Difference Between Dominant and Recessive Alleles
The key difference between dominant and recessive alleles is that dominant alleles are the alleles that give the phenotype, masking over the other phenotype, while recessive alleles are the alleles that are suppressed by the dominant allele.
Usually, a chromosome contains a number of genes, and they exist in specific places. If genes exist in the same location in the homologous chromosomes, they are said to have the same locus. Since they are present in the same loci of the maternal and paternal chromosome, these genes have the same trait. They are the alternative forms of a gene; we call these alleles. Alleles can be dominant or recessive. A dominant allele always gives the phenotype it codes while the recessive allele gives the phenotype only when it is present in the homozygous state. Actually, dominance and recessivity are the phenotypic correlation of two alleles.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Dominant Alleles
3. What are Recessive Alleles
4. Similarities Between Dominant and Recessive Alleles
5. Side by Side Comparison – Dominant vs Recessive Alleles in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Dominant Alleles?
The dominant allele is the strongest allele among the two forms of a gene present in the same loci of the maternal and paternal chromosome. The trait of the dominant allele is always expressed when the gene occurs in both homozygous dominant and heterozygous states.
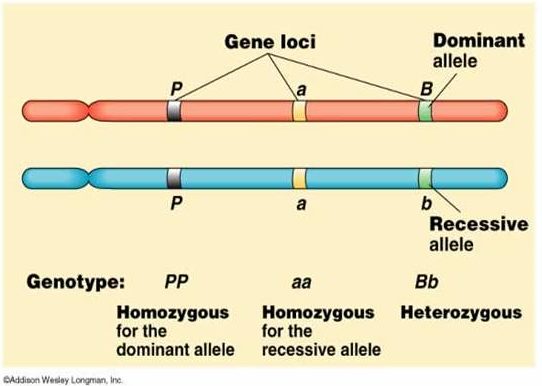
Figure 01: Dominant and Recessive Alleles
For example, if we consider the dominant allele as (A) and recessive allele as (a), then in the case of homozygous, we can write the two alleles as AA. In the case of heterozygous, we can write it as Aa. In both situations, the dominant allele can express its phenotype over recessive allele. Thus, the dominant allele masks the phenotype of the recessive allele.
What are Recessive Alleles?
The recessive allele is the weaker allele among the two alleles of a gene. It is expressed only in the case of homozygous. In the case of heterozygous, the dominant allele masks the phenotype of the recessive allele. For instance, if we consider the dominant allele as (A) and recessive allele as (a), the recessive allele can express its phenotype only in the case of ‘aa’. Thus, it is not expressed in its Aa state due to the effect of the dominant allele.
What are the Similarities Between Dominant and Recessive Alleles?
- Dominant and recessive alleles are two possible forms of a gene.
- Both encode for a trait.
- Also, both are at the same locus.
- Furthermore, when they are present in the homozygous state, they give their respective phenotypes.
What is the Difference Between Dominant and Recessive Alleles?
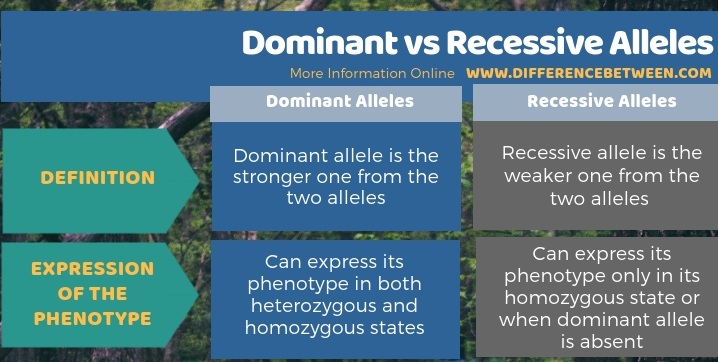
Dominant allele is the stronger allele from the two alleles, and the weaker one is the recessive allele. A dominant allele can express its phenotype in both its heterozygous and homozygous states, but a recessive allele can express its phenotype only in its homozygous state or when the dominant allele is absent. So, this is the key difference between dominant and recessive alleles.
Below infogrphic shows the difference between dominant and recessive alleles, comparatively.
Summary – Dominant vs Recessive Alleles
Each parent contributes one allele to each gene. Therefore, each gene generally has two alleles. Moreover, there are two types of alleles as dominant allele and recessive allele. The dominant allele is the stronger allele that determines the phenotype. It can mask the phenotype of the weaker allele, which is the recessive allele. The recessive allele can express its phenotype only when it is present in the homozygous recessive state. But dominant allele can express its phenotype in both homozygous dominant and heterozygous states. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between dominant and recessive alleles.
Reference:
1. “Dominance (Genetics).” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 22 Apr. 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Genotype” By GETaiwan NTU (CC BY-SA 2.0) via Flickr
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26wzqagp5meqXqiusNmraxlopqwpr%2FSoq2eZZGhuaa4xKxm