What is the Difference Between Emulsification and Homogenization
The key difference between emulsification and homogenization is that emulsification is the formation of an emulsion through the dispersion of an immiscible liquid in another immiscible liquid, whereas homogenization is the formation of a homogenous solution through mixing two miscible liquids.
Emulsification and homogenization are two types of analytical techniques that are useful in making solutions with different chemical and physical properties.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Emulsification
3. What is Homogenization
4. Emulsification vs Homogenization in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Emulsification vs Homogenization
What is Emulsification?
Emulsification is the process of dispersing one immiscible liquid in another immiscible liquid. There are some common emulsifying agents such as detergents and soaps. The emulsification process is usually carried out in industries through the mechanical mixing of ingredients of the emulsion inside different types of mixers.
An emulsifier is a chemical agent that allows us to stabilize an emulsion. That means it prevents the separation of liquids that usually do not mix with each other. It does so by increasing the kinetic stability of the mixture. One good example of an emulsifier is surfactants. There are two types of emulsifiers as lipophilic emulsifiers and hydrophilic emulsifiers.
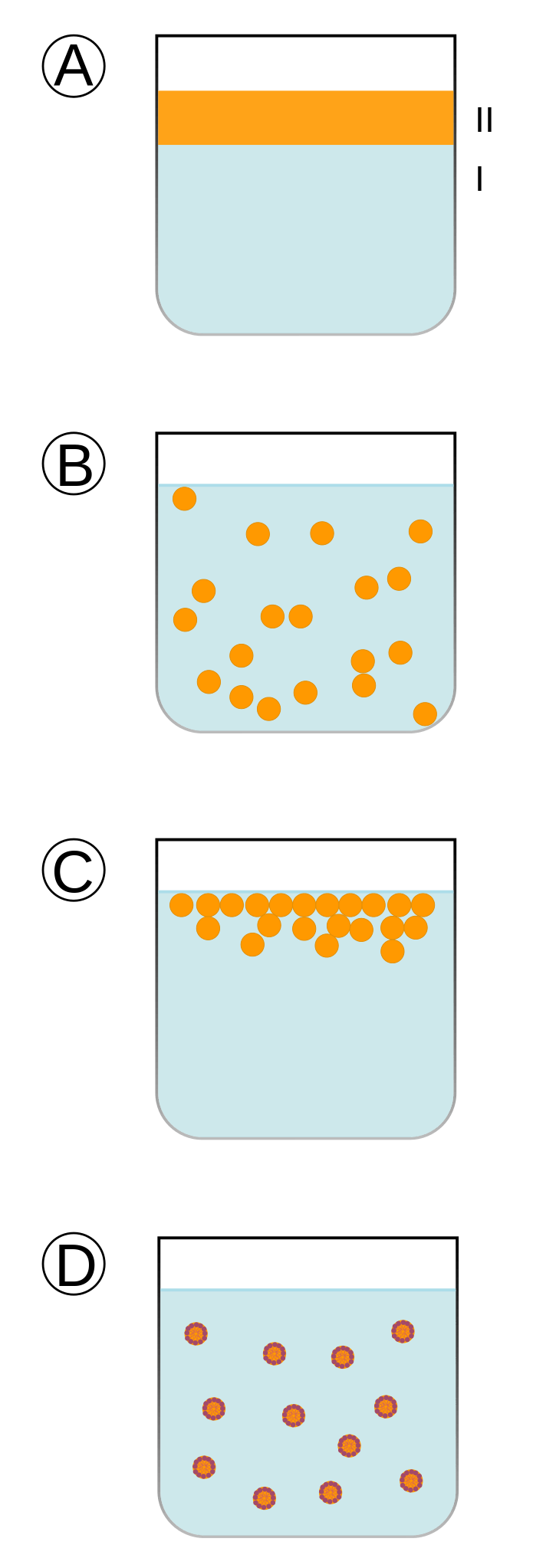
Figure 01: Formation of an Emulsion
Typically, there are three major aims of an emulsification process. First and foremost, it needs to ensure the physicochemical stability of the product. The second aim is the determination of the characteristic structure of the batter, which greatly influences the fat and moisture separation inside food during cooking. The final aim is to create a typically sensory property such as appearance, texture, savor or noise.
