Difference Between DL Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate and D Alpha Tocopherol
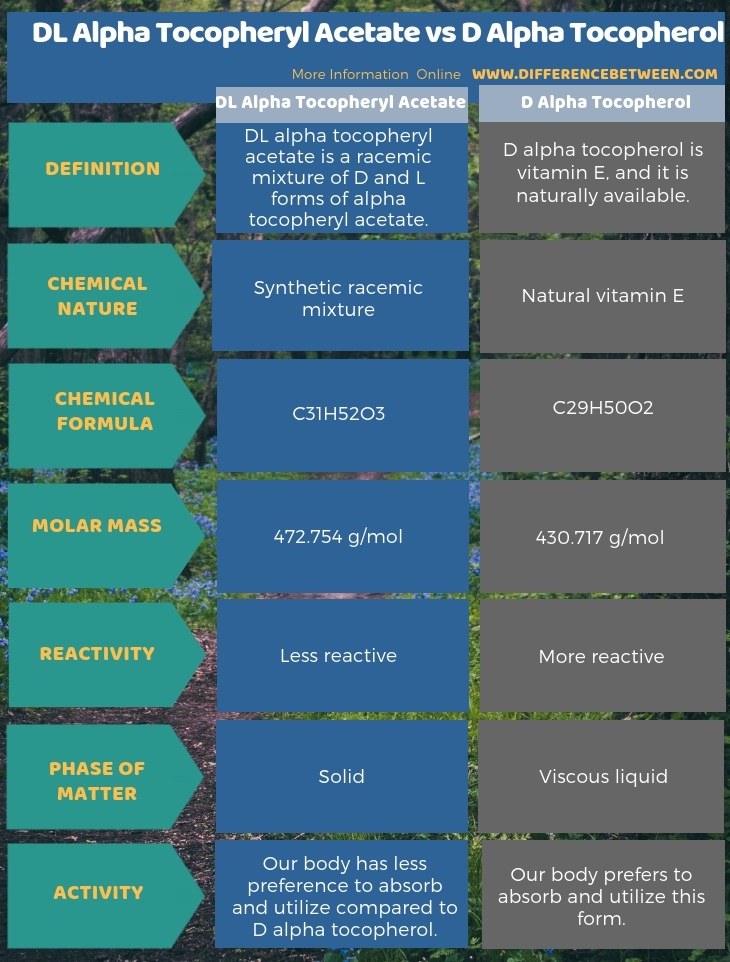
The key difference between DL alpha tocopheryl acetate and D alpha tocopherol is that the DL alpha tocopheryl acetate occurs as a synthetic racemic mixture whereas the D alpha tocopherol is a natural compound.
DL alpha tocopheryl acetate is a derivative of D alpha tocopherol. It is an ester form of D alpha tocopherol. Although the bioavailability of these two compounds is nearly equal to each other, there are differences between DL alpha tocopheryl acetate and D alpha tocopherol.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is DL Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate
3. What is D Alpha Tocopherol
4. Side by Side Comparison – DL Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate vs D Alpha Tocopherol in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is DL Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate?
DL alpha tocopheryl acetate is a racemic mixture of D and L forms of alpha tocopheryl acetate. Hence, it is a form of a synthetic mixture of tocopherol molecules, and it is one of the most potent antioxidant tocopherols. The chemical formula of alpha tocopheryl acetate (D or L form) is C31H52O3. Therefore, the molar mass of this compound is 472.754 g/mol.
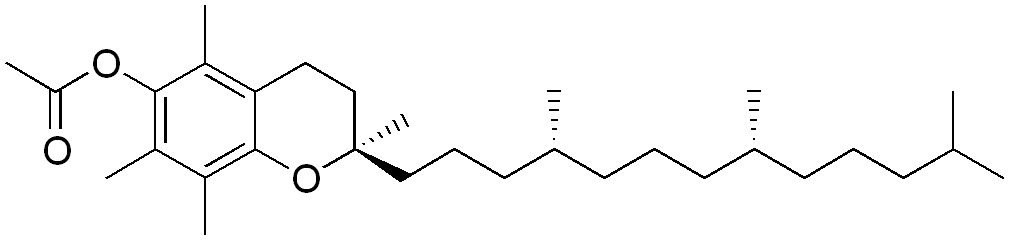
The antioxidant activity of this compound is due to the presence of phenolic hydrogen on the 2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol nucleus. Moreover, it has four methyl groups on 6-chromanol nucleus as well. However, the natural D form of alpha-tocopherol is more active than this racemic mixture. Apart from that, this racemic mixture contains alpha tocopherol in its ester form (acetate ester), that’s why we call it DL alpha tocopheryl acetate. Also, this compound is more resistant to oxidation; thus, the supplements containing this acetate form has a long shelf life. However, the bioavailability of this compound is nearly equal to the free alpha-tocopherol form.
What is D Alpha Tocopherol?
D alpha tocopherol is vitamin E, and it is naturally available. The chemical formula is C29H50O2. Thus, the molar mass is 430.717 g/mol. Moreover, it is a fat-soluble vitamin.
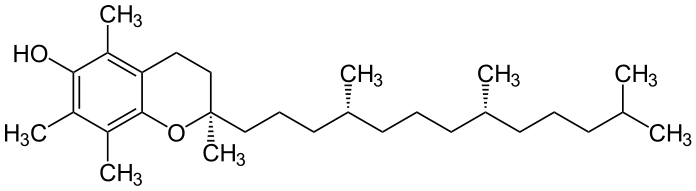
Furthermore, it is a potent antioxidant that is believed to be important in protecting cells from oxidative stress. Also, this is the more active form and the most bioavailable form of tocopherol. Therefore, our body prefers to absorb and utilize this form. Moreover, it appears as a yellow-brown viscous liquid. The melting point and boiling points are 3.5 °C and 200 to 220 °C respectively.
What is the Difference Between DL Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate and D Alpha Tocopherol?
DL alpha tocopheryl acetate is a racemic mixture of D and L forms of alpha tocopheryl acetate while D alpha tocopherol is vitamin E, and it is naturally available. The key difference between DL alpha tocopheryl acetate and D alpha tocopherol is that the DL alpha tocopheryl acetate occurs as a synthetic racemic mixture whereas the D alpha tocopherol is a natural compound. Moreover, the natural D form of alpha-tocopherol is more active than DL alpha tocopheryl acetate.
As another significant difference between DL alpha tocopheryl acetate and D alpha tocopherol, DL alpha tocopheryl acetate is available in solid form while D alpha tocopherol is in yellow-brown viscous liquid form. The below infographic provides more information on the difference between DL alpha tocopheryl acetate and D alpha tocopherol.
Summary – DL Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate vs D Alpha Tocopherol
DL alpha tocopheryl acetate is an ester derivative of D alpha tocopherol. The key difference between DL alpha tocopheryl acetate and D alpha tocopherol is that the DL alpha tocopheryl acetate occurs as a synthetic racemic mixture whereas the D alpha tocopherol is a natural compound.
Reference:
1. “Alpha-Tocopherol Acetate.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine. Available here
2. “Alpha-Tocopherol.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Tocopheryl acetate”By Edgar181 – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”Alpha-Tocopherol”By NEUROtiker – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26wy2aYpaiYlnq1u8Kop6Gdoq65bq3CnquarJVirq%2BwjJ1kmqSgna5uwM6cpqmglae8rXs%3D