What is the Difference Between Eugenol and Isoeugenol
The key difference between eugenol and isoeugenol is that eugenol has a clove-like odour, whereas isoeugenol has a floral odour.
Eugenol and isoeugenol are structural isomers of each other. We can distinguish them from each other through their odour because both these are aromatic compounds. Moreover, there are chemical and physical differences between eugenol and isoeugenol as well.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Eugenol
3. What is Isoeugenol
4. Eugenol vs Isoeugenol in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Eugenol vs Isoeugenol
What is Eugenol?
Eugenol is an allyl guaiacol substance having the chemical formula C10H12O2. It is a chain-substituted guaiacol substance and is a member of allylbenzene compounds. It appears as a colourless or pale yellow coloured compound, and it is an aromatic, oily liquid substance. We can extract this substance from certain essential oils such as clove, nutmeg, cinnamon, basil, and bay leaf. Moreover, it is present in high concentrations in clove bud oil and in clove leaf oil. As a characteristic feature, the eugenol compound has a pleasant, spicy, clove-like scent.
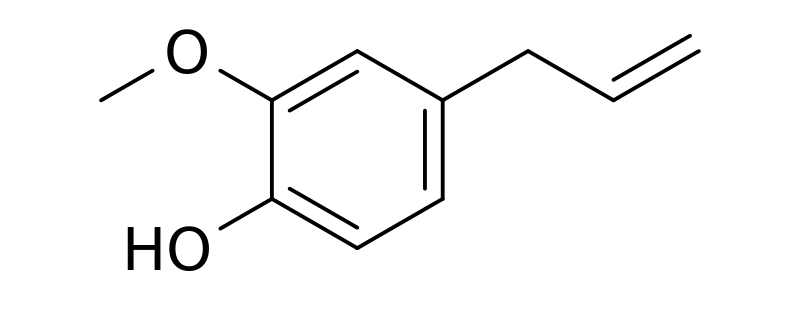
Figure 01: The Chemical Structure of Eugenol
The major applications of the eugenol compound include the manufacture of perfumes, flavourings and essential oils. Moreover, we can use this substance in local antiseptics and anaesthetic applications. In addition, the combination of eugenol with zinc oxide gives zinc oxide eugenol, and it has restorative and prosthodontic applications (mainly in dentistry).
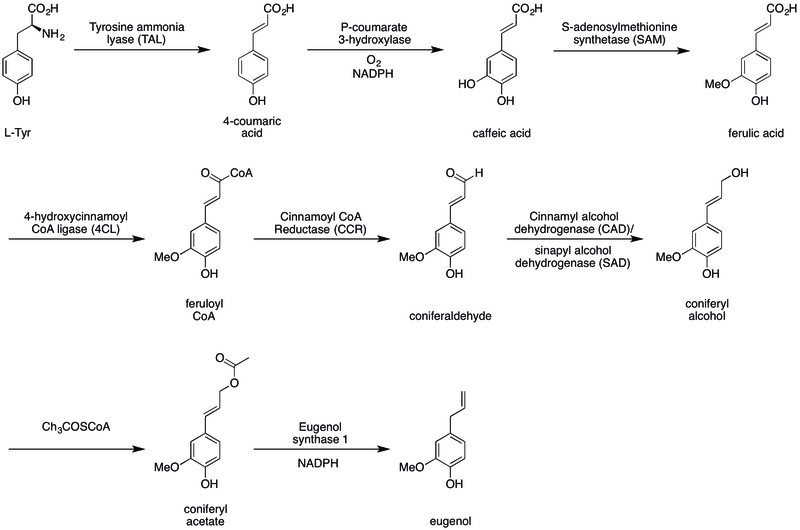
Figure 02: The Conversion of Tyrosine into Eugenol
When considering the biosynthesis of eugenol, it starts with tyrosine amino acid. In this process, the L isomer of tyrosine is used, and it converts into p-coumaric acid in the presence of the tyrosine ammonia-lyase enzyme. Thereafter, this p-coumaric acid converts into caffeic acid in the presence of a p-coumarate 3-hydroxylase enzyme, oxygen, and NADPH. Eventually, the caffeic acid converts into eugenol via some other simple conversions.
What is Isoeugenol?
Isoeugenol is a type of phenylpropene, and it is a substituted guaiacol. We can find this substance existing in essential oils of plants like ylang-ylang, and it is also a component in wood smoke and liquid smoke. Moreover, we can synthesize isoeugenol from eugenol.