There are three major ways of performing emulsification. They include: emulsification depending on the surface tension theory, depending on the repulsion theory, and depending on viscosity modification.
What is Homogenization?
Homogenization is a chemical process that is useful in making a mixture of two mutually non-soluble liquids the same throughout. We can achieve this homogenization by turning two immiscible liquids into an emulsion. There are two types of homogenization processes: primary and secondary homogenization. In the primary homogenization process, the emulsion forms directly from separate liquids, whereas in the secondary homogenization process, the emulsion forms when the size of the droplets in an existing liquid is reduced. We can perform homogenization using a homogenizer.
Generally, homogenizers that are used in current industries have plunger-like pumps and valves, sometimes nozzles or interaction micron chambers. The three major factors that affect a perfect homogenization include cavitation nozzle size, impact valve operation and high shear liquid microchamber.
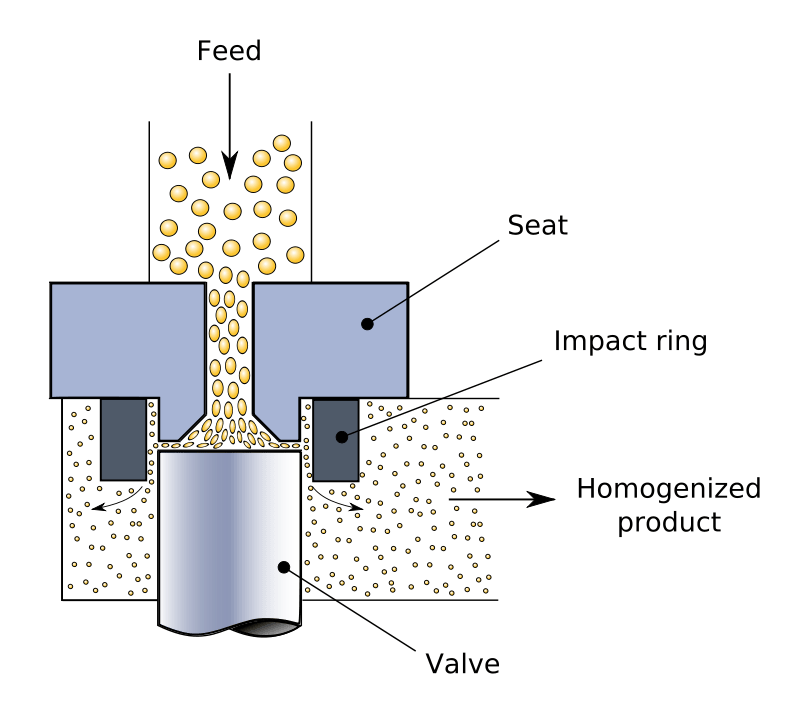
Figure 02: Process of Homogenization
There are several applications of the homogenization process, including milk processing, which has been the oldest application of a homogenizer. The other applications include the manufacture of syrups, soft drinks, and cola products.
What is the Difference Between Emulsification and Homogenization?
Emulsification and homogenization are two types of analytical techniques that are useful in making solutions with different chemical and physical properties. The key difference between emulsification and homogenization is that emulsification is the formation of an emulsion through the dispersion of an immiscible liquid in another immiscible liquid, whereas homogenization is the formation of a homogenous solution through mixing two miscible liquids.
The following infographic lists the differences between emulsification and homogenization in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Emulsification vs Homogenization
Emulsification and homogenization are two types of analytical techniques that are useful in making solutions with different chemical and physical properties. The key difference between emulsification and homogenization is that emulsification is the formation of an emulsion through the dispersion of an immiscible liquid in another immiscible liquid, whereas homogenization is the formation of a homogenous solution through mixing two miscible liquids.
Reference:
1. “Emulsification.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Emulsions” By Fvasconcellos 14:24, 17 April 2007 (UTC) – Own work, after Image:Emulsions.png by Ike9898 (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Homogenizing valve” By Valvola_omogeneizzatrice.svg: Daniele Pugliesiderivative work: Daniele Pugliesi (talk) – Valvola_omogeneizzatrice.svg (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyepK6ko56zqq%2FAraCopl2Wu6V5x6ikqJ%2BVo7a7rdOipqdn