Difference Between Male and Female Drosophila melanogaster
The key difference between male and female Drosophila melanogaster is that male organism has a short abdomen with fewer stripes while the female organism has a long abdomen with more stripes.
The male and female Drosophila melanogaster are important organisms used in most genetic studies. They are also known as fruit flies. They are usually dependent on ripened fruits and are often found buzzing around ripened fruits.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Male Drosophila melanogaster
3. What is Female Drosophila melanogaster
4. Similarities Between Male and Female Drosophila melanogaster
5. Side by Side Comparison – Male vs Female Drosophila melanogaster in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Male Drosophila melanogaster?
Drosophila melanogaster is also known as the fruit fly. Over the years, they have shown vital importance in many genetic studies. These organisms are yellowish-brown in colour. The males have few stripes in their bodies; these mostly meld together and become darker towards the back of the abdomen. The male Drosophila melanogaster has five large red eyes and also possess antennae.
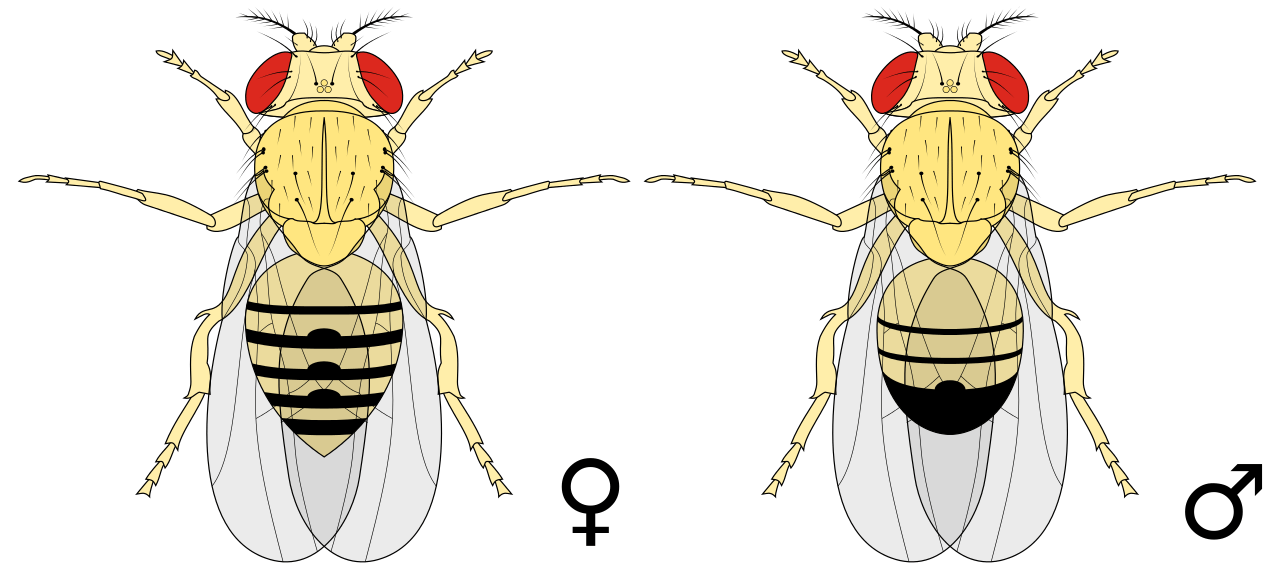
Figure 01: Male and Female Drosophila melanogaster
The male fly is smaller in size due to the shorted abdomens in comparison to females. It is mainly due to the short and blunt abdomen of the male Drosophila melanogaster. The appendages are also different in male organisms. They have short spaced bristles on the legs, which enable them to be distinguished from the female Drosophila. In addition to these, the male has complex sex structures such as testicles, visible on the ventral surface.
What is Female Drosophila melanogaster?
The female Drosophila melanogaster or the female fruit fly is also yellow-brown in colour. However, their pattern on stripes varies as more number of stripes are seen in female organisms. They are placed far apart and not thick in nature. These stripes are black in colour and light in female Drosophila melanogaster. The abdomen of the female organism is much longer and pointed than that of the male fruit fly. Moreover, there are no bristle-like structures in the appendages of the female organisms.
