What is the Difference Between MOF and COF
The key difference between MOF and COF is that MOF contains metal atoms or clusters as nodes with organic linkers, whereas COF contains non-metal nodes.
The term MOF stands for Metal Organic Framework, while the term COF stands for Covalent Organic Framework.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is MOF
3. What is COF
4. MOF vs COF in Tabular Form
5. Summary – MOF vs COF
What is MOF?
MOF or metal organic frameworks are compounds containing metal ions or clusters that are coordinated to organic ligands forming 1D, 2D, or 3D structures. These compounds fall into a subclass of coordination polymers due to their special feature of being often porous. In the MOFs, the organic ligands are sometimes named “struts” or “linkers”.
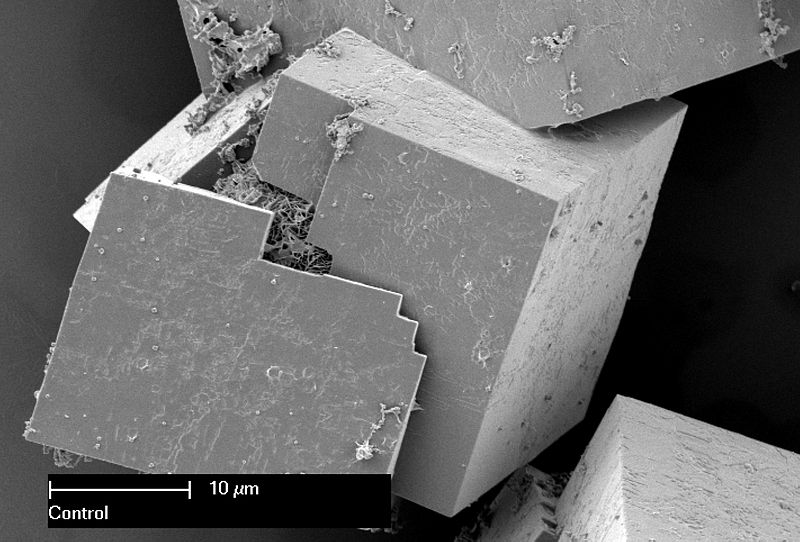
Figure 01: Electron Microscope Image of the Seed inside the MOF Crystals
Formally, we can name a metal-organic framework as a coordination network having organic ligands with potential voids. This type of coordination network can undergo coordination compound extending through the repetition of coordination entities. This extension occurs in one dimension but with the cross-linking between two or more chain structures, loops, or spiral structures, which causes the extension of the MOF in two or three dimensions.
Sometimes the pores in MOFs are stable during the elimination of the solvent. Therefore, we can refill that space with another compound. This feature makes MOFs useful for the storage of gases, including hydrogen and carbon dioxide gas. Moreover, MOFs are important in gas purification, gas separation, water remediation, catalysis and as supercapacitors.
What is COF?
COF or covalent organic frameworks are compounds that can form 2D or 3D structures, including covalent bonds between organic entities. These compounds form from the reaction between organic precursors, and the reaction gives strong covalent bonds forming porous, stable, and crystalline materials. These porous crystalline structures usually contain secondary building unit(s) that can assemble to form a periodic and porous framework. In this formation, an infinite number of frameworks form through different secondary building unit combinations, which leads to unique properties of the material. These unique properties make the compound important in separations, storage, and heterogeneous catalysis.
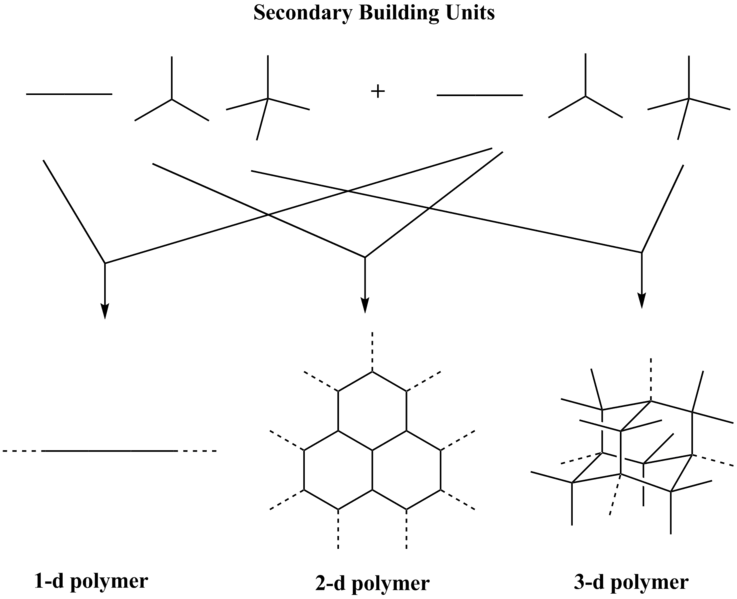
Figure 02: Different Secondary Building Units
The synthesis of covalent organic frameworks is done using a boron condensation reaction, where a molecular dehydration reaction occurs between boronic acids. Another method that can be used for this synthesis is triazine based trimerization.
What is the Difference Between MOF and COF?
The term MOF stands for Metal Organic Framework, while the term COF stands for Covalent Organic Framework. The key difference between MOF and COF is that MOF contains metal atoms or clusters as nodes with organic linkers, whereas COF contains non-metal nodes. Moreover, MOF can exist in 1D, 2D, or 3D structures, whereas COF occurs in 2D and 3D structures. Moreover, MOFs are important in gas purification, gas separation, water remediation, catalysis and are useful as supercapacitors, while COFs are useful in gas storage and separation, which include hydrogen storage and methane storage, for luminescence, carbon capture, catalysis, etc.
The following table presents the difference between MOF and COF in more detail.
Summary – MOF vs COF
MOF stands for Metal Organic Framework while COF stands for Covalent Organic Framework. The key difference between MOF and COF is that MOF contains metal atoms or clusters as nodes with organic linkers whereas COF contains non-metal nodes.
Reference:
1. Vaid, T.P., et al. “Structure-Directing Effects of Ionic Liquids in the Ionothermal Synthesis of Metal–Organic Frameworks.” IUCrJ, International Union of Crystallography, 30 June 2017.
Image Courtesy:
1. “CSIRO ScienceImage 11637 Scanning electron microscope image of the seed inside the MOF crystals” By CSIRO, (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Reticular figure” By Yoonsun – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoympp9lkaOxbq%2FOn2Y%3D