What is the Difference Between Humic Acid Fulvic Acid and Humin
The key difference between humic acid fulvic acid and humin is that humic acid is the water-insoluble portion of soil that can dissolve at a different pH value, and fulvic acid is the water-soluble portion of the soil, whereas humin is insoluble in water at any pH.
Humic acid is the major component of humic substances, and it is an organic compound. Fulvic acid is a type of organic acid that occurs as a component of humus. Humin is a carbon-based macromolecular substance that occurs in soil or as a byproduct of saccharide-dependent biorefinery processes.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Humic Acid
3. What is Fulvic Acid
4. What is Humin
5. Humic Acid vs Fulvic Acid vs Humin in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Humic Acid vs Fulvic Acid vs Humin
What is Humic Acid?
Humic acid is the major component of humic substances, and it is an organic compound. It is the major organic fraction of soil, peat, and coal. Moreover, we can find it as a component in many upland organic fractions of upland streams, dystrophic lakes, and ocean water.
Earlier, humic acid was defined as an organic acid where the conjugate base of this acid is humate. According to this definition, humic acid is an organic substance that is extracted from soil that can coagulate upon acidification with a strong-base extract.
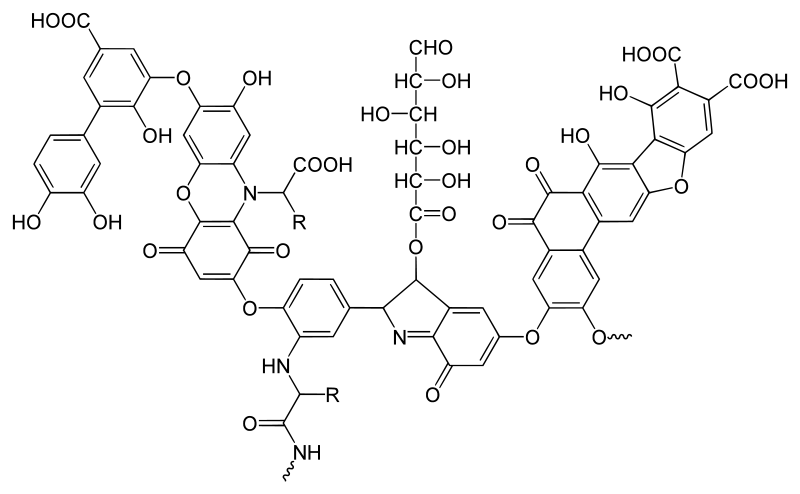
Figure 01: A Typical Humic Acid Structure
When humic acid is taken alone as an isolate, it is the result of a chemical extraction that comes from soil organic matter or dissolved organic matter, which represents humic molecules that are distributed throughout the soil water.
What is Fulvic Acid?
Fulvic acid is a type of organic acid that occurs as a component of humus. These are natural compounds. It occurs as a fraction of soil organic matter. Fulvic acid is similar to humic acid but with a slight difference in water solubility and color.
We can extract fulvic acid at high pH conditions by treating soil humus with a solution of NaOH. The dissolution of fulvic acid is favored by the dissociation and ionization of the carboxylic acid group and phenol group at high pH. There is an insoluble fraction of humus that remains after the leaching by NaOH known as humin. Followed by the extraction of fulvic acid using alkaline solutions, we can separate it from the reaction mixture by further acidification of the leachate. However, high molecular weight fulvic acid compounds can remain in the solution after the precipitation of the high molecular weight humic acids through acidification at pH = 1.
Furthermore, fulvic acid forms through microbial degradation of plant matter in soil having sufficient oxygen content. However, this compound does not readily synthesize. This is because of the extremely complex nature of this compound.
What is Humin?
Humin is a carbon-based macromolecular substance that occurs in soil or as a byproduct of saccharide-dependent biorefinery processes. In soil chemistry, we can see that soil contains both organic and inorganic compounds. Inorganic compounds are mostly minerals. We can divide the organic components in the soil into several fractions: soluble components, including humic acids, and insoluble components, including humin substances. The portion of humin in soil takes up about 50% of the organic matter in the soil. Humin has very complicated molecular structures. Therefore, we cannot find them as pure compounds but as mixtures with other compounds.
Moreover, humin compounds form during the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into small, high-valued organic compounds such as HMF. This type of humin substance forms as either liquids or solids based on the process conditions used.
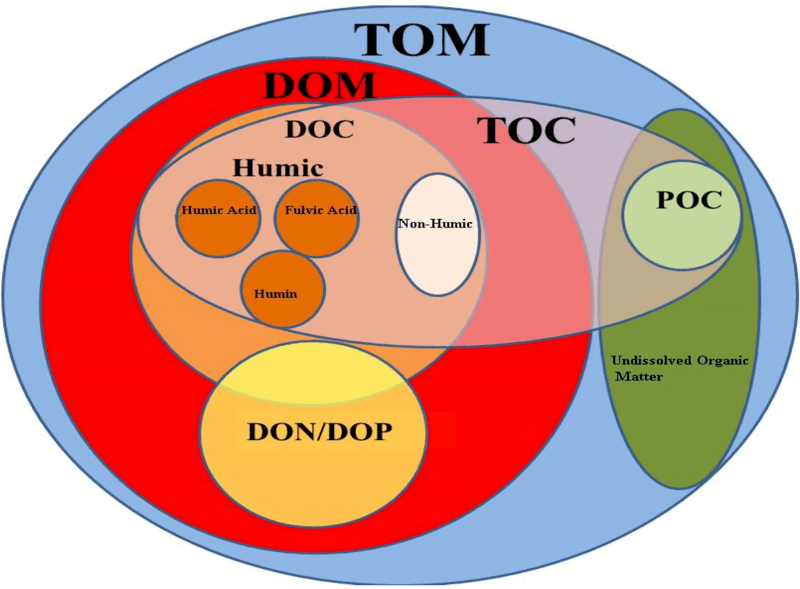
Figure 02: Organic Matter in the Soil
Generally, humin is not considered a dangerous substance. This means these substances are generally not flammable, explosive, susceptible to oxidation, corrosive, or eco-toxic. Furthermore, if we heat humin, it can form macroporous known named as humin foam. However, these materials do not present any critical fire behavior due to the highly porous structure.
What is the Difference Between Humic Acid Fulvic Acid and Humin?
Humic acid is a major component of humic substances, and it is an organic compound. Fulvic acid is a type of organic acid that occurs as a component of humus. Humin is a carbon-based macromolecular substance that occurs in soil or as a byproduct of saccharide-dependent biorefinery processes. The key difference between humic acid fulvic acid and humin is that humic acid is the water-insoluble portion of soil that can dissolve at a different pH value, and fulvic acid is the water-soluble portion of soil, whereas humin is insoluble in water at any pH.
The below infographic presents the differences between humic acid fulvic acid and humin in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Humic Acid vs Fulvic Acid vs Humin
Humic acid, fulvic acid, and humin are important components in soil. They are different in chemical structure and appearance mainly. The key difference between humic acid fulvic acid and humin is that humic acid is the water-insoluble portion of soil that can dissolve at a different pH value, and fulvic acid is the water-soluble portion of soil, whereas humin is insoluble in water at any pH.
Reference:
1. “Humic Acids, The Definition.” Triferto.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Humic acid” By Yikrazuul – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Forms of organic matter” By Todd Pagano, Morgan Bida and Jonathan E. Kenny from MDPI (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyhrKahk2KupLXDZp2upKaesG6twqKbZpmemXqpwcyipWg%3D