Difference Between Dominance and Epistasis
Key Difference – Dominance vs Epistasis
Dominance and epistasis are two situations which explain the occurrence of phenotypes from genes. Dominance describes how different alleles of a gene influence the expression of the phenotype and which allele is actually responsible for the observable phenotype. Epistasis describes the relationship between genes for the same phenotype and how alleles of one gene contribute to the effect of the phenotype of another gene. Therefore, dominance explains the masking effect of different alleles of the same gene on a particular phenotype while epistasis explains the masking effects of one gene on the phenotype of another gene. This is the key difference between dominance and epistasis.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Dominance
3. What is Epistasis
4. Side by Side Comparison – Dominance and Epistasis
5. Summary
What is Dominance?
Genes have different versions called alleles. Normally a gene has two alleles located on the homologous chromosomes. The relationship between genotype and phenotype can easily be described due to the contribution of the great scientist Gregor Mendel and his concept of dominance. According to Mendel’s theory, these two alleles are designated with names of dominant allele and recessive allele. As an example, if the height of the pea plant is decided by a gene which has two alleles A and a, and if genotypes AA, Aa and aA results in same height, it can be concluded that allele A is dominant for the character and a is recessive for the character as shown in the figure 01.
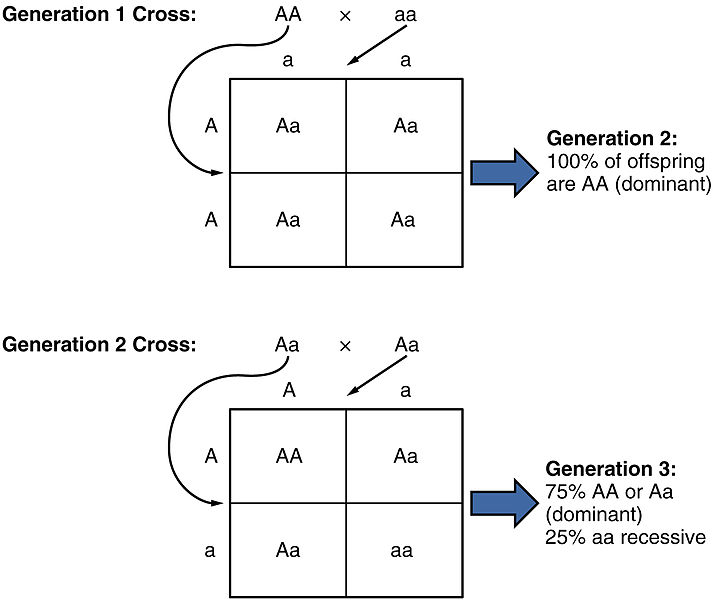
Figure 01: Mendel’s Concept of Dominance
However, beyond Mendel’s concept, we know some genes exist in multiple alleles and they are not completely dominant or recessive always. Therefore, the concept of dominance cannot always be applied. Incomplete dominance and codominance are two such incidents which cannot be described by Mendel’s first law. In incomplete dominance, parent’s traits can always be blended in heterozygous offsprings. In codominance, both alleles are simultaneously expressed in the heterozygous offsprings.
What is Epistasis?
Epistasis is a phenomenon in genetics which describes the contribution and relationship of the two or more gene loci to decide one phenotype. In other words, epistasis can be defined as an interaction of genes in which the effect of one allele of a gene influences the effect of alleles of another gene. As an example, if a pigment is produced via the action of two genes; gene 1 and gene 2, without the expression of both genes, pigment cannot be synthesized because gene 1 is responsible for the production of the intermediate molecule from the precursor molecule and intermediate will convert into pigment by the expression of gene 2. Therefore, the relationship between two genes is required for the final production of pigment which gives the phenotype. This is known as epistasis. Epistasis can also be used to refer to genes which mask the effects of another gene.
A mutation of one gene or two mutations on gene loci can result in a different effect on the phenotype. Epistasis can be classified into different forms such as positive epistasis, negative epistasis, antagonistic epistasis and synergistic epistasis based on the mutations and the magnitude.
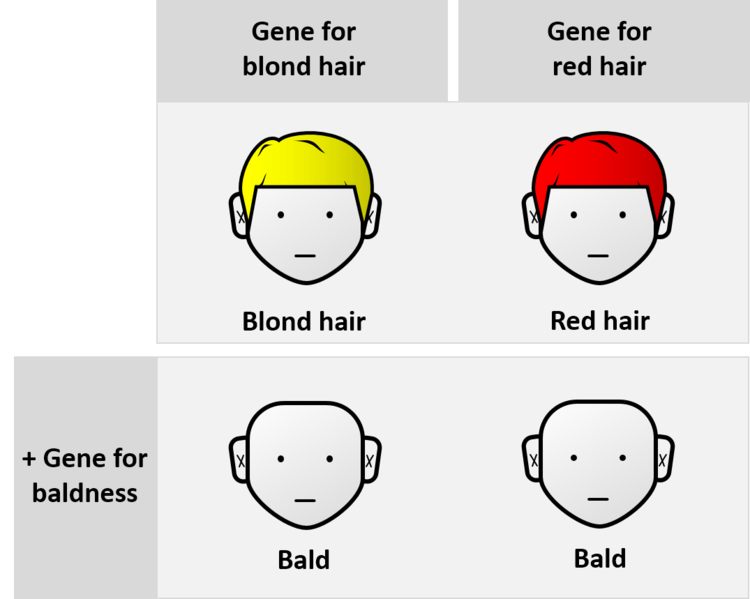
Figure 2: Epistasis genes of hair color and baldness
What is the difference between Dominance and Epistasis?
Dominance vs Epistasis | |
| The concept of dominance is applied for different alleles of the same gene in which one allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive | Epistasis refers to the relationship between genes and describes how an allele of one gene effects on the phenotype of the another gene. |
| Phenotype | |
| The phenotype is believed to be the dominance character. | The phenotype results from the contribution of the genes. |
Summary – Dominance and Epistasis
Dominance and epistasis are two common words used in genetics when describing the phenotypes in relation to alleles and gene expressions. Dominant and recessive alleles are the two versions of one gene. The allele which is responsible for the result of the phenotype is known as a dominant allele and said to be the dominance character of that phenotype. Epistasis is a phenomenon that happens between genes and the relationship of the genes is responsible for the expression of the final phenotype. Alleles of one gene can influence the phenotype of another gene. One mutation in alleles of one gene will result in a different phenotype than expected in epistasis. This is the difference between dominance and epistasis.
References
1.Wilkie, A. O. “The molecular basis of genetic dominance.” Journal of Medical Genetics. U.S. National Library of Medicine, Feb. 1994. Web. 20 Mar. 2017.
2. Phillips, Patrick C. “Epistasis—the essential role of gene interactions in the structure and evolution of genetic systems.” Nature reviews. Genetics. U.S. National Library of Medicine, Nov. 2008. Web. 20 Mar. 2017
3.Ilona Miko. “Genetic Dominance: Genotype-Phenotype Relationships.” Nature News. Nature Publishing Group, 2008. Web. 20 Mar. 2017
Image Courtesy:
1.”Epistatic hair” By Thomas Shafee – Own work (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”2924 Mendelian Pea Plant Cross” By OpenStax College – Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. Jun 19, 2013. (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26wzqagp5memLJurc2dZK%2BrXZq9qr%2FTmqqiq18%3D