Difference Between Tissue and Cell
The key difference between tissue and cell is that tissue is a collection of similar cells carrying out similar or related functions while cell is the smallest fundamental unit of structure and function in living organisms.
Cells are the building blocks of tissues; tissues make organ systems, and finally, all these together form an organism. There are different types of cell, as well as different types of tissues, but the basic properties of cells and tissues do not overlap with each other. Therefore, this article intends to discuss the basic difference between cell and tissue after analyzing some basic characteristics about them.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is a Tissue
3. What is a Cell
4. Similarities Between Tissue and Cell
5. Side by Side Comparison – Tissue vs Cell in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is a Tissue?
A tissue is an assemblage of cells of the same origin. The assemblage mainly focuses on fulfilling one common function. It is important and should be noticed that the tissues are present only in the multicellular animals and plants. The cells in a tissue may not be identical to each other, but the origin is the same for each one. There is always a substance known as the plasma between cells to keep it as a unit.
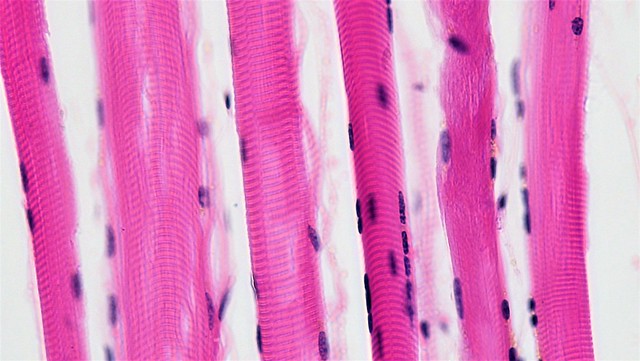
Figure 01: Muscle Tissue
There are four main types of tissues in animals: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. These four types of tissues are present in all the multicellular animals in general, and the proportions of each type of tissue vary among species as well as individuals according to the genome.
Tissues account for all the activities performed by an organism, and all these basic types of tissues function as a whole unit through coordinating via hormonal and nervous signals. Generally, the nervous tissues coordinate a particular function, and muscle tissues execute it with the assistance of connective and epithelial tissues.
What is a Cell?
Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. A cell could be either the whole unit of an organism (unicellular organisms) or the very basic unit of a large multicellular animal or tree. However, all these large multicellular organisms such as elephants or whales, start their lives as a basic cell formed from a sperm cell and an ovum. However, a typical cell consists of several types of organelles, such as mitochondria, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, ribosomes, nucleus, and some more.
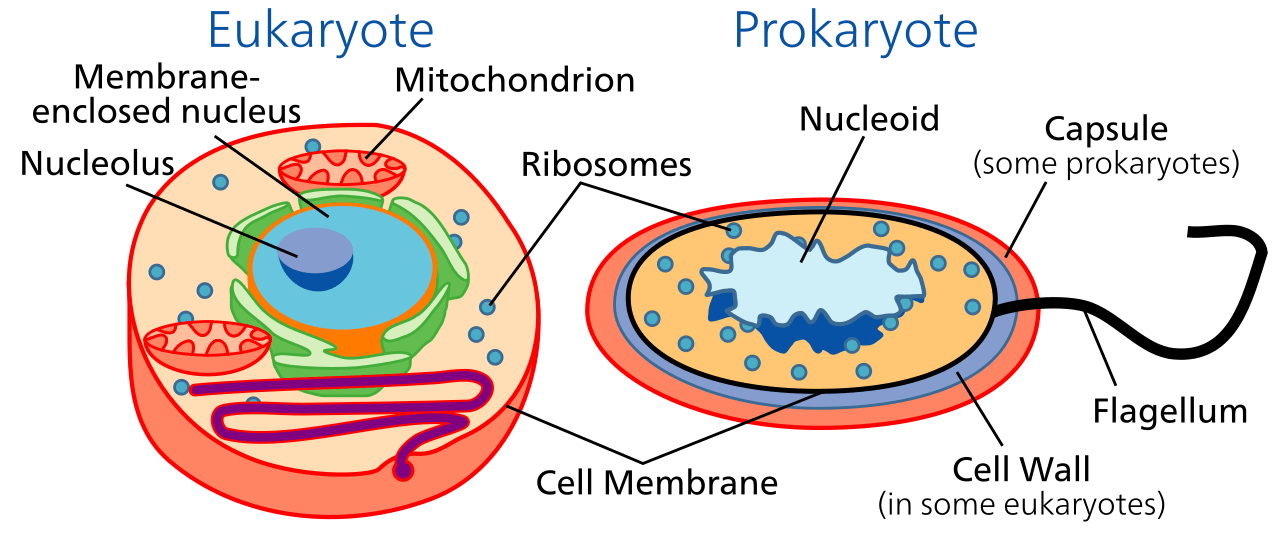
Figure 02: Cells
These minute organelles have different functions; interestingly the proportions of the density of these organelles vary according to the basic function of a particular cell. The nucleus contains all the genetic information of the cell and regulates all the activities inside a cell. Mitochondria are responsible for performing metabolic activities. Additionally, the Golgi complex and lysosomes help in defending the cells. Each cell has a defined margin formed by the cell membrane, and this membrane is semi-permeable. Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, unlike prokaryotic cells.
Every function of the body occurs inside a cell; hence, the importance of each cell of a particular animal or plant could never be underestimated. The importance could be clearly understood when a slight alteration of a particular cell results in deadly cancer or an irreversible mutation.
What are the Similarities Between Tissue and Cell?
- Cell and tissue are two levels of the cellular organization of a multicellular organism.
- Importantly, the tissue is a collection of cells working together.
- Tissues and cells are found in living organisms.
- Also, both cell and tissue fulfil different functions inside an organism.
What is the Difference Between Tissue and Cell?
The tissue is a group of cells that are working together in order to carry out a similar function while the cell is the basic structural and functional unit of an organism. Therefore, this is the key difference between tissue and cell. Furthermore, both unicellular and multicellular organisms possess cells, but only multicellular organisms have tissues. Moreover, a further difference between tissue and cell is their size. That is; a tissue is a macroscopic structure while a cell is a microscopic structure.
The below info-graphic presents more facts on the difference between tissue and cell, comparatively.

Summary – Tissue vs Cell
Cell and tissue are two levels of the cellular organization of a multicellular organism. Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of an organism, while tissue is a group of cells working together for a similar function. So, this is the key difference between tissue and cell. Furthermore, all unicellular and multicellular organisms have a cell or cells, while only multicellular organisms have tissues.
Reference:
1. “Tissues, Organs, & Organ Systems.” Khan Academy, Khan Academy, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Fibers” By Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library (Public Domain) via Flickr
2. “Celltypes” By Science Primer (National Center for Biotechnology Information). Vectorized by Mortadelo2005. – SVG version of Image:Celltypes.png (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau27AyKyqrp1dlruledWsZJydnKF8