Difference Between Ionization and Dissociation
Key Difference – Ionization vs Dissociation
Ionization and dissociation are two important processes in chemistry. Ionization and dissociation are often confused, especially in the case of dissolving of ionic compounds. One might think that dissolving ionic compounds results in ionization since ionic compounds dissolve in water, producing charged particles or ions. But this is an instance of dissociation since ionic compounds are already made out of ions. Hence, the key difference between ionization and dissociation is that ionization is the production of new ions by gain or loss of electron whereas dissociation is the split or separation of ions which already exist in a compound.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Ionization
3. What is Dissociation
4. Side by Side Comparison – Ionization vs Dissociation
5. Summary
What is Ionization?
Ionization is the process which produces a charged atom or a molecule by gain or loss of an electron. This process produces a charged particle. In this process, electrically neutral atoms become electrically charged particles. This charge can be either positive or negative. That is dependent on the gain or loss of an electron. If an atom or a molecule loses an electron, it will become positively charged whereas if it gains an electron from the outside, it will become negatively charged. Ionization process is usually irreversible, which means, if an atom or molecule gains an electron, it does not release that electron back; if an atom loses an electron, it will not take an electron back. That happens when the loss or gain of this electron causes a stable ion, which obeys the octet rule.
Sometimes the term ionization gets confused with dissociation. If an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (NaCl) is considered, it will form ions when dissolved in water. Although this forms ions, this is not ionization. Since the solid NaCl is split into its ions or their ionic bonds are broken, it cannot be termed as ionization. Thus, the split of an ionic bond is not an ionization process because an electron has already given to one atom by the other atom and only an electrostatic attraction exists. Hence, it can be said that compounds having ionic bonds will not take part in ionization. Although ionic compounds cannot undergo ionization, covalent compounds having covalent bonds between atoms can undergo ionization process. This is because electron sharing occurs in in covalent bonds and ionization of those compounds will produce new charged particles which were absent in the previous compound. But ionization only occurs in polar covalent compounds having atoms with a considerable difference in electronegativity. Otherwise, ionization will not occur due to strong covalent bonding. Ionization also takes place in metals. There, positively charged metal ions are produced by releasing electrons from metal atoms.
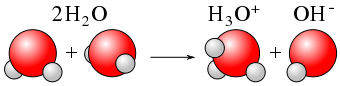
Figure 01: Ionization
What is Dissociation?
Dissociation refers to break or split of a compound into smaller particles. Dissociation process can result in products that are either electrically charged or neutral. This does not involve the gain or loss of electrons by the atoms. Unlike ionization process, dissociation is the separation of ions which already existed in a compound. Sometimes, dissociation may also produce neutral particles. For example, the breakdown of N2O4 results in the production of two molecules of NO2. Dissociation processes are reversible most of the times. This means, separated ions can be re-arranged to produce the previous compound. For example, as mentioned above, the dissolving of NaCl is a dissociation process and it produces two charged particles. But, solid NaCl can be obtained again with given proper conditions, which proves the dissociation is reversible. Unlike ionization, dissociation takes place in ionic compounds.
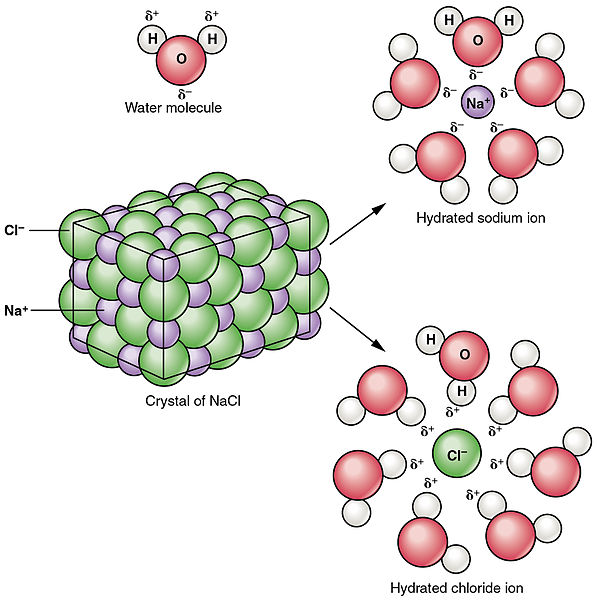
Figure 02: Dissociation of Sodium Chloride in Water
What is the difference between Ionization and Dissociation?
Ionization vs Dissociation | |
| Ionization is the process which produces new charged particles. | Dissociation is the separation of charged particles which already exist in a compound. |
| Initial Compound | |
| Ionization involves polar covalent compounds or metals | Dissociation involves ionic compounds. |
| Product | |
| Ionization always produces charged particles | Dissociation produces either charged particles or electrically neutral particles. |
| Process | |
| Ionization process is irreversible. | Dissociation is reversible. |
| Bonds | |
| Ionization involves covalent bonds between atoms | Dissociation involves ionic bonds in compounds. |
Summary – Ionization vs Dissociation
Ionization and dissociation are two different processes. Therefore, it is very important to understand the difference between these two processes. The key difference between ionization and dissociation is that dissociation is the process of separation of charged particles which already existed in the compound whereas ionization is the formation of new charged particles which were absent in the previous compound.
References:
1. Hamza, S. A., 2014. Slide share. [Online] Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/sheikhamirhamza/dssociation-vs-ionizationppt [Accessed 29 05 2017].
2. Chang, R., 2010. Chemistry. 10th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Image Courtesy:
1. “214 Dissociation of Sodium Chloride in Water-01” By OpenStax College – Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. Jun 19, 2013. (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Autoprotolyse eau” By Cdang – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau261zqegs5mknryvecCnm2auo2Kxqr%2FSqJqimaSevK97