Difference Between Gattermann and Gattermann Koch Reaction
The key difference between Gattermann and Gattermann Koch reaction is that Gattermann reaction uses a mixture of hydrogen cyanide and hydrochloric acid, whereas Gattermann Koch reaction uses carbon monoxide instead of hydrogen cyanide.
Gattermann Koch reaction is a variation of Gattermann reaction. The mechanism of Gattermann reaction was discovered by the German scientist Ludwig Gattermann while the mechanism of Gattermann Koch reaction was developed by Ludwig Gattermann and Julius Koch.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Gattermann Reaction
3. What is Gattermann Koch Reaction
4. Side by Side Comparison – Gattermann vs Gattermann Koch Reaction in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Gattermann Reaction?
Gattermann reaction is an organic substitution reaction in which we can formylate aromatic compounds. It is named after the German chemist Ludwig Gattermann. Further, this reaction can take place in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts. Moreover, the formylation is done using a mixture of HCN (hydrogen cyanide) and HCl (hydrochloric acid). The Lewis acid catalyst we use mostly is AlCl3.
Furthermore, for simplification, we can replace the HCN/HCl mixture by zinc cyanide. Then, this method becomes safer as well because zinc cyanide is not that toxic like HCN. Moreover, it is important to note that Gattermann reaction is important in introducing aldehyde groups to the benzene ring.
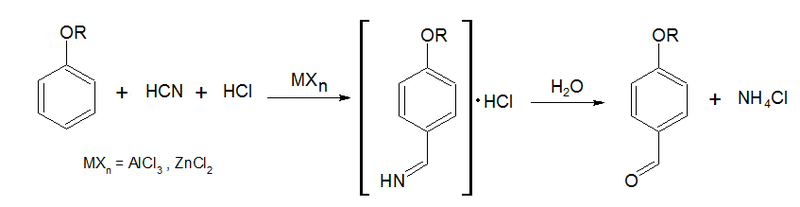
Since the major application of this reaction is to formylate aromatic compounds, we can name it as Gattermann formylation; we sometimes name it as Gattermann salicylaldehyde synthesis. Besides, this reaction is closely similar to Friedel-Craft reactions.
What is Gattermann Koch Reaction?
Gattermann Koch reaction is a variation of Gattermann reaction, and this reaction involves the use of carbon monoxide instead of hydrogen cyanide (HCN). Therefore, unlike the Gattermann reaction, we cannot apply Gattermann Koch reaction to phenol and phenol ether substrates.
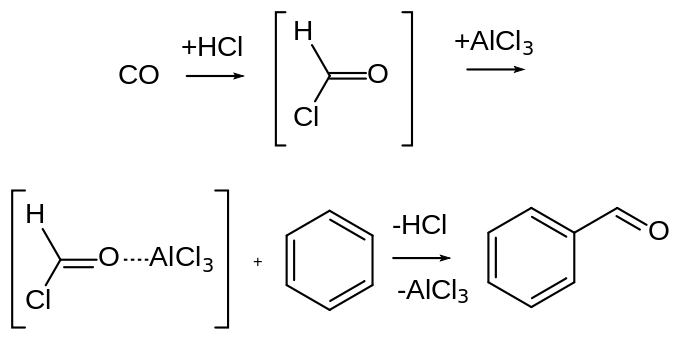
Furthermore, this reaction usually uses zinc chloride as the catalyst, and it requires the presence of a trace amount of copper(I) chloride as a co-catalyst.
What is the Difference Between Gattermann and Gattermann Koch Reaction?
Gattermann Koch reaction is a variation of Gattermann reaction. Gattermann reaction is an organic substitution reaction in which we can formylate aromatic compounds. Gattermann Koch reaction is a variation of Gattermann reaction and involves the use of carbon monoxide instead of hydrogen cyanide (HCN). Therefore, the key difference between Gattermann and Gattermann Koch reaction is that Gattermann reaction uses a mixture of hydrogen cyanide and hydrochloric acid, whereas Gattermann Koch reaction uses carbon monoxide instead of hydrogen cyanide.
Furthermore, Gattermann Koch reaction usually uses zinc chloride as the catalyst, and it requires the presence of a trace amount of copper(I) chloride as a co-catalyst. However, in the Gattermann reaction, the catalyst is usually aluminium chloride. Apart from that, unlike Gattermann reaction, we cannot apply Gattermann Koch reaction to phenol and phenol ether substrates.
Below infographic sumarizes the difference between Gattermann and Gattermann Koch reaction.
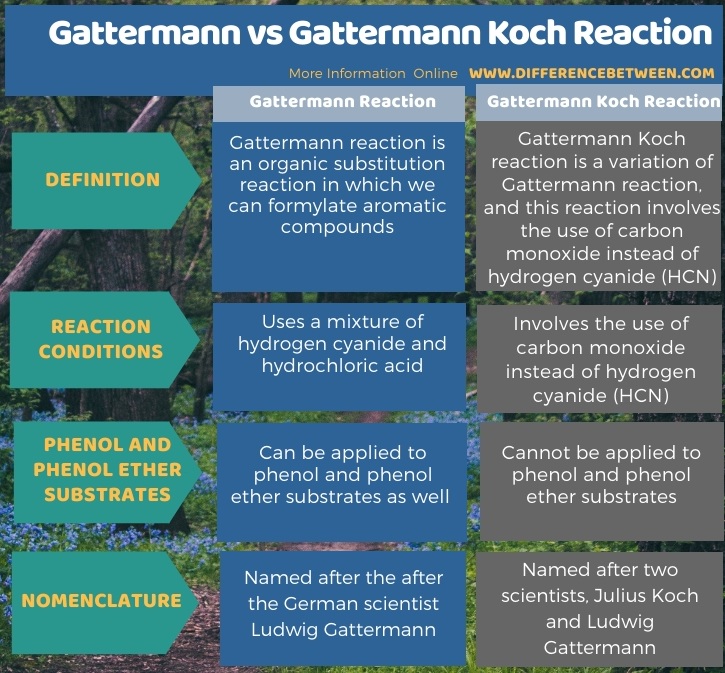
Summary – Gattermann vs Gattermann Koch Reaction
Gattermann Koch reaction is a variation of Gattermann reaction. The key difference between Gattermann and Gattermann Koch reaction is that Gattermann reaction uses a mixture of hydrogen cyanide and hydrochloric acid, whereas Gattermann Koch reaction uses carbon monoxide instead of hydrogen cyanide. Gattermann reaction was named after the German scientist Ludwig Gattermann while Gattermann Koch reaction was named after two the scientists, Julius Koch and Ludwig Gattermann.
Reference:
1.“Gattermann Reaction – Discovery, Mechanism & Examples.” BYJUS, Byju’s, 6 July 2018, Available here.
2.“Gattermann Reaction.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 1 July 2019, Available here.
3. “Gattermann Koch Reaction Mechanism – Detailed Explanation With Illustrations.” BYJUS, Byjus, 25 Jan. 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Gattermann aldehyde synthesis” By Mephisto spa – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Gattermann-Koch” By Matthias M. – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26zwK2rnqqdlruvecCnm2afkanBpr7MmqWnZZuksKl50Z6YnKyZpLtw