Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription
The key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription is that the prokaryotic transcription takes place in the cytoplasm while the eukaryotic transcription takes place inside the nucleus.
In a cell, DNA carries information from generation to generation controlling the activities of a cell. Moreover, DNA is responsible for synthesizing all proteins that have a functional as well as a structural role in a cell. Therefore, by synthesizing such proteins, DNA controls the activities of a cell. A gene that contains the genetic information to produces a protein should be expressed in order to synthesize the respective protein. Gene expression occurs via two main steps namely transcription and translation. Hence, transcription is the first step of gene expression. It is followed by translation. During the transcription, the genetic information on DNA transforms into a three letter genetic code sequence in the mRNA. During the translation, the mRNA is converted into a chain of polypeptides.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Prokaryotic Transcription
3. What is Eukaryotic Transcription
4. Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription
5. Side by Side Comparison – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Transcription in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Prokaryotic Transcription?
Prokaryotic transcription takes place in the cytoplasm. Also, it is always occur coupled with translation. Transcription in the prokaryotic cell has four stages: binding, initiation, elongation and termination. RNA polymerase is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of the mRNA strand. Binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter sequence is the first step in transcription. In a bacterial cell, only one kind of RNA polymerase exists which synthesizes all classes of RNA: mRNA, tRNA and rRNA. RNA polymerase found in Escherichia coli (E coli) consists of two α subunits and two β subunits and a sigma factor.
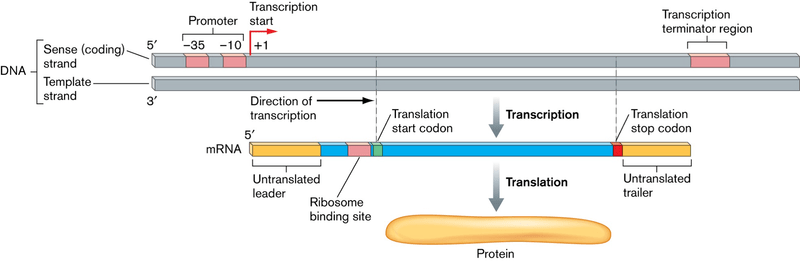
Figure 01: Prokaryotic Transcription
When this sigma factor binds to the DNA promoter sequence resulting in the unwinding of DNA double helix, initiation takes place. Using one of the DNA strands as a template, RNA polymerase synthesizes the RNA strand moving along the DNA strand unwinding the helix in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Hence, during the elongation step, this RNA strand grows from 5′ to 3′ forming a short hybrid with the DNA strand. Once the termination sequence meets, elongation of the mRNA sequence ceases. In prokaryotes, there are two types of termination; factor-dependent termination and intrinsic termination. Factor dependent termination needs Rho factor, and intrinsic termination happens when the template contains a short GC rich sequence near the 3′ end after several uracil bases.
What is Eukaryotic Transcription?
Eukaryotic transcription takes place in the nucleus. Similar to prokaryotic transcription, eukaryotic transcription also occurs via four steps, i.e. binding, initiation, elongation and termination. However, eukaryotic transcription is more complex than the prokaryotic transcription.
In a eukaryotic cell, three different kinds of RNA polymerases are present; they are namely, RNA pol I, II and III and they differ from their location and types of RNA they synthesize. RNA polymerase binds with the DNA at the promoter region with the help of transcriptional factors. When the DNA helix unwinds into single strands, RNA polymerase catalyzes the synthesis of mRNA sequence from the template strand. This RNA strand grows from 5′ to 3′ forming a short hybrid with the DNA strand, and that is called elongation. Elongation is ceased with the transcription of a special sequence called a termination signal. Termination is controlled by a variety of signals which vary with the enzyme involved.

Figure 02: Eukaryotic Transcription
Moreover, the initial RNA sequence that results from the transcription is a premature RNA sequence. It contains junk sequences. Hence, prior to translation, some modifications occur in order to produce mature mRNA. These modifications include RNA splicing, 5’ capping, 3’ adenylation, etc. Once the modifications happen, mRNA sequence travels to the cytoplasm. Unlike in prokaryotes, eukaryotic transcription does not occur simultaneously with the translation.
What are the Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription?
- Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription follow the same mechanism.
- Also, both have similar steps.
- At the end of both processes, an mRNA is produced.
- Furthermore, RNA polymerase catalyzes both transcription processes.
- Besides, both processes use DNA template to produce a mRNA sequence.
What is the Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription?
