Difference Between Parasitism and Mutualism
The key difference between parasitism and mutualism is that parasitism is a type symbiotic relationship that occurs between two species in which parasite lives inside or on the host organism and gains benefits at the expense of the host while mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship in which both species gain benefits from the interaction.
Symbiotic associations are specific interactions between two or more species that live together. Some symbiotic interactions are beneficial while some are harmful. There are three types of symbiotic associations as mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Commensalism is a relationship between two parties in which one party gains benefits without harming or benefitting the other party. Orchids are a good example of commensalism. They grow on tall trees to get sunlight and obtain mineral nutrients from the barks of the host trees. Whereas, mutualism is an interaction which is beneficial for both parties in the interaction. On the other hand, parasitism is a kind of symbiosis in which one organism benefits at the expense of the other party.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Parasitism
3. What is Mutualism
4. Similarities Between Parasitism and Mutualism
5. Side by Side Comparison – Parasitism vs Mutualism in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Parasitism?
Parasitism is a symbiotic association in which parasite lives in and on the host organisms and gains benefits at the expense of the host. Thus, parasitism exists between a parasite and a host. Parasite harms the host by damaging the host tissues and ultimately causing diseases or death of the host.
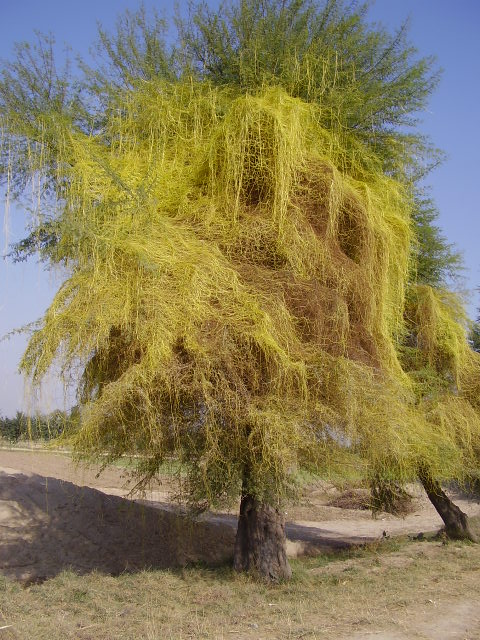

Figure 01: Total parasite – Cuscuta
There are two types of parasitism as semi or partial-parasitism and total parasitism. Semi parasitism is a phenomenon the parasite obtains only water and mineral from the host by haustoria. Loranthus is a good example of semi parasitism. In total parasitism, the parasite obtains organic food and mineral nutrients from the host plant. Cuscuta is a total parasite. Also, while semi-parasitic plants are green in color and are photosynthetic, total parasitic plants are not photosynthetic.
What is Mutualism?
Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship where both parties benefit from each other. There are many mutualistic interactions. One such mutual association is the mycorrhizae. It is an association between the roots of higher plants and a fungus. The fungus helps the plant to absorb water and minerals. At the meantime, the fungus obtains nutrients/ organic food from the higher plant. A bacterium called Rhizobium resides in legume plant root nodules. Also, this is a symbiotic relationship. Rhizobium is able to fix atmospheric nitrogen and fulfill the nitrogen requirement of the plant while the plant provides food and shelter to the bacterium.
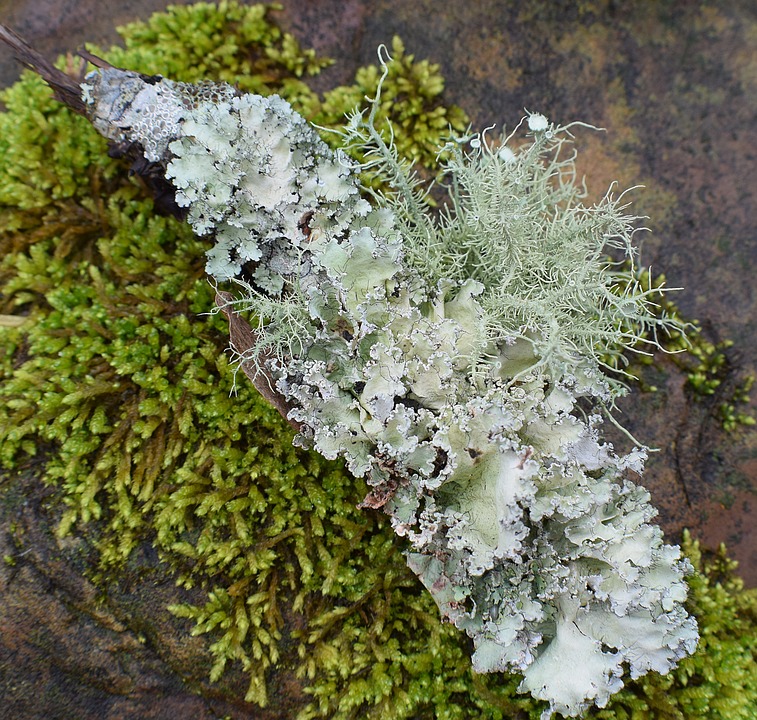

Figure 02: Lichen
In coralloid root, the mutual association exists between the root of Cycas and Anabaena, which is a cyanobacterium. The plant obtains fixed nitrogen due to the presence of Anabaena, and the cyanobacterium obtains protection and nutrients from the plant. Another mutual relationship exists between Azolla leaf and Anabaena. Similar to the previous case, the plant obtains fixed nitrogen due to the presence of cyanobacterium, and the cyanobacterium obtains protection and shelter from the plant. Another popular mutual relationship is lichen, which is an association between green algae and a fungus. The algae are protected from desiccation and fungus obtains organic food due to the presence of green algae.
