Difference Between Linked and Unlinked Genes
Key Difference – Linked vs Unlinked Genes
Genes are the specific DNA sequences in chromosomes. There are 46 chromosomes in the human genome. Among them, 22 homologous pairs are called autosomes and one pair is known as sex chromosome. Thousands of genes are located on each chromosome. Some genes are closely situated in the same chromosome while some genes are far away from each other. During the gamete formation, homologous chromosomes separate from each other to form haploid cells. When genes are very close to each other, they tend to be inherited together. This is known as a genetic linkage. The genes which are located on the same chromosome and are likely to be inherited together are known as linked genes. Not all genes are linked. Genes which are located on different chromosomes or genes that are farther away from each other are known as unlinked genes. The key difference between linked and unlinked genes is that linked genes do not segregate independently while unlinked genes are able to assort independently during the cell division.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Linked Genes
3. What are Unlinked Genes
4. Side by Side Comparison – Linked vs Unlinked Genes in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What are Linked Genes?
Linked genes are the genes that are located close together on the same chromosome and are likely to be inherited together. Linked genes do not separate during the anaphase 1 and 2 of meiosis during sexual reproduction. Genetic linkage of these genes can be identified by test crosses and is measured by centimorgan (cM). Linked genes are always expressed together in an offspring since linked genes are not assorted independently during cell division. In a normal dihybrid cross, when two heterozygotes are crossed with each other, the expected phenotypic ratio is 9:3:3:1. However, if the genes are linked, this expected ratio changes due to the failure of independent assortment of alleles. If a normal dihybrid cross results in an unexpected ratio, it indicates the genetic linkage.
Linked genes show a lower chance for recombination. These genes also do not follow Mendel’s’ law of independent assortment. Hence, it results in different products than the usual phenotypes. However, linked genes can become unlinked genes during meiosis in the process of homologous recombination, where segments of chromosomes are exchanged. This causes the separation of linked, genes allowing them to be inherited independently. If the genes are linked perfectly, it has a zero recombination frequency.
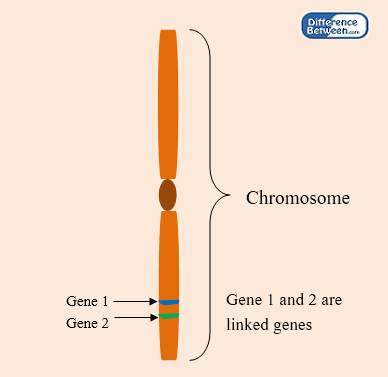
Figure 01: Linked Genes
What are Unlinked Genes?
Genes which are situated on different chromosomes and are inherited independently to gametes during meiosis are known as unlinked genes. Unlinked genes can be located on the same chromosome as well. However, they are situated farther away from each other in order to work independently. Unlinked genes follow Mendel’s’ second law of independent assortment because they are located on different chromosomes and have the ability to segregate independently during meiosis. Unlinked genes are not bound by any connection. Hence, they randomly passed to gametes in combinations.
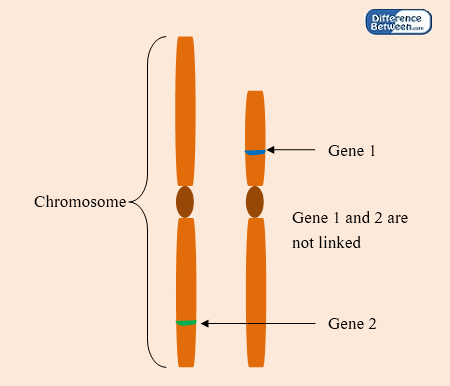
Figure 02: Unlinked Gene
What is the difference between Linked and Unlinked Genes?
Linked vs Unlinked Genes | |
| Linked genes are the genes that are situated closely on the same chromosome and are likely to be inherited together to offspring. | Unlinked genes are the genes situated in different chromosomes or far away on the same chromosomes and are inherited independently. |
| Closeness | |
| Linked Genes are located very close to each other. | Unlinked Genes are located farther away from each other. |
| Behavior according to Mendel’s’ Second Law | |
| Linked genes do not follow Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. | Unlinked Genes follow Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. |
| Independent Assortment | |
| Linked genes do not assort into gametes independently. | Unlinked genes assort into gametes independently. |
| Chromosome | |
| Linked Genes are located on the same chromosome. | Unlinked Genes are located on different chromosomes. |
| Phenotypic Ratios | |
| Linked Genes show unexpected phenotypic ratios. | Unlinked Genes follows expected ratios 9:3:3:1 |
Summary – Linked vs Unlinked Genes
Linked genes are found very closely on the same chromosome. They are likely to be inherited together to offspring. These genes cannot be assorted independently during the meiosis. Unlinked genes are found on different chromosomes and are inherited independently to offspring. They are able to pass randomly into gametes in any combination. This is the difference between linked and unlinked genes.
Download PDF Version of Linked vs Unlinked Genes
You can download PDF version of this article and use it for offline purposes as per citation notes. Please download PDF version here Difference Between Linked and Unlinked Genes.
References:
1. “Genetic Linkage”. Learn Genetics. N.p., n.d. Web. Available here. 12 June 2017.
2. “Genetic linkage.” Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 03 June 2017. Web. Available here. 12 June 2017.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau264yKeinpxdlruledWsZK6mnJ67rLHDZp6eppWofA%3D%3D