme trait or phenotype prefers over the other during the directional selection. Thus, one extreme trait is selected against the other extreme trait. Therefore, this results in a population graph drift. This is due to the fact that the allele frequency changes over time causing a genetic drift.
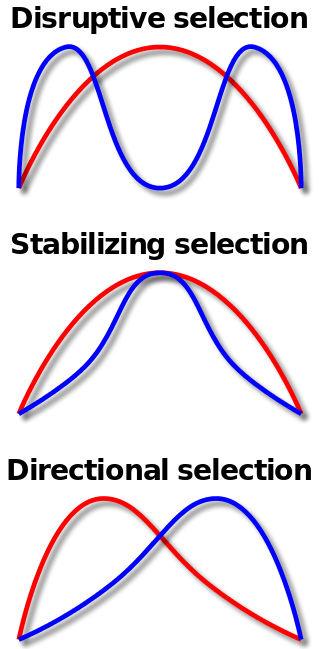
Figure 01: Directional Selection
The classic example of directional selection is the evolution of the giraffe neck. The extreme trait which is the short-necked giraffe could not reach as many leaves to feed, therefore with time the distribution shifted to the long-necked giraffes, which is the other extreme trait.
What is Disruptive Selection?
Disruptive selection is the selection of both the extreme traits due to a disruption of the middle non-extreme trait. This results in a two-peaked curve. This can be explained based on the phenomenon of plant height and their respective pollinators.
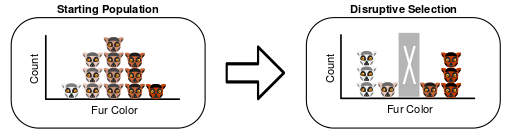
Figure 02: Disruptive Selection
Consider, if there are separate pollinators for tall, short and medium plants and when the pollinators of the medium plant disappear, what will happen? The population of plants will eventually shift towards the two extreme traits; short and tall. Thus, this population is termed as a polymorphic population as there is more than one form is existing.
What are the Similarities Between Directional and Disruptive Selection?
- Directional and Disruptive Selection are based on the theory of natural selection suggested by Charles Darwin.
- Both express extreme traits or phenotypes.
- They are not the most common type of natural selection.
What is the Difference Between Directional and Disruptive Selection?
The directional and disruptive selection are two types of natural selection methods. However, they are not the most common ways of natural selection. Directional selection explains the evolution of one extreme trait over the time while disruptive selection explains the evolution of both extreme phenotypes or traits over the time. Therefore, the difference between directional and disruptive selection is that the directional selection prefers and selects only one extreme trait among the two extreme traits whereas the disruptive selection favours both extreme traits together.
The below infographic details the difference between directional and disruptive selection in tabular form.
Summary – Directional vs Disruptive Selection
Natural selection is one of the theories put forward to explain evolution. Thus, these are different modes of natural selection. The directional and disruptive selection explains how the extreme traits are preferred over the non – extreme trait. The main difference between directional and disruptive selection is that in directional selection only one extreme trait is preferred whereas in disruptive selection both extreme traits are preferred.
Reference:
1.Boundless. “Boundless Biology.” Lumen, Open SUNY Textbooks. Available here
2.“Natural Selection.” SparkNotes, SparkNotes. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.Selectiontypes-n0 images (vector)”By File:Selectiontypes-n0 images.png (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”Disruptive Selection”By Keith Chan – Own work, (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26wyKucnKyZpLuiuIyapZ1llJ7As8HPraCvnV2osq2xwq2gqKZf