What are the Similarities Between Parasitism and Mutualism?
- Parasitism and mutualism are two types of symbiotic interactions.
- Two or more species involve in these types of interactions.
- Also, both are essential interactions between organisms in order to maintain healthy ecosystems.
What is the Difference Between Parasitism and Mutualism?
Parasitism is an association where only one parasite is benefitted at the expense of the host. Whereas, mutualism is a symbiotic relationship where both parties benefit from each other. So, this is the key difference between parasitism and mutualism. Also, a significant difference between parasitism and mutualism is that the parasite harms the host by damaging the host tissues and ultimately causing disease or death to the host. But, in mutualism, none of the species is harmed. Thus, parasitism is beneficial for the parasite while mutualism is beneficial for both parties.
Moreover, the parasite needs the host while the host does not need the parasite. But in mutualism, both species need the presence of each other. Hence, we can consider this also as a difference between parasitism and mutualism. Additionally, a further difference between parasitism and mutualism is that the parasitism is a kind of specific interaction while mutualism is not a very specific interaction. Parasitism exists in Cuscuta, mosquito and human, lice on human, tapeworms in cow, etc. In contrast, the relationship between bees and flowers, digestive bacteria and humans, oxpeckers and zebras, clownfish and sea anemone, etc. show mutualism.
Below info-graphic summarizes the difference between parasitism and mutualism.
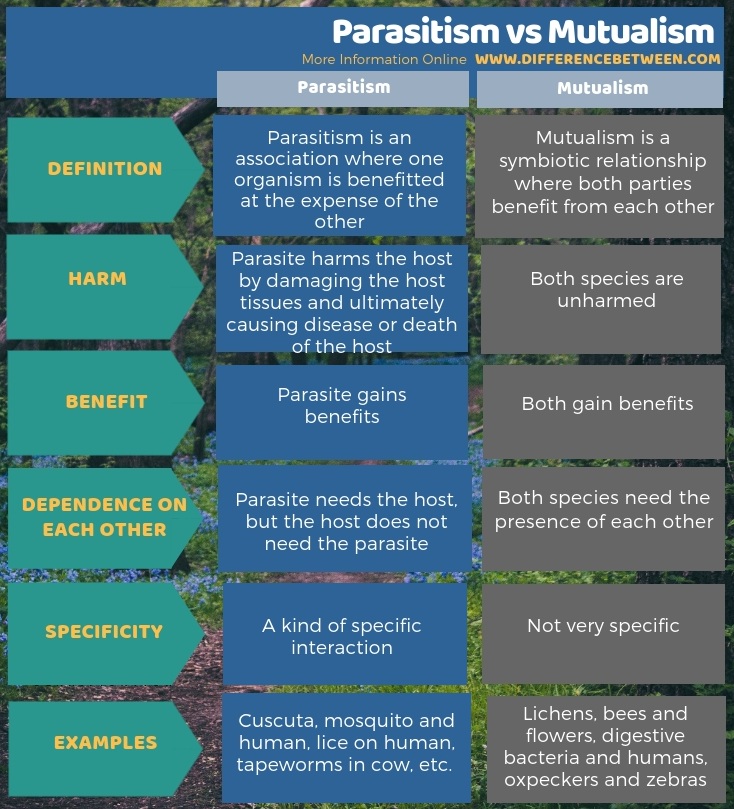
Summary – Parasitism vs Mutualism
Parasitism and mutualism are two different symbiotic relationships. Parasitism occurs between a parasite and a host. The parasite lives in or on the host organism. In this interaction, only the parasite gains benefits while harming the host. On the other hand, Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship where both parties benefit from each other. Thus, this is a summary of the difference between parasitism and mutualism.
Reference:
1. “Symbiosis.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 9 Mar. 2019, Available here.
2. “Mutualism.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 24 Aug. 2018, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Cuscuta parasite plant” By Khalid Mahmood – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “2046695” (CC0) via Pixabay
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau268wKuYrKGknsCuecCnm2auo2K6tsDUmqOiq51k