Difference Between Stable and Metastable
The key difference between stable and metastable is that the term stable refers to the state of a material being truly unchanging whereas the term metastable refers to the state of a material where a change cannot be observed because the changing is too slow to be observed.
The terms stable and metastable are used mainly in physical chemistry in order to get an idea of the state of a material/substance where we can describe the changing or unchanging nature of that substance. The term metastable is used when we can observe an unchanging nature due to the very slow changing that occurs, which is unobservable at first sight.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Stable
3. What is Metastable
4. Side by Side Comparison – Stable vs Metastable in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Stable?
The term stable refers to the phase of matter which is truly unchanging. In other words, it is the state where matter can have the least energy state, or it is the lowest possible energy state of matter for a dynamic system. This state of matter is called the ground state. The following diagram shows the stable, unstable and metastable state of matter in a dynamic system.
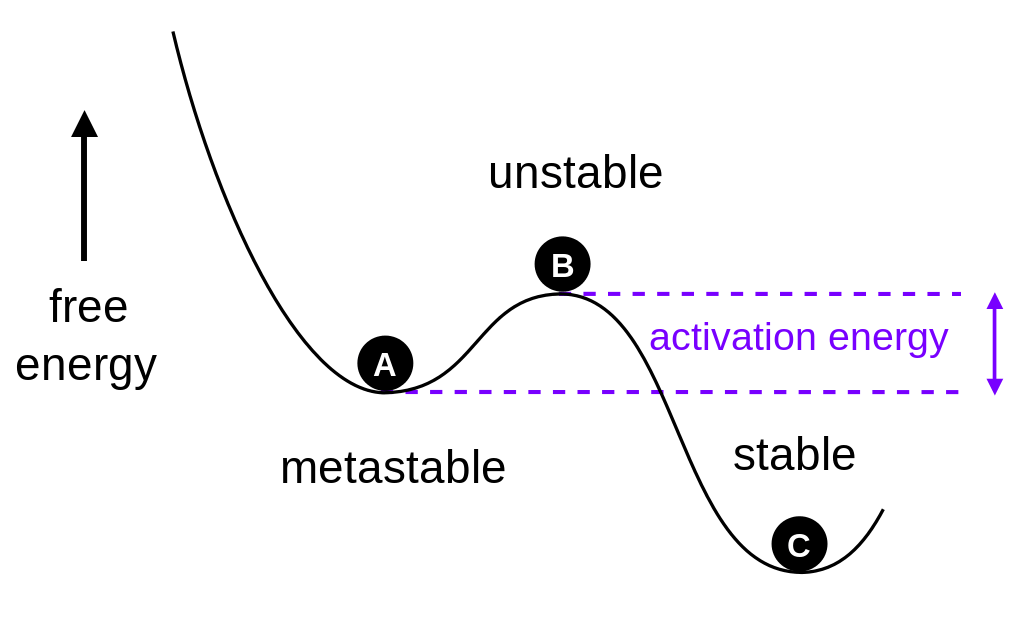
The term metastable refers to the phase of matter that is apparently unchanging but truly unchanging. In other words, this term is used for systems where we cannot observe a changing in that system because the changing is too slow to be observed. The phenomenon that discusses the metastable nature of a system is called the metastability.
Unlike the stable phase of matter, the metastable phase has considerably high energy in a dynamic system when compared to the lowest energy level possible for that system. The following figure shows a system having both metastable and stable phases of matter.
