What is the Difference Between Communicating and Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus
The key difference between communicating and noncommunicating hydrocephalus is that communicating hydrocephalus is the condition that allows the cerebrospinal fluid to enter the brain ventricles while noncommunicating hydrocephalus is the condition that obstructs the flow of cerebrospinal fluid to the ventricles.
Hydrocephalus is an abnormal building up of fluids in the ventricles within the brain. The excess fluid causes the ventricles to widen, pressurizing the tissues of the brain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is the clear fluid that protects and provides a cushioning effect on the brain and spine. Communicating hydrocephalus and noncommunicating hydrocephalus are two types of hydrocephalus observed in individuals based on the ability of CSF to flow within the ventricles.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Communicating Hydrocephalus
3. What is Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus
4. Similarities – Communicating and Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus
5. Communicating vs Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Communicating vs Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus
What is Communicating Hydrocephalus?
Communicating hydrocephalus, also known as non-obstructive hydrocephalus, is the condition where CSF flow is blocked after it leaves the ventricles. It is mainly caused due to defective absorption of CSF that results from conditions such as intracranial hemorrhage or meningitis.
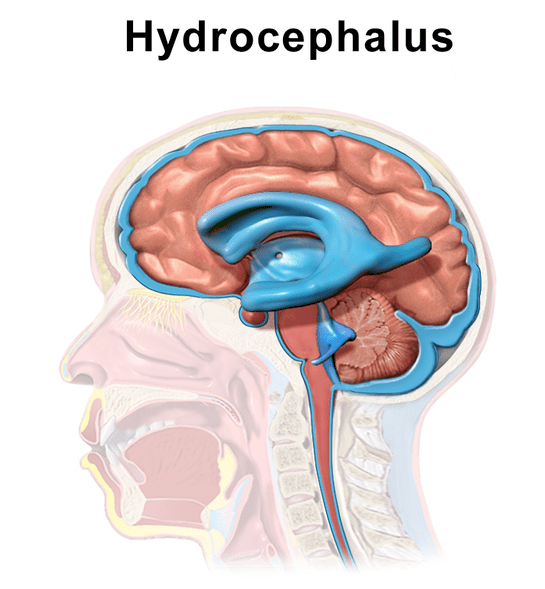
Figure 01: Hydrocephalus
Furthermore, overproduction of CSF and venous drainage insufficiency can also cause communicating hydrocephalus. In addition, scarring and fibrosis of the subarachnoid space following infectious, inflammatory, or hemorrhagic events can also prevent reabsorption of CSF, causing diffuse ventricular dilatation.
Common symptoms of communicating hydrocephalus include headache, abnormal vision, nausea, vomiting, poor coordination, sleepiness, irritability, and abnormal movements. Moreover, subarachnoid hemorrhage, meningitis, and leptomeningeal carcinomatosis arise due to persistent communicating hydrocephalus.
What is Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus?
Noncommunicating hydrocephalus is the condition that takes place when the flow of CSF is blocked along a narrow passage connecting the ventricles of the brain. A common cause for noncommunicating hydrocephalus is the narrowing of the aqueduct of Sylvius, which is a small passage located between the third and fourth ventricles of the brain.
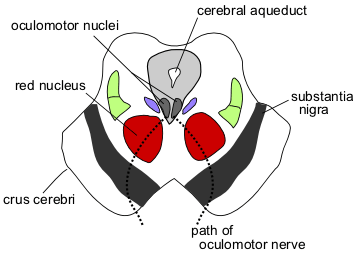
Figure 02: Cerebral Aqueduct
This condition is also called obstructive hydrocephalus. There are four main outcomes of noncommunicating hydrocephalus, including foramen of Monro obstruction, obstruction of aqueduct of Sylvius by lesions, fourth ventricle obstruction, and the obstruction of foramina of Luschka and foramen of Magendie.
Headache, abnormal vision, nausea, vomiting, poor coordination, sleepiness, irritability, and abnormal movements are some common symptoms of noncommunicating hydrocephalus. Moreover, posterior fossa mass lesions, intraventricular mass lesions, and aqueductal stenosis arise as a result of noncommunicating hydrocephalus.
What are the Similarities Between Communicating and Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus?
- Communicating and noncommunicating hydrocephalus take place due to abnormal building up of CSF in the ventricles.
- They are caused due to congenital, inherited through genetic abnormalities, or acquired tumors, strokes, or infections in the brain and spinal cord.
- Both conditions show common symptoms such as headache, abnormal vision, nausea, vomiting, poor coordination, sleepiness, irritability, and abnormal movements.
- Both are diagnosed through neurological examinations and brain imaging.
What is the Difference Between Communicating and Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus?
Communicating hydrocephalus is the condition that allows the cerebrospinal fluid to enter the brain ventricles, while noncommunicating hydrocephalus is the condition that obstructs the flow of cerebrospinal fluid to the ventricles. Thus, this is the key difference between communicating and noncommunicating hydrocephalus. Moreover, CSF flow in and out is facilitated during communicating hydrocephalus, while no CSF flow takes place during noncommunicating hydrocephalus.
The below infographic presents the differences between communicating and noncommunicating hydrocephalus in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Communicating vs Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition with abnormal building up of fluids in the ventricles within the brain, causing excess CSF to widen, pressurizing the tissues of the brain. Communicating hydrocephalus is the condition that allows the cerebrospinal fluid to enter the brain ventricles, while noncommunicating hydrocephalus is the condition that obstructs the flow of cerebrospinal fluid to the ventricles. Furthermore, communicating hydrocephalus is caused due to the overproduction or under-resorption of cerebrospinal fluid in ventricles, whereas noncommunicating hydrocephalus is caused due to obstructions in the cerebrospinal fluid flow in narrow passages within ventricles. So, this is the summary of the between communicating and noncommunicating hydrocephalus.
Reference:
1. “Communicating and Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus.” Hydrocephalus Association, 9 Mar. 2021.
2. “Hydrocephalus.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 3 Sept. 2021.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Hydrocephalus” By BruceBlaus – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Cn3nucleus” By English Wikipedia, originally: Girlza (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoycpqalpaO2pK3ToqWgZZGjsW66zqeaqKWdqruqr8CtoKefXZ3Gpb7OnJypoJGhwrR7