Difference Between Monosaccharide and Polysaccharide
The key difference between monosaccharide and polysaccharide is that monosaccharide is an individual sugar molecule whereas polysaccharide is a combination of several sugar molecules.
Saccharides are sugars. Saccharides are in four major types as monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides according to the number of sugar molecules present in the saccharide compound.

CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Monosaccharide
3. What is Polysaccharide
4. Side by Side Comparison – Monosaccharide and Polysaccharide in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Monosaccharide?
Monosaccharides are simple sugar molecules that are the basic units of carbohydrates. Therefore, they are the fundamental forms of carbohydrates (oligosaccharides and polysaccharides). These simple sugars have the general formula of CnH2nOn. These are the building blocks of polysaccharides. Moreover, we cannot get simpler molecules from the hydrolysis of monosaccharides.
Monosaccharides have different classes according to the number of carbon atoms present in the molecule. For example, triose (3), tetrose (4), pentose (5), hexose (6) and heptose (7). Monosaccharides have different functions in cells. First, monosaccharides are useful in producing and storing energy in cells. Second, monosaccharides are useful in forming long fibers such as cellulose.
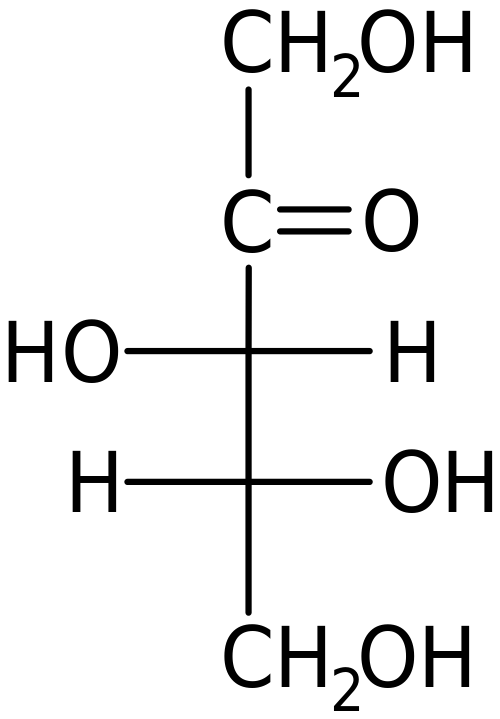
Figure 01: Structure of a Ketose
When considering the monosaccharide structure, there is a carbonyl group (one carbon atom bonds with an oxygen atom via a double bond) and a hydroxyl group (-OH group). Other than these two groups, all other carbon atoms have a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group bonded to them. If the carbonyl group occurs at the end of the carbon chain of the monosaccharide, then it is an aldose. But if it is in the middle of the carbon chain, then it is a ketose.
What is Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are macromolecular carbohydrates that form via the combination of a large number of simple sugar units with each other via glycosidic bonds. It is the form in which most of the important carbohydrates occur. There are two forms of linear structures or branched structures. Linear structures can pack with each other to form rigid carbohydrate structures but branched forms do not pack tightly.
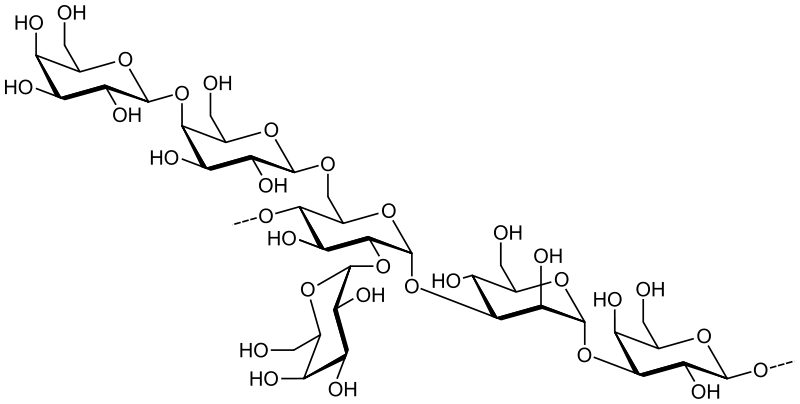
Figure 02: A Branched Polysaccharide
The general formula of a polysaccharide is Cx(H2O)y in which x is a large number between 200 to 2500. However, as a general rule, these compounds contain more than ten simple sugar units. The most important examples of these macromolecules include cellulose and starch in plants and glycogen in animals.
What is the Difference Between Monosaccharide and Polysaccharide?
Monosaccharide vs Polysaccharide | |
| Simple sugar molecules that are the basic units of carbohydrates | Macromolecular carbohydrates formed by the combination of a large number of simple sugar units with each other via glycosidic bonds |
| Chemical Formula | |
| The general formula of monosaccharides is CnH2nOn where n is a small, whole number. | The general formula of polysaccharides is Cx(H2O)y in which x is a large number between 200 to 2500. |
| Number of Monomers | |
| Single molecules | Consists of a large number of molecules |
| Ring Structures | |
| Have a single ring structure in their chemical structure | Have some ring structures in their chemical structure |
| Nature | |
| Monomers | Polymers |
| Taste | |
| Taste sweet | Tasteless |
| Reducing Strength | |
| Reducing sugars | Non-reducing sugars |
Summary – Monosaccharide vs Polysaccharide
Saccharides are sugars. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that make up the complex structure of carbohydrates. The difference between monosaccharide and polysaccharide is that monosaccharide is an individual sugar molecule whereas polysaccharide is a combination of several sugar molecules.
Reference:
1. Editors. “Monosaccharide – Definition, Function, Structure and Examples.” Biology Dictionary, Biology Dictionary, 29 Apr. 2017. Available here
2. “Polysaccharide.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 13 May 2018. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.’DXylulose Fischer’By Christopher King – Own work, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.’Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii capsular polysaccharide’By Ninjatacoshell – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau265zqemrJmTmLWivsidnGaZnpl6sbvLsqqam5OdrrO1w55m