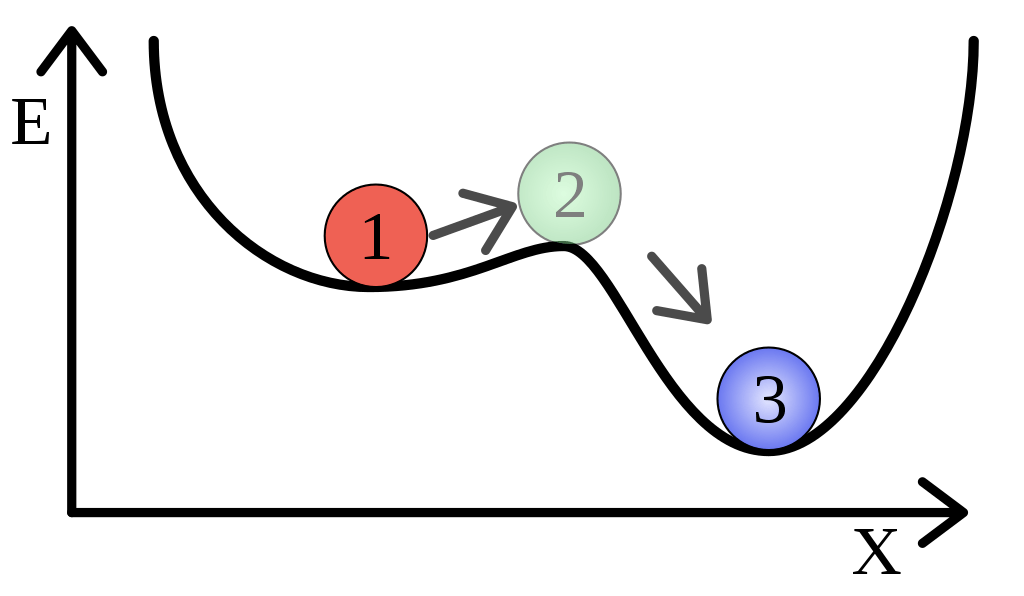
The metastable state of matter can range from melting solids, boiling liquids and subliming solids to super-cooled liquids or superheated liquid-gas mixtures. Usually, the metastable phases of matter are common in condensed matter and crystallography.
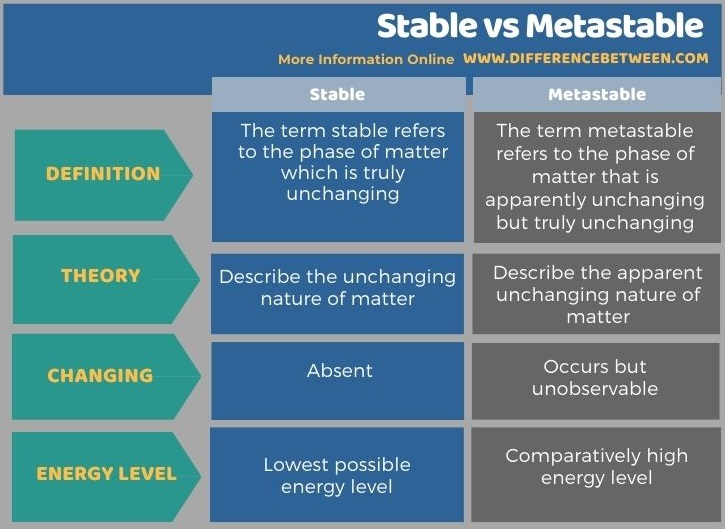
The terms stable and metastable are used in physical chemistry in order to get an idea of the changing nature of a material. The key difference between stable and metastable is that the term stable refers to the state of a material being truly unchanging whereas the term metastable refers to the state of a material where a change cannot be observed because the changing is too slow to be observed. In other words, the term stable describes the unchanging nature of matter, while the term metastable describes the apparent unchanging nature of matter. Moreover, stable has the lowest possible energy level whereas metastable has a comparatively high energy level.
Below infographic tabulates the differences between stable and metastable for side-by-side comparison.
Summary – Stable vs Metastable
The terms stable and metastable are used in physical chemistry in order to get an idea of the changing nature of a material. The key difference between stable and metastable is that the term stable refers to the state of a material being truly unchanging whereas the term metastable refers to the state of a material where a change cannot be observed because the changing is too slow to be observed.
Reference:
1. “Metastability.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 19 Oct. 2020, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
.”Thermodynamic stability EN” By Woudloper – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Meta-stability”By Georg Wiora (Dr. Schorsch) – self made drawing (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26%2F05qZpZ1dlrulecyeq5qrpJavrbGO