Difference Between Homologous and Homeologous Chromosomes
The key difference between homologous and homeologous chromosomes is that homologous chromosomes are chromosomes with common ancestry while homeologous chromosomes are chromosomes that have an ambiguous nature and are partially homologous.
Chromosomes are the structural components that carry genetic information of an organism. The nuclear material in eukaryotes is arranged to form chromosomes, which are compact structures of nucleic acids and proteins. Moreover, there are different types of chromosomes based on the manner in which they undergo cell division. Homologous and homeologous chromosomes are two types of chromosomes that play an important role in the field of genetics.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Homologous Chromosomes
3. What are Homeologous Chromosomes
4. Similarities Between Homologous and Homeologous Chromosomes
5. Side by Side Comparison – Homologous vs Homeologous Chromosomes in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Homologous Chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are the chromosomes that are similar in length, the composition of the gene and the position of the centromere. However, the alleles in chromosomes may differ, which lead to variations in offspring of the same parents. In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes. Among these 23 pairs, 22 are homologous chromosome pairs and the remaining pair is a sex chromosome pair. In females, sex chromosome pair is homologous while in males, it is not homologous.
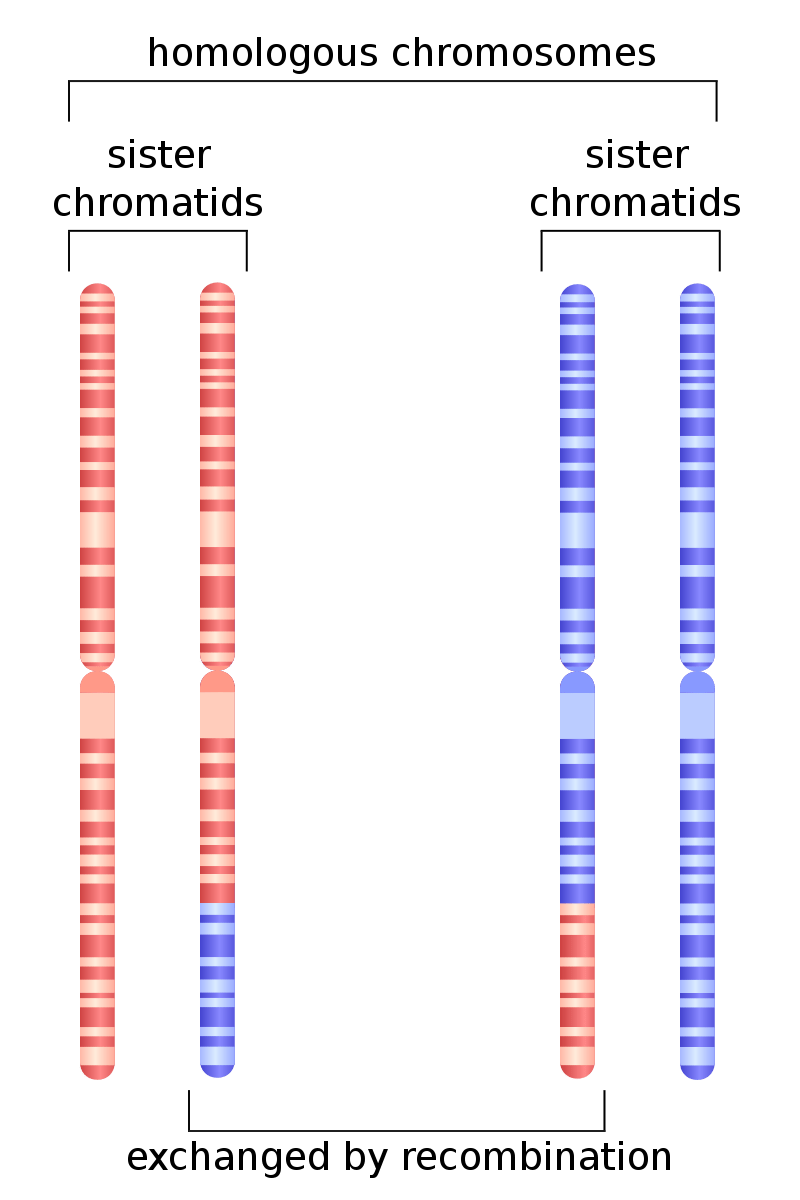
Figure 01: Homologous Chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes play a key role in both types of cell divisions: mitosis and meiosis. In meiosis, homologous chromosomes undergo cross over and genetic recombination. This results in the genetic variation of offspring. The process of genetic cross-over of the homologous chromosomes plays a major role in the evolution process. During mitosis, homologous chromosomes do not undergo genetic cross-over. This result in less variation; therefore, daughter cells are identical to the parent. However, mutations that take place during cell division can lead to altered phenotypes, resulting from mutated homologous chromosomes.
