Difference Between Homodimer and Heterodimer
The key difference between homodimer and heterodimer is that homodimer is a protein made from two identical proteins, while heterodimer is a protein made from two different proteins.
Protein is a biomolecule composed of amino acid chains. A protein dimer is a quaternary protein structure formed from the union of two protein monomers or two amino acid chains. Generally, they bind with each other by non-covalent bonds. Protein dimers are either homodimers or heterodimers. A homodimer has two identical proteins which are non-covalently bound. Heterodimer has two different proteins bound together. This protein dimer interaction is important in regulation and catalysis.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is a Homodimer
3. What is a Heterodimer
4. Similarities Between Homodimer and Heterodimer
5. Side by Side Comparison – Homodimer vs Heterodimer in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is a Homodimer?
Homodimer is a type of protein dimer composed of two identical monomers. The monomers bind with non-covalent bonds. Generally, there are 18 mean numbers of H bonds in homodimers. Moreover, the correlation coefficient between H-bonds and interface residues in homodimer is 0.85. Furthermore, the maximum number of H bonds per-interface residue of homodimer is 0.44. Not only that, but there are more intermolecular H bonds in homodimers too. However, the density of H bonds per-interface residue is lower in homodimers.
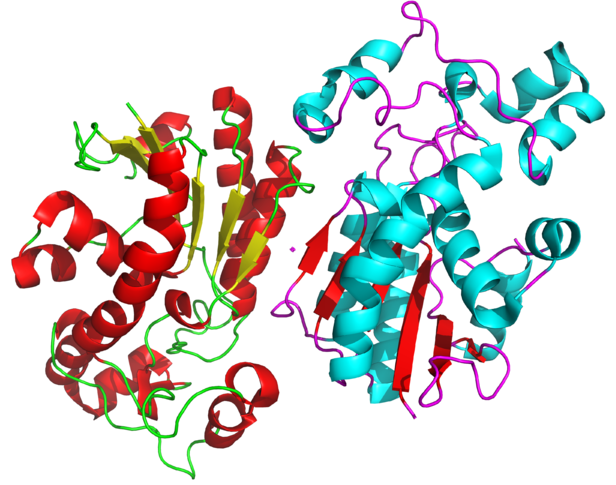
Figure 01: Homodimer
When considering examples for homodimers, the class 1 RNAs are homodimers. In this homodimer, R1 protein is responsible for nucleotide reduction while R2 protein is responsible for the housing the diiron tyrosyl array. Another protein homodimer is thyroglobulin produced by the thyroid gland. Xanthine oxidase and etanercept are also protein homodimers.
What is a Heterodimer?
The heterodimer is a type of protein dimer complexed from two non-identical monomers. In other words, a heterodimer is a protein composed of two different protein monomers. Generally, there are 12 mean numbers of H bonds in heterodimers. Moreover, the correlation coefficient between H-bonds and interface residues in heterodimer is 0.83. Furthermore, the maximum number of H bonds per-interface residue of the heterodimer is 0.65. Compared to homodimers, there are less intermolecular H bonds in heterodimers. However, the density of H bonds per-interface residue is higher in heterodimers.
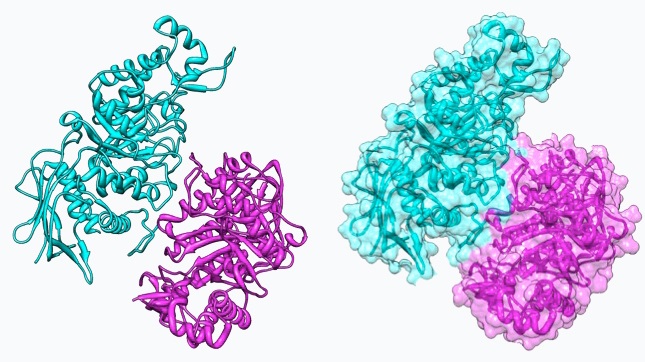
Figure 02: Heterodimer
Enzyme reverse transcriptase is a heterodimer composed of two different amino acids chains. Another example of a heterodimer is opioid receptors. Moreover, tubulin is a heterodimer protein.