There are two forms of isoeugenol as the cis isomer and the trans isomer. The cis isomer of isoeugenol appears as a liquid, whereas the trans isomer of isoeugenol appears as a crystalline substance. This substance is very useful in manufacturing vanillin. In addition, it is responsible for the mould-inhibiting effect of smoke on meat and cheese.
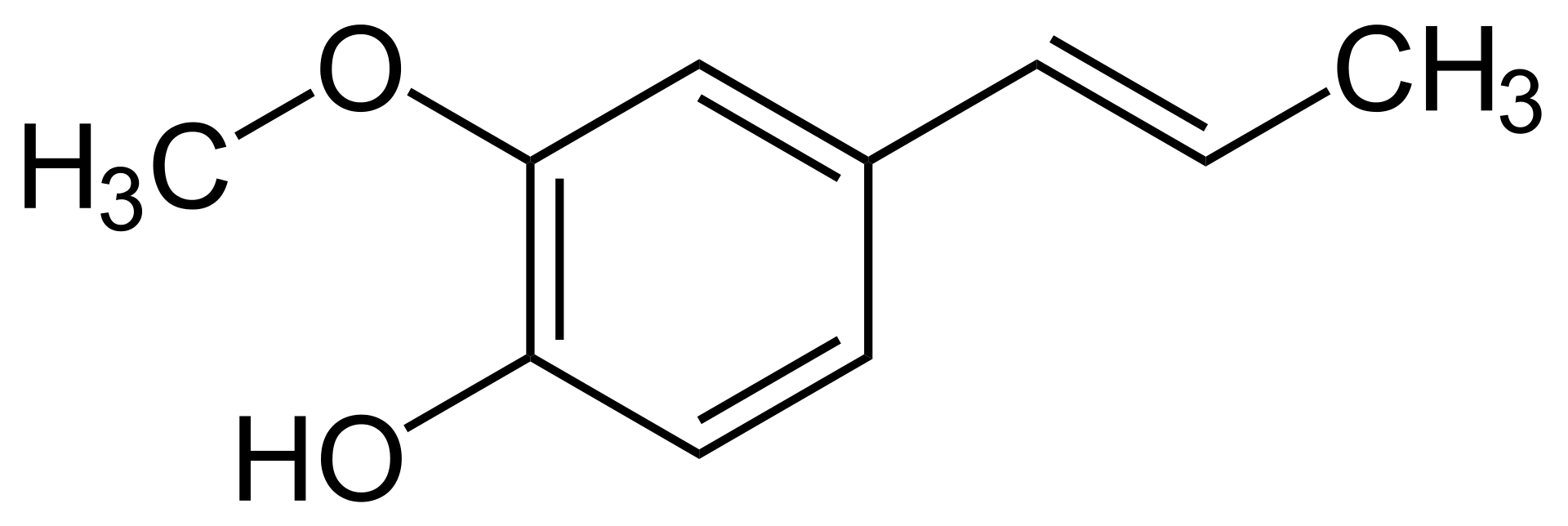
Figure 03: The Chemical Structure of Isoeugenol
However, some people show an allergy to isoeugenol; the common symptom is a hive-like reaction. This symptom comes when they are exposed to the fragrance of soaps, bath tissues, shampoos, detergents, and topical cosmetic applications containing this substance. Furthermore, we can check sensitivity to this substance using a clinical patch test.
What is the Difference Between Eugenol and Isoeugenol?
Eugenol and isoeugenol are isomers of each other. Eugenol is an allyl guaiacol substance having the chemical formula C10H12O2. Isoeugenol is a type of phenylpropene, and it is a substituted guaiacol. The key difference between eugenol and isoeugenol is that eugenol has a clove-like odour, whereas isoeugenol has a floral odour. In addition, eugenol is a pale yellow color liquid whereas the trans isomer of isoeugenol is a crystalline substance while its cis isomer is an oily liquid.
The following table shows a side by side comparison of the difference between eugenol and isoeugenol.
Summary – Eugenol vs Isoeugenol
Eugenol is an allyl guaiacol substance having the chemical formula C10H12O2. Isoeugenol is a type of phenylpropene and a substituted guaiacol. The key difference between eugenol and isoeugenol is that eugenol has a clove-like odour, whereas isoeugenol has a floral odour.
Reference:
1. “Eugenol (C10H12O2) – STRUCTURE, MOLECULAR Mass, Properties and Uses.” BYJU’S, 31 Mar. 2021.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Eugenol2DCSD” By Fuse809 (talk) – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Eugenol biosynthesis” By Kkrug12 – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
3. “Isoeugenol” By NEUROtiker ⇌ – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyerKCdnqS5bq3NnWSiq5%2BawqixzaijaA%3D%3D