What is the Difference Between 1 Butene and 2 Butene
The key difference between 1 butene and 2 butene is that 1-butene has a double bond between carbon atoms at the end of the carbon chain, whereas 2-butene has a double bond between carbon atoms at the middle of the compound.
Butene is an organic compound having the chemical formula C4H8. “Butylene” is a synonym for the same compound. This compound has four carbon atoms and eight hydrogen atoms. There is a double bond between two carbon atoms. Therefore, it is an unsaturated compound. It falls under the category of alkenes. It is a colorless gas at room temperature and pressure. We can find this gas as a minor constituent in crude oil. Thus, we can obtain this compound via catalytic cracking in a refinery.
Due to the presence of the double bond, this compound has isomers. There are four major isomers: they are, But-1-ene, (2Z)-but-2-ene, (2E)-but-2-ene and 2-methylprop-1-ene (isobutylene). All these isomers exist as gases. We can liquefy them by two methods: we can lower the temperature or increase the pressure. These gases have distinct odors. Moreover, they are highly flammable. The double bond makes these compounds more reactive than alkanes with a similar number of carbon atoms. When considering the applications of this compound, we can use them as monomers in the production of polymers, in the production of synthetic rubber, in the production of HDPE and LLDPE, etc.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is 1 Butene
3. What is 2 Butene
4. 1 Butene vs 2 Butene in Tabular Form
5. Summary – 1 Butene vs 2 Butene
What is 1-Butene?
1-butene is an organic compound having the chemical formula CH3CH2CH=CH2. It is also known as 1-butylene. It appears as a colorless gas that can be made into a colorless liquid. We can classify this substance as a linear alpha-olefin.
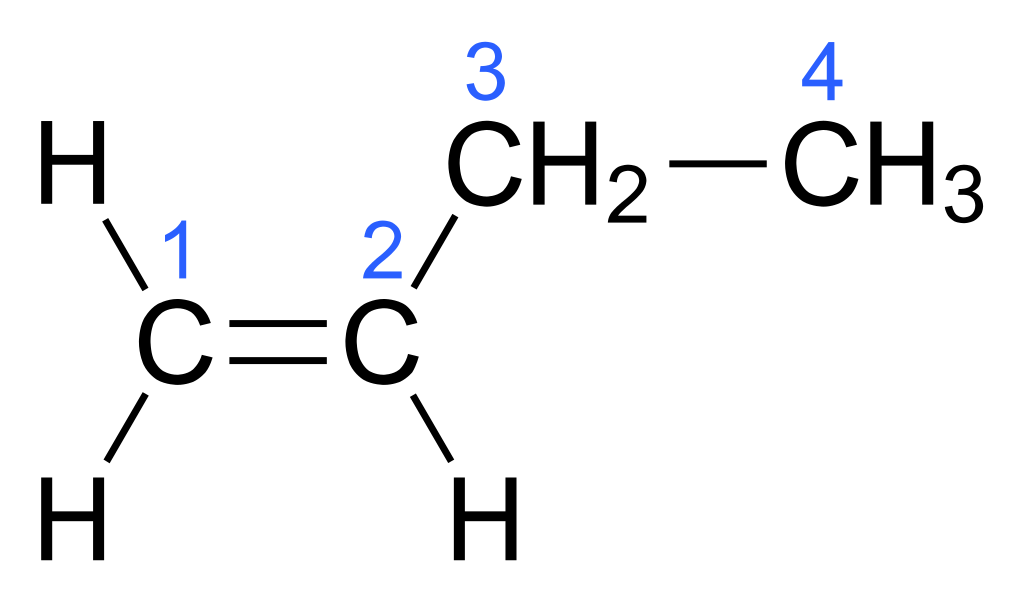
Figure 01: The Chemical Structure of 1-Butene
We can produce 1-butene via the separation from crude C4 refinery streams and through ethylene dimerization. Separation from the C4 refinery creates a mixture of 1- and 2- butane compounds. The ethylene dimerization process produces only the terminal alkene. We can distill the product given by these methods to get a very high purity product. Approximately about 12 billion kilograms of 1-butene were produced in 2011.