In addition, homologous chromosomes show common ancestry and have the ability to replicate themselves during the replicative phase of the cell cycle.
What are Homeologous Chromosomes?
Homeologous chromosomes are not strictly homologous in nature. However, they show an ambiguous nature in their formation. They arise due to the phenomenon of polyploidy taking place during the cell cycle. Polyploidy is the condition where an organism can possess more than one pair of homologous chromosome sets. Therefore, homeologous chromosomes are the key fact in studying the genetic outcomes resulting from polyploidy.
Homeologous chromosomes arise during meiosis where the chromosomes divide unequally due to polyploid condition. Therefore, these chromosomes mainly carry genes resulting from polyploidy. Apart from polyploidy studies, homeologous chromosomes play a key role in many genetic applications such as genetic recombination studies, cytogenetic studies, evolutionary biology and computational biology, etc.
What are the Similarities Between Homologous and Homeologous Chromosomes?
- Both types of chromosomes participate in cell division by meiosis and mitosis.
- They give rise to phenotypic characteristics.
- Both may show phylogenetic similarity.
- The structure of homologous and homeologous chromosomes may look similar.
What is the Difference Between Homologous and Homeologous Chromosomes?
Homologous and homeologous chromosomes differ primarily on their homology as homologous chromosomes undergo complete homology while homeologous chromosomes undergo partial homology. This is mainly due to the occurrence of polyploidy, which results in only homeologous chromosomes and not in homologous chromosomes. There is also a difference between homologous and homeologous chromosomes based on their genetic composition. The below infographic summarizes the difference between homologous and homeologous chromosomes.
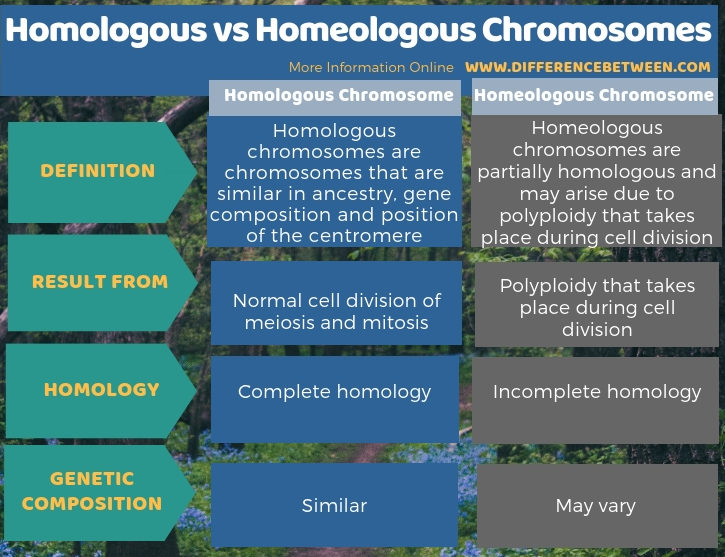
Summary – Homologous vs Homeologous Chromosomes
Homologous and homeologous chromosomes are two types of chromosomes based on the homology. Homologous chromosomes show complete homology between chromosomes while homeologous chromosomes show partial homology between two chromosomes. This is the key difference between homologous and homeologous chromosomes. Homeologous chromosomes originate due to a phenomenon called polyploidy, which takes place during the cell cycle. However, homeologous chromosomes play a very important role in recombination studies and cytogenetics.
Reference:
1. Staughton, John. “Homologous Chromosomes: Definition, Function and Challenges.” Science ABC, Science ABC, 21 May 2019, Available here.
2. Glover, Natasha M, et al. “Homoeologs: What Are They and How Do We Infer Them?” Trends in Plant Science, Elsevier Science, Ltd, July 2016, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “HR in meiosis” By Emw – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau260zqampaeXpMK0ecCnm2agn6KysLjOoKauq12YtbO7zKiqqKWVqHw%3D