Difference Between Electrophoresis and Dielectrophoresis
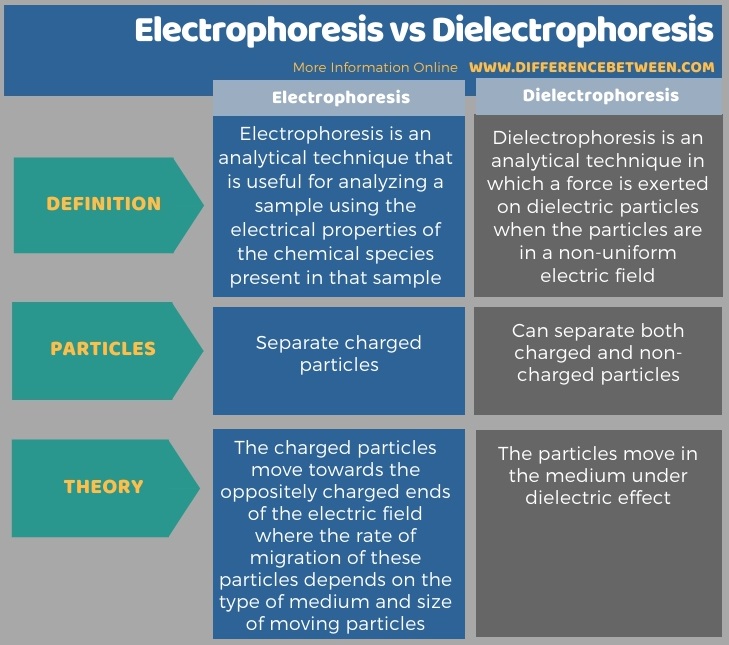
The key difference between electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis is that electrophoresis separates charged particles, whereas dielectrophoresis separate charged or non-charged particles.
Electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis are important analytical techniques in the field of biochemistry. These are separation methods we can use to separate desired particles from a mixture of particles.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Electrophoresis
3. What is Dielectrophoresis
4. Side by Side Comparison – Electrophoresis vs Dielectrophoresis in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Electrophoresis?
Electrophoresis is an analytical technique that is useful for analyzing a sample using the electrical properties of the chemical species present in that sample. Here, we can observe the motion of the dispersed solute in the medium analyzed. Therefore, we can determine the motion of the chemical species relative to the medium.
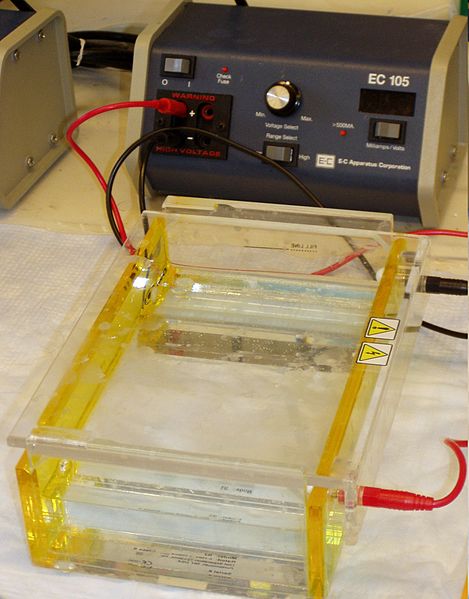

However, this technique requires the creation of some specific conditions. For example, we should provide the medium with influence from a spatially uniform electric field. The theory behind this technique is that different particles of a charged medium move at different migration rates in the presence of an electrical field.
Another term for electrophoresis is “electrokinetic phenomena”. Depending on the type of ion present in the sample, the process of electrophoresis has two categories as cataphoresis and anaphoresis.
Cataphoresis is the electrophoresis of cations (positively charged ions) while anaphoresis is the electrophoresis of anions (negatively charged ions). The most important application of electrophoresis is in the extraction of DNA fragments according to its size.
What is Dielectrophoresis?
Dielectrophoresis is an analytical technique in which a force is exerted on dielectric particles when the particles are in a non-uniform electric field. In this technique, the particles need not be charged in order to separate them. However, the strength of the force exerted on the dielectric particle depends on the type of medium, electrical properties of the particles, shape and size of the particles.
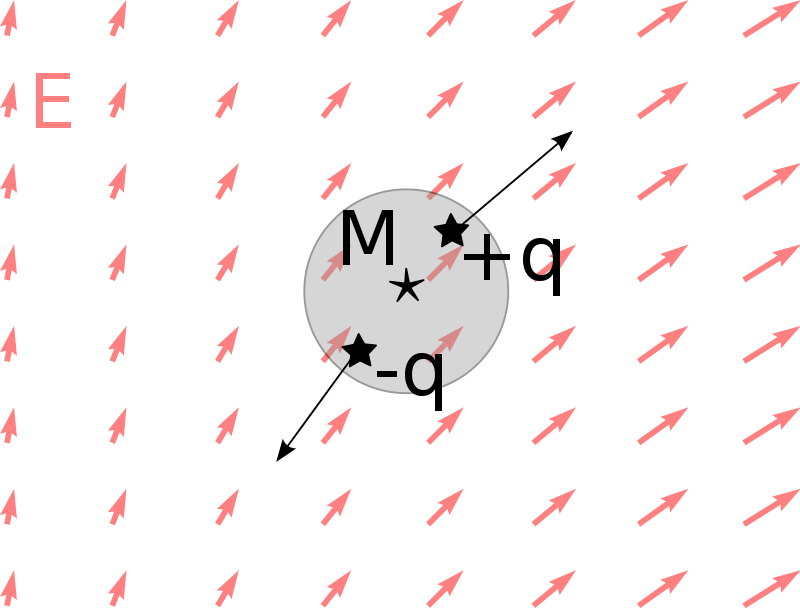
Dielectrophoresis allows the separation of cells, the orientation and manipulation of nanoparticles, etc. Biological cells have dielectric properties. Therefore, this technique has many applications in the field of medicine. For example, we can use it to separate cancer cells from healthy cells. Also, platelets can be separated from other blood cells. Apart from that, dielectrophoresis is useful in the field of semiconductor production.
What is the Difference Between Electrophoresis and Dielectrophoresis?
Electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis are important analytical techniques in the field of biochemistry. Electrophoresis is an analytical technique that is useful for analyzing a sample using the electrical properties of the chemical species present in that sample. In contrast, dielectrophoresis is an analytical technique in which a force is exerted on dielectric particles when the particles are in a non-uniform electric field. The key difference between electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis is that electrophoresis separates charged particles, whereas dielectrophoresis separate charged or non-charged particles.
There is also a theoretical difference between electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis. That is; the theories used in these techniques are different. In electrophoresis, the charged particles move towards the oppositely charged ends of the electric field where the rate of migration of these particles depends on the type of medium and size of moving particles. However, electrophoresis, the particles move in the medium under dielectric effect.
Summary – Electrophoresis vs Dielectrophoresis
Electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis are important analytical techniques in the field of biochemistry. The key difference between electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis is that electrophoresis separates charged particles, whereas dielectrophoresis separate charged or non-charged particles.
Reference:
1. Gascoyne, Peter R C, and Jody Vykoukal. “Particle Separation by Dielectrophoresis.” Electrophoresis, U.S. National Library of Medicine, July 2002, Available here.
2. “Dielectrophoresis.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 27 Feb. 2020, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Gel electrophoresis apparatus” By Jeffrey M. Vinocur – Own work (CC BY 2.5) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Dielectrophoresis” By Raminagrobis – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26xy56araqfpbWwvsSsoKxlkaOxbrDInqOem6SnvLG0zqucrKGjZA%3D%3D