Difference Between Heterozygous and Homozygous Individuals
The key difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals is that a heterozygous individual carries two different alleles (both dominant and recessive) of a gene while homozygous individual carries two copies of the same allele, either dominant or recessive.
Genes exist as alleles or copies. In fact, a gene mainly has two alleles. To be specific, an allele is a version of a gene that results in a distinguishable phenotypic effect. Alleles can be either dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles are expressed fully in the phenotype of a heterozygote. Heterozygous and homozygous individuals are two types of organisms categorized based on the types of alleles present. A heterozygous individual is an organism that possesses both dominant allele and recessive allele. A homozygous individual is an organism that possesses two dominant alleles or two recessive alleles.

CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. Who are Heterozygous Individuals
3. Who are Homozygous Individuals
4. Similarities Between Heterozygous and Homozygous Individuals
5. Side by Side Comparison – Heterozygous vs Homozygous Individuals in Tabular Form
6. Summary
Who are Heterozygous Individuals?
Heterozygous individual is an organism that has two different alleles of a gene. Both types of alleles, i.e., dominant and recessive, are present in the gene.
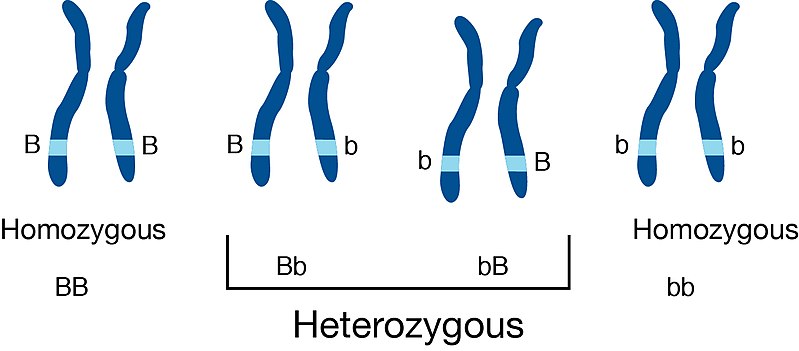
Figure 01: Heterozygous State
Heterozygous individuals are also known as carriers of the recessive allele. This is because they carry the recessive allele though it is unable to produce a phenotypic effect. Most of the time, heterozygous individuals bear the phenotypic effect of the dominant allele.
Who are Homozygous Individuals?
The term homozygous implies that the organism has two copies of the same allele of a gene. If it carries two copies of the dominant allele, it is known as homozygous dominant. Similarly, if it carries two copies of the recessive allele, it is known as homozygous recessive.
Figure 02: Homozygous
If an organism has one of the same type of allele on each of its chromosomes, that organism has a pure trait. Therefore, homozygous individuals have a pure trait since they always possess one type of alleles.
What are the Similarities Between Heterozygous and Homozygous Individuals?
- Both heterozygous and homozygous individuals are a result of the variation of the alleles of a gene.
- Both individuals always carry two alleles.
What is the Difference Between Heterozygous and Homozygous Individuals?
Heterozygous vs Homozygous Individuals | |
| Heterozygous individuals are individuals that possess two different alleles of a gene | Homozygous individuals are individuals that possess either the same two copies of the dominant allele or two copies of the recessive allele |
| Type | |
| One type | Homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive |
| Genotype | |
| Have genotypes either AA or aa | Have genotype Aa |
| Carrier of Recessive Allele | |
| Carriers of the recessive allele | Not carriers of the recessive allele |
| Alleles Present | |
| Possess both alleles | Possess only one type of allele |
Summary – Heterozygous vs Homozygous Individuals
Classification of heterozygous and homozygous individuals stems from the alleles present in a gene of an organism. Heterozygous individuals have two different alleles of a gene. Homozygous individuals have two copies of the same allele, either dominant or recessive. If the two alleles are A and a, genotype of the heterozygous individual is Aa. Similarly, the genotype of the homozygous individual is AA or aa. This is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals.
Reference:
1. Thompson, Elizabeth A. “Genotypes and Phenotypes.” University of Washington Department of Statistics, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Heterozygous” By Darryl Leja, National Human Genome Research Institute – (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Homozygous cross tree method” By Tim DeJulio – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau260xK2cq6eqrrSwwdJmmKecXZ28rrvZsp6oraNitq%2BwyK%2Bgna2RocBw