What is the Difference Between Biogas and Biomethane
The key difference between biogas and biomethane is that biogas forms via anaerobic digestion through microorganisms and is a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, whereas biomethane forms via the fermentation of organic matter and contains about 90% methane and other components.
In brief, biogas and biomethane are end products of the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. Biomethane is a type of biogas.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Biogas
3. What is Biomethane
4. Biogas vs Biomethane in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Biogas vs Biomethane
What is Biogas?
Biogas is a mixture of gases containing methane and carbon dioxide. This gas is produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. Biogas is a renewable energy source. Typically, biogas is produced from anaerobic digestion involving anaerobic organisms. Sometimes, anaerobic digestion occurs involving methanogen inside an anaerobic digester, biodigester or bioreactor.
Primarily, biogas consists of methane, carbon dioxide, and small amounts of hydrogen sulfide, moisture, and siloxane. Among these gases, methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide can be combusted or oxidized in the presence of oxygen. This combustion releases energy, allowing the biogas to be useful as a fuel. We can use it for fuel cells and also for heating purposes, which include cooking. In addition, it is useful in gas engines to convert energy into electricity and heat.
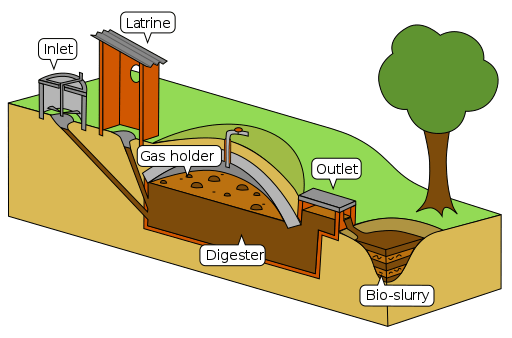
Generally, biogas becomes compressible after removing carbon dioxide, similar to the compression of natural gas into CNG. We can use this compressed gas in motor vehicles. According to European research, biogas can replace about 17% of the vehicle fuel requirements.
Biogas production involves microorganisms, including methanogens and sulfate-reducing bacteria that can perform anaerobic respiration. Moreover, biogas can refer to the gas that forms naturally or industrially. Naturally, methane forms in anaerobic environments by methanogens and in aerobic zones by methanotrophs. In biogas production plants, manufacturers use anaerobic digesters that can treat farm waste and energy crops.
What is Biomethane?
Biomethane is the methane gas that is formed from the fermentation of organic matter. It is also known as renewable natural gas or sustainable natural gas. It is a type of biogas having a quality that is similar to fossil natural gas. Biomethane contains about 90% methane or greater. Upgrading the quality of this gas allows the possibility to distribute the gas via existing gas grids within the existing appliances.
There are several different ways of methanizing carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which include bio methanation, Sabatier process and some electrochemical processes. The production process gives about 70% efficiency when used for biomass. We can minimize the cost of production by maximizing the production scale and through the location of an anaerobic digestion plant that is near the transportation links for the sources of biomass. There are three main processes we can use to make biomethane including, anaerobic digestion of organic material, production via the Sabatier reaction, and thermal gasification of organic material.
However, biomethane can cause the production of environmental pollutants such as carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, hydrogen sulfide, and particulates. Moreover, the escape of unburnt methane can cause the greenhouse effect.
What is the Difference Between Biogas and Biomethane?
Biogas and biomethane are end products of the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. Biomethane is a type of biogas. The key difference between biogas and biomethane is that biogas forms via anaerobic digestion through microorganisms and it is a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, whereas biomethane forms from the fermentation of organic matter and contains about 90% methane and other components.
The below infographic lists the differences between biogas and biomethane in tabular form for side by side comparison
Summary – Biogas vs Biomethane
Biogas and biomethane are end products of the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. Biomethane is a type of biogas. The key difference between biogas and biomethane is that biogas forms via anaerobic digestion through microorganisms, and it is a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, whereas biomethane forms from the fermentation of organic matter and it contains about 90% methane and other components.
Reference:
1. “Carbonology.” Desotec.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Biogas plant” By Tkarcher – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyboKifkah6orrDZpmip52awamtzZ5m