What are the Similarities Between Homodimer and Heterodimer?
- Homodimer and heterodimer are two types of protein dimmers.
- Both have two monomers.
- They are quaternary protein structures.
- Dimers are common in catalysis and regulation.
What is the Difference Between Homodimer and Heterodimer?
Homodimer is a protein dimer composed of two identical protein monomers while heterodimer is a protein dimer composed of two different protein monomers. So, this is the key difference between homodimer and heterodimer. Furthermore, there are 18 mean numbers of H bonds in homodimers while there are 12 mean numbers of H bonds in heterodimers.
Moreover, another difference between homodimer and heterodimer is that the correlation coefficient between H-bonds and interface residues is 0.85 in homodimers while it is 0.83 in heterodimers.
The below infographic of the difference between homodimer and heterodimer shows more comparisons between both dimers.
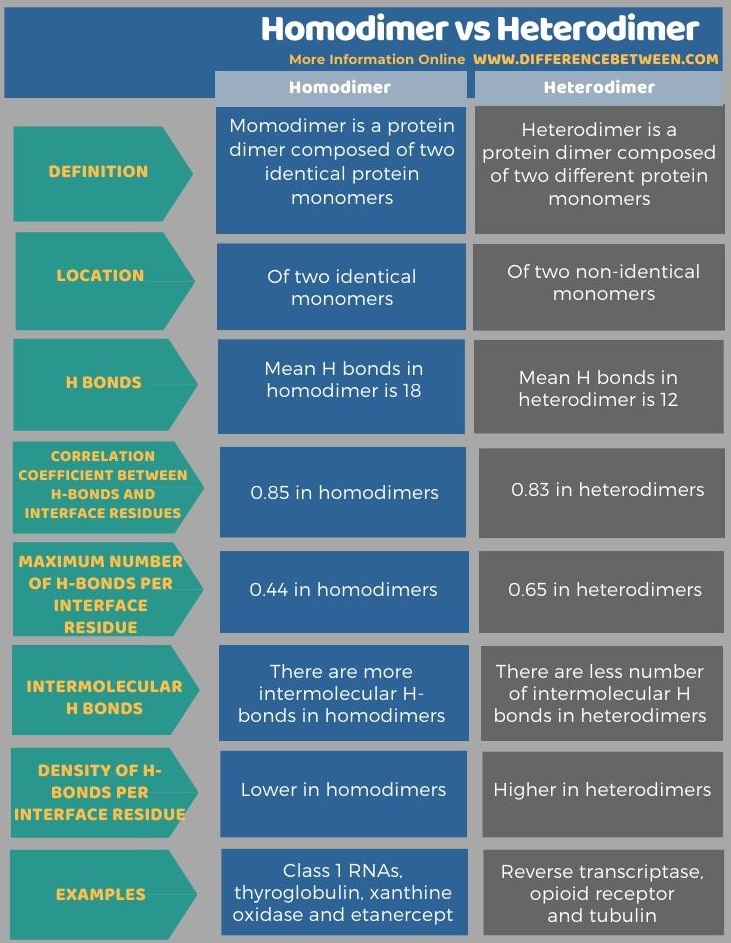
Summary – Homodimer vs Heterodimer
Protein dimers are common in catalysis and regulation. They can be either homodimers or heterodimers. Homodimers are composed of two identical protein monomers. In contrast, heterodimers are composed of two non-identical protein monomers. Thus, this is the key difference between homodimer and heterodimer.
Reference:
1. “Protein Dimer”. En.Wikipedia.Org, 2020, Available here.
2. “Heterodimer – An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics”. Sciencedirect.Com, 2020, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Homodimer B-type PGM” By Nsae – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Hexosaminidase A (heterodimer, with van der Waals interactions)” By Codyshafer 2011 (talk) – Own work (Original text: I (Codyshafer 2011 (talk)) created this work entirely by myself. (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau260zqamnaGdmr9urc2dZKGdpJq%2FsLDIppyrZw%3D%3D