Difference Between DNA Vaccine and Recombinant Vaccine
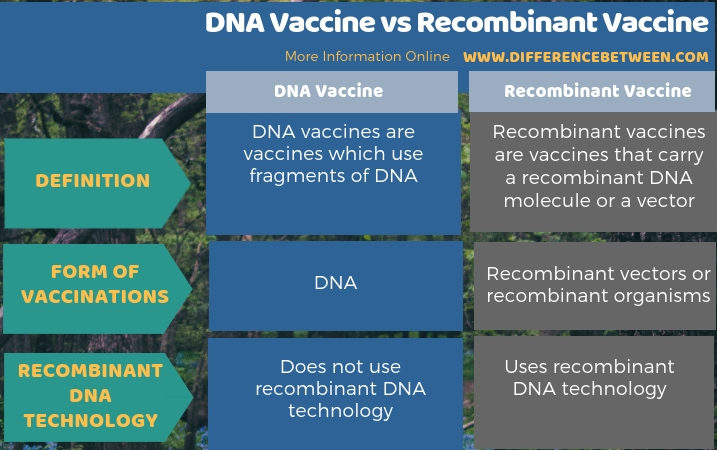
The key difference between DNA vaccine and recombinant vaccine relies on the preparation of vaccines. DNA vaccine preparation takes place using desired genes or DNA fragments, while recombinant vaccine preparation takes place using a recombinant molecule or a vector containing the desired gene fragment.
Vaccinations can be used as prophylactic treatment methods as well as therapeutic agents against infection. There are many forms of vaccinations. DNA and recombinant vaccines are the newest forms. Moreover, these vaccines are still under research.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is DNA Vaccine
3. What is Recombinant Vaccine
4. Similarities Between DNA Vaccine and Recombinant Vaccine
5. Side by Side Comparison – DNA Vaccine vs Recombinant Vaccine in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is a DNA Vaccine?
DNA vaccines are vaccines that contain DNA. They contain DNA that code for a specific protein that could act against pathogens. Ideally, they either code for antigens that mimic the pathogen to activate the host immune response or directly code for antibodies against a specific pathogen.
Furthermore, the administration of DNA vaccines takes place via encapsulating the DNA in a protein carrier. Upon entry, it will reach the target organ where they will remove its protein capsule and release the DNA. Then, this DNA will undergo transcription and translation using the host cellular mechanisms to give rise to the required protein.
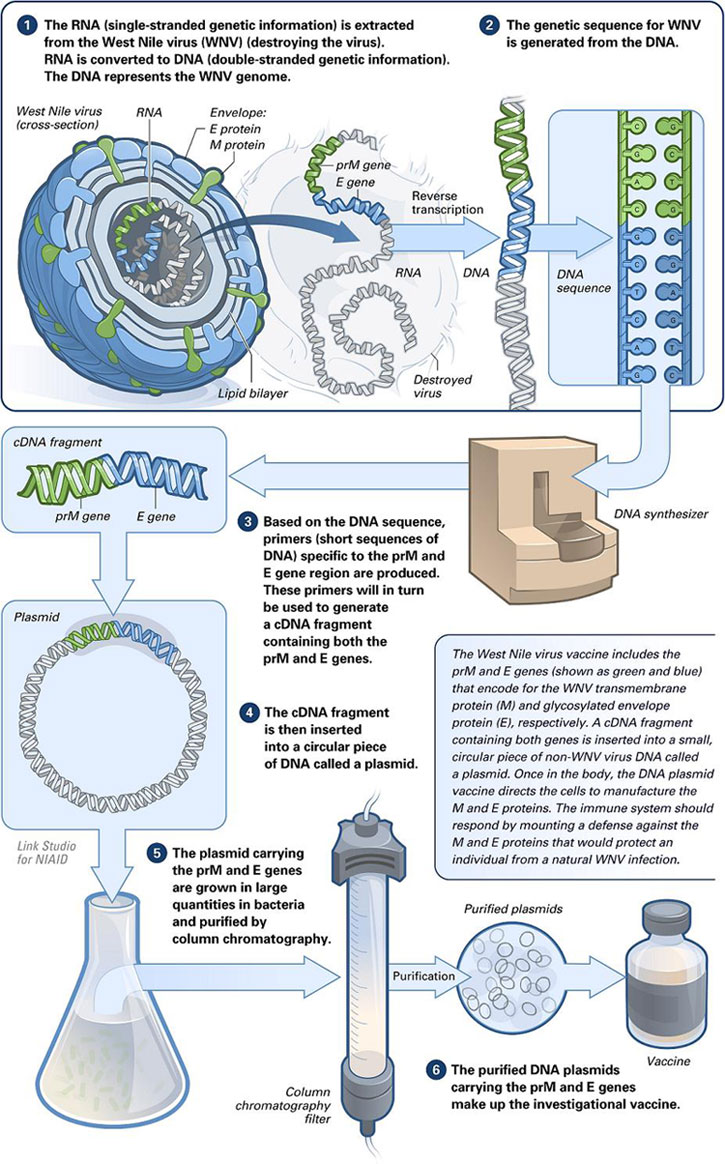
Figure 01: DNA Vaccine
However, the FDA has not still approved DNA vaccines for human use. They are currently under trial. DNA vaccines are thought to play an important role in viral infections.