What is 2-Butene?
2-butene is an organic compound having the chemical formula CH3CH=CHCH3. It is an acyclic alkene having four carbon atoms. We can identify it as the simplest alkene showing cis-trans isomerism. In other words, 2-butene can be found in two geometric isomers as the cis isomer and trans isomer. These compounds are named respectively as cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene.
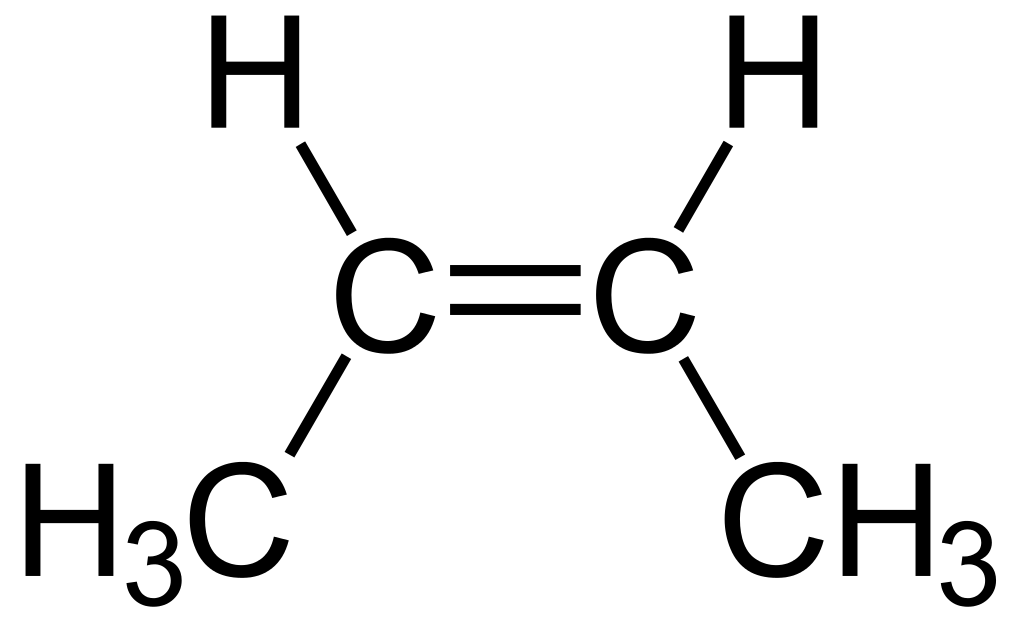
Figure 02: Cis-2-Butene
2-butene is a petrochemical compound that forms from the catalytic cracking process of crude oil. Moreover, we can produce it through the dimerization of ethylene. Generally, it is very difficult to separate the two isomers of 2-butene through distillation. This is because of the proximity of the boiling points of these isomers.
There are different uses of 2-butene, which include production of gasoline and butadiene, production of solvent butanone through hydration to 2-butanol followed by oxidation, etc. In most industrial applications, the separation of two isomeric forms from each other is unnecessary because both isomers behave similarly in desired reactions.
What is the Difference Between 1 Butene and 2 Butene?
The key difference between 1-butene and 2-butene is that 1-butene has a double bond between carbon atoms at the end of the carbon chain, whereas 2-butene has a double bond between carbon atoms at the middle of the compound.
The below infographic presents the differences between 1 butene and 2 butene in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – 1 Butene vs 2 Butene
1-butene is an organic compound having a chemical formula CH3CH2CH=CH2, while 2-butene is an organic compound having a chemical formula CH3CH=CHCH3. The key difference between 1 butene and 2 butene is that 1-butene has a double bond between carbon atoms at the end of the carbon chain, whereas 2-butene has a double bond between carbon atoms at the middle of the compound.
Reference:
1. “2-Butene.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Image Courtesy:
1. “1-butene” By JaGa – Own work (Original text: Self-made using BKChem and Inkscape) (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Cis-2-Buten” By NEUROtiker – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoxqZJutpJq7pnnAp5tmal2XwrWxzZ5m