Prokaryotic transcription takes place in the cytoplasm. On the other hand, eukaryotic transcription takes place in the nucleus. This is the key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription. Furthermore, prokaryotic transcription produces polycistronic mRNA while eukaryotic transcription produces monocistronic mRNA. Thus, it is also a difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription. Also, one more difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription is that the prokaryotic transcription involves one type of RNA polymerase while eukaryotic transcription involves three types of RNA polymerases.
Moreover, another difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription is that the transcription and translation are coupled in prokaryotes while they are not coupled in eukaryotes. Furthermore, in prokaryotes, post-transcriptional modifications are not taking place while in eukaryotes, post-transcriptional modification occurs. Thus, it is also a difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription.
Below infographic on the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription provides more information on the differences.
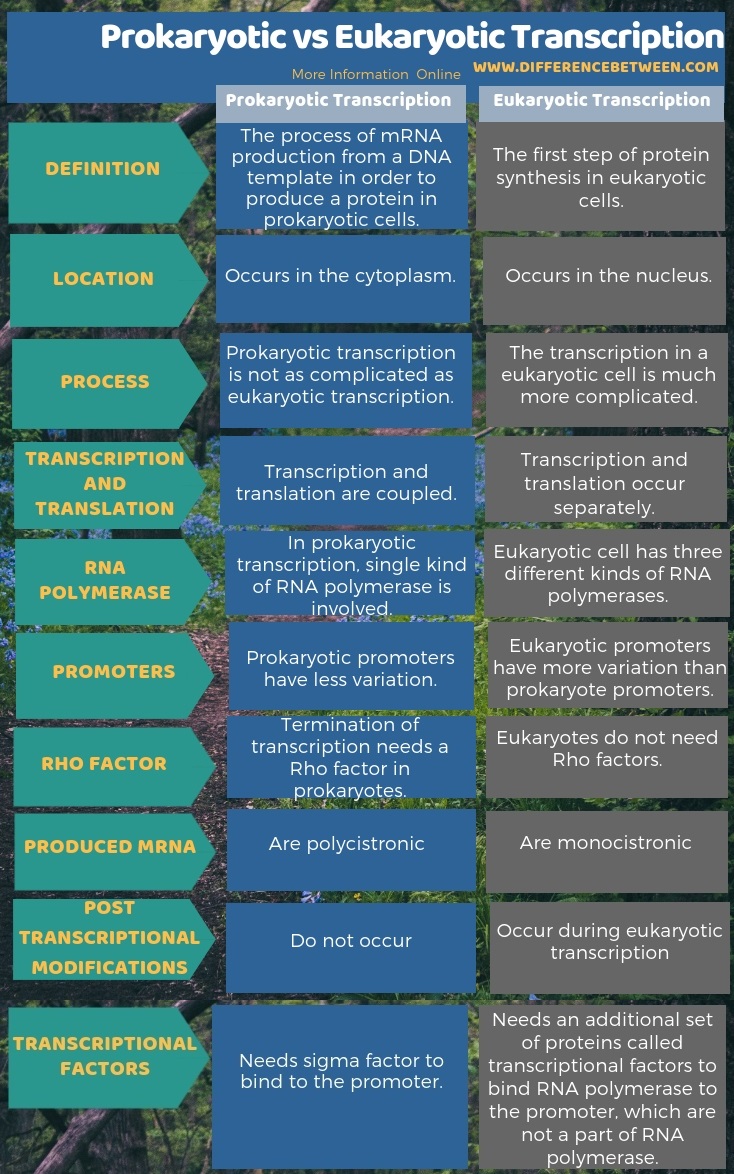
Summary – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Transcription
Transcription is the first step of gene expression, which is followed by translation. Though the transcription mechanism is the same in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are several differences between them. The key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription is that the prokaryotic transcription occurs in the cytoplasm while the eukaryotic transcription occurs in the nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotic transcription involves only one RNA polymerase while eukaryotic transcription involves three types of RNA polymerases. Moreover, the mRNA sequence of prokaryotes is polycistronic while in eukaryotes, mRNA sequence is monocistronic. Not only that, in eukaryotes, post-transcriptional modifications occur while in prokaryotes, they do not occur. This is the summary of the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription.
Reference:
1. Cooper, Geoffrey M. “Transcription in Prokaryotes.” Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 1 Jan. 1970. Available here
2. “Eukaryotic Transcription.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 17 Jan. 2019. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Bacterial Protein synthesis”By Joan L. Slonczewski, John W. Foster – Microbiology: An Evolving Science, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”Eukaryotic Transcription”By Frank Starmer (CC BY 1.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau2680aiimqqppMGqr4yapZ1lpqh6psHKmqmyp6SesG7A0ZqlrJuinr21tc6nZg%3D%3D