Advantages and Disadvantages
DNA vaccines, which are third-generation vaccines, have great advantages over the other vaccines as mentioned below.
- Risk of infection is minimum
- Antigen presentation can be achieved
- Easy to develop
- Highly stable
- Long term persistence
However, DNA vaccines also have a major disadvantage. They show the possibility of bringing mutations in the host DNA. Therefore, extensive research should be performed before administering a DNA vaccine to humans.
What is a Recombinant Vaccine?
Recombinant vaccination relies on administering a recombinant biological agent as a form of therapy against infection. During this procedure, plasmid vectors, yeast, bacteriophages, and adenoviruses are commonly used as recombinants to deliver the required protein to the host against the infection.
Figure 01: rVSV-ZEBOV – a recombinant, replication-competent vaccine
Moreover, recombinant DNA technology is a process of gene manipulation under in vitro. An introduction of a foreign gene into a vector takes place first. Then the recombinant vector or the recombinant molecule should be included in the target organism. Once the DNA enters in, it expresses and produces the desired product within the targeted host, which can fight against the infection.
What are the Similarities Between DNA Vaccine and Recombinant Vaccine?
- DNA vaccine and recombinant vaccine are two novel vaccines.
- These vaccines involve administering DNA fragments of genes to the host.
- They are administered intravenously.
- Both are third-generation vaccines.
- Furthermore, they are more promising against viral infections.
- Moreover, both methods are highly sensitive and specific.
What is the Difference Between DNA Vaccine and Recombinant Vaccine?
The key difference between DNA vaccine and recombinant vaccine is that the DNA vaccines use fragments of DNA, while the recombinant vaccines use recombinant vectors or viral agents as vaccinations.
Below infographic summarizes the difference between DNA vaccine and recombinant vaccine.
Summary – DNA Vaccine vs Recombinant Vaccine
Overall, DNA vaccines and recombinant vaccines are novel methods of vaccination. DNA vaccines consist of fragments of DNA that can code for proteins capable of fighting against infections. In contrast, recombinant vaccines are vaccines that consist of recombinant vectors or organisms bearing the desired gene. These recombinants then infect the host and produce the required proteins. Moreover, these techniques are of high specificity and sensitivity. However, the risk of developing mutations is high. Therefore, extensive research and trials take place before the approval of these vaccines. Thus, this summarizes the difference between DNA vaccine and recombinant vaccine.
Reference:
1. Nascimento, I P, and L C CLeite. “Recombinant Vaccines and the Development of New Vaccine Strategies.” Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, Dec. 2012, Available here.
2. “DNA Vaccination.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 8 July 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Making of a DNA vaccine” By CDC/ Dr. Frederick A. Murphy – This media comes from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Public Health Image Library (PHIL) (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Ebola virus em” By Unknown – NIAID Begins Clinical Trial of West Nile Virus Vaccine on National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases) site (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26wzZpkr5mTmLavsYyapZ1lopqwsLnBoqWapqRiw6KvwqKlnmc%3D