Difference Between Gypsum and Plaster of Paris
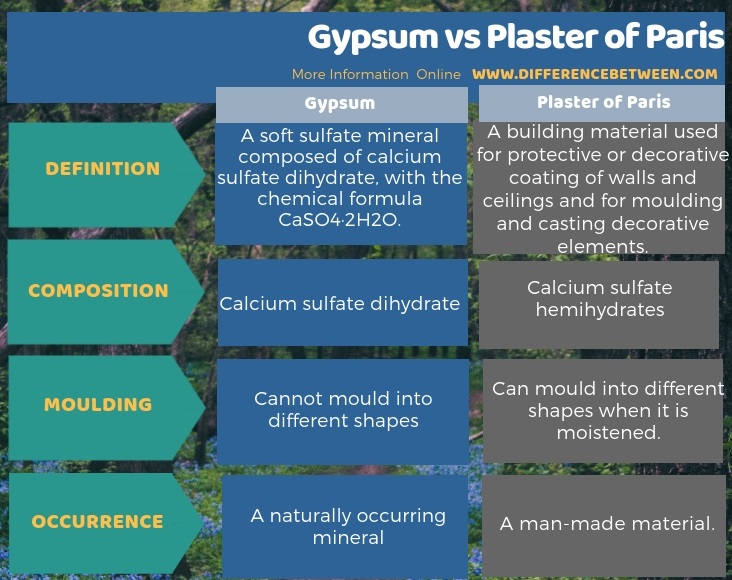
The key difference between gypsum and plaster of Paris is that the Gypsum contains calcium sulfate dihydrate whereas the plaster of Paris contains calcium sulfate hemihydrates.
Gypsum is a naturally occurring mineral. Plaster of Paris and gypsum both contain calcium sulfate’s hydrate form, but their water content in a molecule differs from each other. Therefore, this is the main difference between gypsum and plaster of Paris.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Gypsum
3. What is Plaster of Paris
4. Side by Side Comparison – Gypsum vs Plaster of Paris in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Gypsum?
Gypsum is a hydrated calcium sulfate mineral with the molecular formula CaSO4·2H2O. This is the most common sulfate mineral. It is a rock-forming mineral, which can grow up to very large sizes. Usually, the colour of the crystal is white or colourless but can have other shades of colours like grey, red or yellow too. Crystals also can occur as either transparent or translucent. Gypsum is a soft crystal, which we can even scratch it by a fingernail. Further, it is a flexible material, and its thermal conductivity is low. Gypsum is slightly soluble in water, and when we heat it, water will evaporate and can achieve the anhydride solid state again. Gypsum exists in many places all over the world (in UK, Russia, Canada, Africa, Asia, USA and Europe). However, Gypsum is abundant in Colorado and Mexico in the USA.
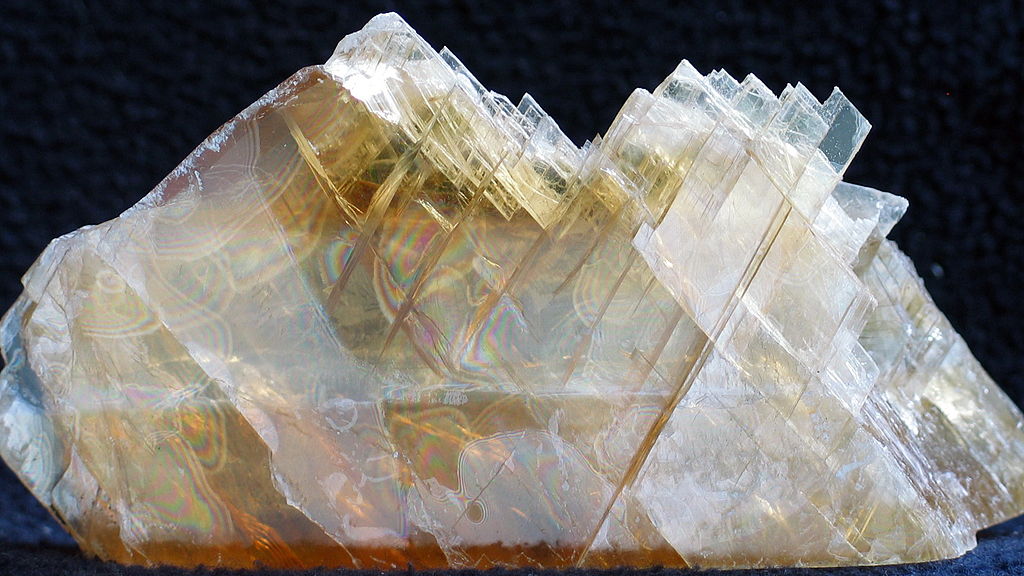

Figure 01: Appearance of Gypsum
Formation and Types
The major route of formation for this material is from precipitation of marine water. While forming the minerals, water or unwanted material can trap inside the crystal which is the cause of different coloured crystals. Furthermore, there are three types of gypsum. They are as follows:
- Selenite
- Alabaster
- Satin spar
Selenite is crystalline in nature and appears transparent or translucent. Alabaster grows into massive mineral beds. It has a light colour or lightly tinted colour (due to impurities). On the other hand, the satin spar is fibrous or silky in nature. We can use this material for making plaster of Paris, some cement, fertilizer (ammonium sulfate fertilizer) and as an ornamental stone. Also, gypsum is useful as manure, and it is a good source of sulfur. Moreover, it has the capability of becoming plastic like when we heat it up to 175 oC. This nature of Gypsum is important in producing plaster of Paris. If the content of CaSO4·2H2O in gypsum is high, it is very effective in producing fertilizer, plaster of Paris and cement. Therefore, there is a high demand for pure gypsum, which has at least 80% CaSO4·2H2O content.