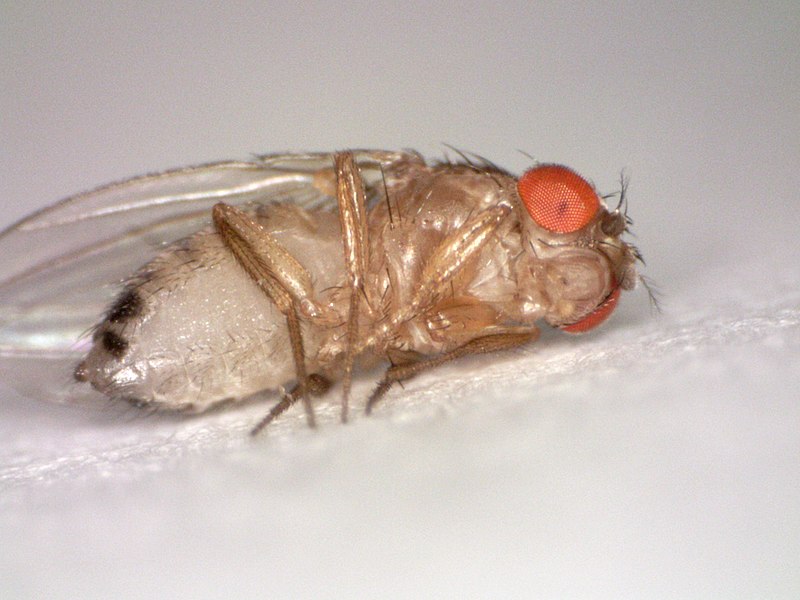

Figure 02: Female Drosophila melanogaster
The sex identification of female organisms is not an easy task as the male organisms. There is less visibility of the genitalia in females. Therefore, this is also a factor that determines the difference between male and female Drosophila melanogaster.
What are the Similarities Between Male and Female Drosophila Melanogaster?
- They are fruit flies that depend primarily on ripen fruits.
- Both are yellow-brown in colour.
- Moreover, both have an abdomen, head, thorax, eyes, and antennae.
- They belong to the broad kingdom of Animalia.
- Also, they are widely used in genetic studies.
- Both show varying characteristics during mating.
What is the Difference Between Male and Female Drosophila Melanogaster?
The key difference between male and female Drosophila Melanogaster is the shape of their body. While the female is long and pointed, the male is short and blunt. Moreover, even though they show similar movement patterns, the presence of bristles in appendages is only seen in the male form. So, this is a major difference between male and female Drosophila Melanogaster. Furthermore, the presence of visible genitalia is also a distinguishing feature or a difference between male and female Drosophila Melanogaster.
The below infographic summarizes the difference between male and female Drosophila Melanogaster.
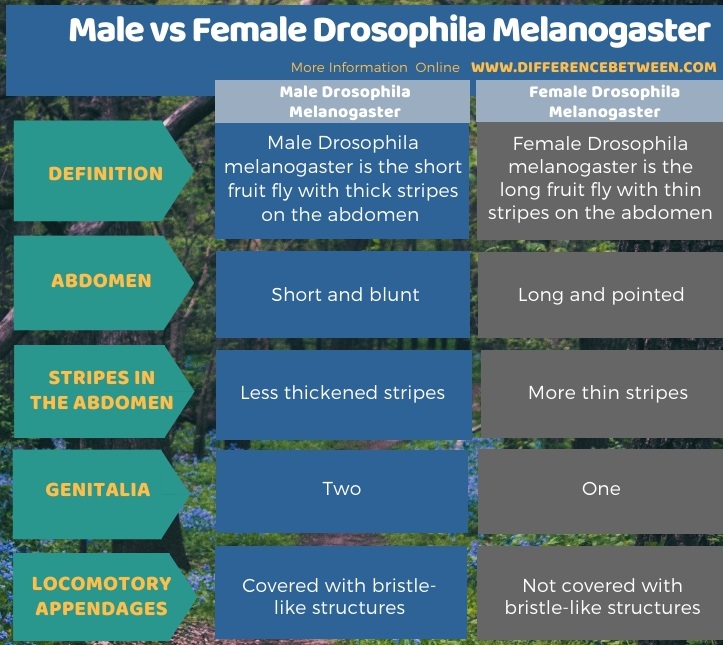
Summary – Male vs Female Drosophila Melanogaster
Male and female Drosophila melanogaster are widely used as genetic models to study the transfer of genetics and to approve theories of genetic studies. The main difference between male and female Drosophila Melanogaster is the shape of the body; the females have long pointed abdomens while the males have short blunt abdomens. Their difference is also characterized by the pattern of stripes in their abdomen, the visibility of their genitalia and the nature of their appendages.
Reference:
1. Apte, Manasi S, and Victoria H Meller. “Sex Differences in Drosophila Melanogaster Heterochromatin Are Regulated by Non-Sex Specific Factors.” PloS One, Public Library of Science, 8 June 2015, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Biology Illustration Animals Insects Drosophila melanogaster” By Madboy74 – Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Unconscious female Drosophila melanogaster (ventral view)” By Hannah Davis – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau265wKWcZpmemXqnscyao55llKe8tLvPoaClmV2isq2tzaiemqukmr9w