What is the Difference Between CO and Co
The key difference between CO and Co is that CO is an inorganic compound consisting of carbon and oxygen atoms, whereas Co is the metal named Cobalt.
CO and Co are two different chemical substances. CO is a colourless, odourless, and tasteless, flammable gas consisting of a carbon atom and an oxygen atom per molecule. Cobalt is a chemical element having the chemical symbol Co and atomic number 27.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is CO
3. What is Co
4. CO vs Co in Tabular Form
5. Summary – CO vs Co
What is CO?
CO is the chemical formula of carbon monoxide. It is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, flammable gas consisting of a carbon atom and an oxygen atom per molecule. Carbon monoxide gas is slightly less dense than air. In high concentrations, carbon monoxide is toxic to animals who use haemoglobin as the oxygen carrier in the blood. Furthermore, this gas is also known as carbonous oxide, carbon(II) oxide, flue gas, and monoxide.
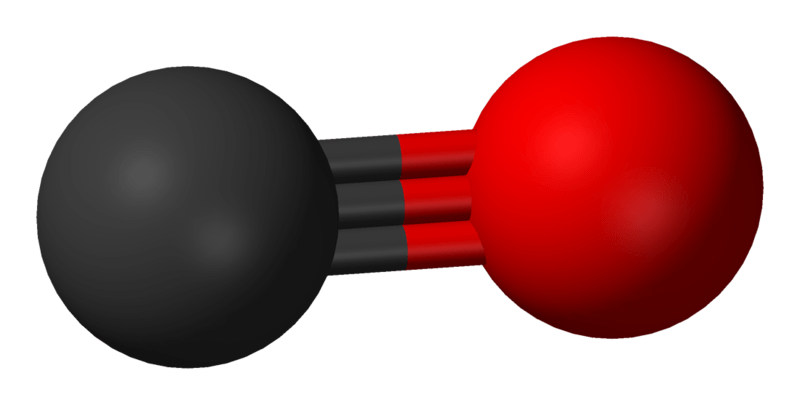
Figure 01: Ball-and-Stick Model of Carbon Monoxide
When considering the chemical structure of carbon monoxide, there is one carbon atom bonded to one oxygen atom through a triple bond containing two pi bonds and one sigma bond. We can identify carbon monoxide as the simplest oxocarbon, and it is isoelectronic with other triple-bonded diatomic species having ten valence electrons, e.g. cyanide ion.
We can prepare carbon monoxide using the partial oxidation of carbon-containing compounds such as carbon dioxide. Another important source is coal gas. Iron smelting also produces this toxic gas as a byproduct.
What is Co?
The term Co refers to cobalt metal. Cobalt is a chemical element having the chemical symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is a metal and a d-block element in the periodic table. Cobalt is in group 9 and period 4. Furthermore, we can classify it as a transition metal. Cobalt does not occur as an individual metal on earth’s crust; instead, cobalt exists in combination with other elements. However, we can produce the free element using the smelting process. Cobalt is a hard, lustrous bluish-gray metal.
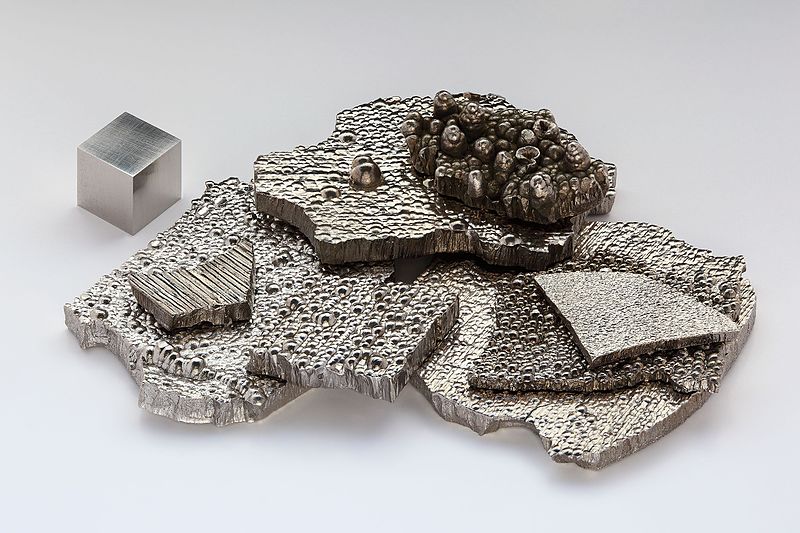

Figure 01: Cobalt
The atomic mass of cobalt is 58.93 amu. We can give the electron configuration of cobalt metal as [Ar] 3d7 4s2. At standard pressure and temperature, it is in the solid-state. The melting point and boiling points are 1495 °C and 2927 °C, respectively. The most common oxidation states of cobalt are +2, +3 and +4. Its crystal structure is a hexagonal close-packed structure.
Moreover, cobalt is a ferromagnetic material. This means it is highly attracted to magnets. The specific gravity of this metal is 8.9, which is a very high value. Halogens and sulfur can attack this metal. However, it is a weakly reducing metal. We can protect it via oxidation by a passivating oxide film.
When considering the production of cobalt, we can use ores of cobalt such as cobaltite, erythrite, glaucodot, and skutterudite. However, manufacturers often obtain this metal by reducing the cobalt byproducts of nickel and copper mining.
What is the Difference Between CO and Co?
CO is a colourless, odourless, and tasteless, flammable gas consisting of a carbon atom and an oxygen atom per molecule. Cobalt is a chemical element having the chemical symbol Co and atomic number 27. So, the key difference between CO and Co is that CO is an inorganic compound consisting of carbon and oxygen atoms, whereas Co is the metal named Cobalt.
The below infographic presents the differences between CO and Co in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – CO vs Co
CO and Co are two different substances having different chemical and physical properties. The key difference between CO and Co is that CO is an inorganic compound consisting of carbon and oxygen atoms, whereas Co is the metal named Cobalt.
Reference:
1. “Cobalt – Element Information, Properties and Uses: Periodic Table.” RSC.
2. “Carbon Monoxide.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Carbon-monoxide-3D-balls” By Benjah-bmm27 – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Kobalt electrolytic and 1cm3 cube” By Alchemist-hp (talk) – Own work (FAL) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoycpmaZnpl6pLuO