What is Plaster of Paris?
We can produce plaster of Paris from gypsum. People used this material from the ancient times. Plaster of Paris got its name because earlier people living in areas near Paris used this material widely, to make plaster and cement. They also used it to do ornamental work on ceilings and cornices. Plaster of Paris contains the calcium sulfate hemihydrates (CaSO4·0.5H2O).
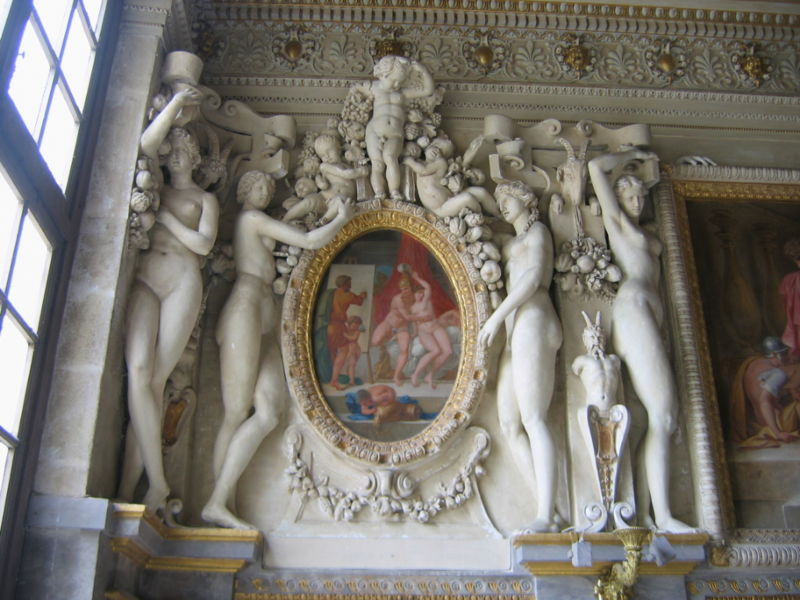

Figure 02: Use of Plaster of Paris for Decorative Purposes
We can prepare this compound by heating the gypsum which contains calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4·2H2O) to a temperature of about 150 oC (120-180 oC). we should add certain additives when heating. Plaster of Paris is a fine, white powder. When it becomes hydrated, we can use it to mould things, and if we allow it to dry, it hardens and retains whatever the shape it is set before drying.
What is the Difference Between Gypsum and Plaster of Paris?
Gypsum is a naturally occurring soft sulfate mineral whereas plaster of Paris is a building material that we use for protective or decorative coating purposes. Both these materials contain calcium sulfate as the major constituent. Although both gypsum and plaster of Paris contain calcium sulfate as the major component, they have differently hydrated calcium sulfate. Hence the two materials become different from each other. Therefore, the key difference between gypsum and plaster of Paris is that Gypsum contains calcium sulfate dihydrate whereas plaster of Paris contains calcium sulfate hemihydrates. Moreover, another difference between gypsum and plaster of Paris is that we can mould plaster of Paris into different shapes when we moisten it while we cannot do this for gypsum.
Summary – Gypsum vs Plaster of Paris
The production of plaster of Paris is mainly from gypsum. However, there are few differences between gypsum and plaster of Paris. Among them, the key difference between gypsum and plaster of Paris is that the gypsum contains calcium sulfate dihydrate whereas the plaster of Paris contains calcium sulfate hemihydrates.
Reference:
1. “Gypsum.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 10 Oct. 2018. Available here
2. “Plaster.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 27 Sept. 2018. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Gips – Lubin, Poland”By Elade53 – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”Fontainebleau escalier roi5″By No machine-readable author provided. (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26z2KmqrqVdlruledWsZKmkkajBpr6MqJ1mqJGntrR7