What is the Difference Between Proteinogenic and Non-proteinogenic Amino Acids
The key difference between proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids is that proteinogenic amino acids are involved in the generation of proteins, whereas non-proteinogenic amino acids are not involved in the synthesis of amino acids.
Proteinogenic amino acids are the amino acids that are incorporated into proteins through the translation process biosynthetically. Non-proteinogenic amino acids are the amino acids that are not naturally incorporated into proteins.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Proteinogenic Amino Acids
3. What are Non-proteinogenic Amino Acids
4. Proteinogenic vs Non-proteinogenic Amino Acids in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Proteinogenic vs Non-proteinogenic Amino Acids
What are Proteinogenic Amino Acids?
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated into proteins through translation biosynthetically. This term refers to the “protein-creating amino acids”. According to research studies, there are 22 genetically encoded or proteinogenic amino acids. Among them, 20 amino acids are among the standard genetic code, while the other two amino acids are incorporated into proteins through specific mechanisms.

Figure 01: List of Proteinogenic Amino Acids
Generally, in eukaryotes, there are only 21 proteinogenic amino acids which include the 20 standard genetic coding amino acids and selenocysteine. Among these amino acids, humans can generate 12 amino acids from each other or from the molecules of intermediary metabolism. However, the rest of the amino acids (9 amino acids) must be taken from outside, usually in their protein-derivative forms. Therefore, these amino acids are known as essential amino acids; this list includes histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
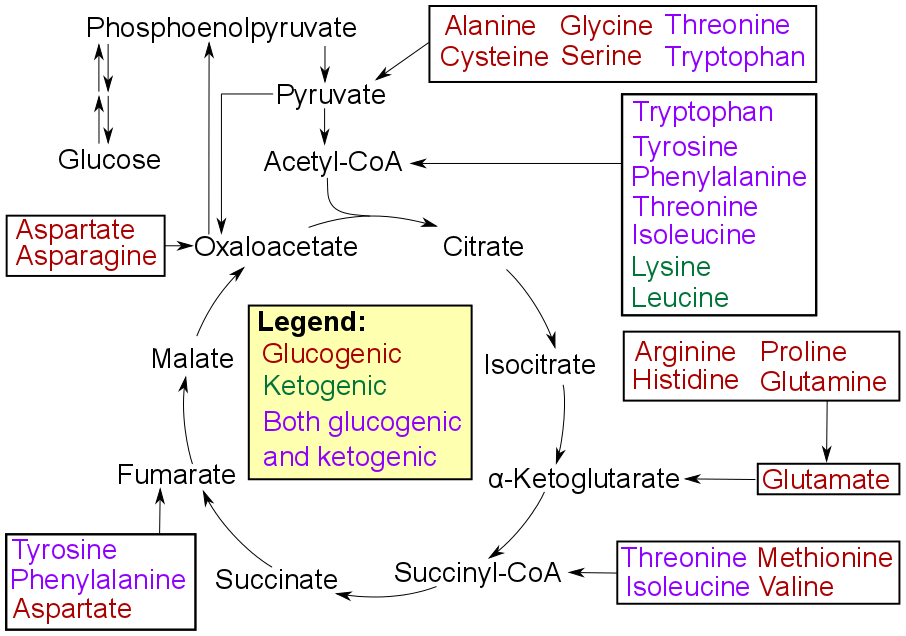
Figure 02: Catabolism of Proteinogenic Amino Acids
We can classify these amino acids according to the properties of the end products of the reactions that they take part in. These classes include glucogenic amino acids, ketogenic amino acids, and other amino acids that can be catabolized into both glucogenic and ketogenic products.
What are Non-proteinogenic Amino Acids?
Non-proteinogenic amino acids are the amino acids that are not naturally incorporated into proteins. These are also named non-coded amino acids. There are about 140 naturally occurring non-proteinogenic amino acids. These amino acids are important as intermediates in biosynthesis, in the post-translational formation of proteins, in physiological roles, in natural and man-made pharmacological compounds, etc.
Non-proteinogenic amino acids can be natural or synthetic. These amino acids are not naturally encoded or found in the genetic code of living organisms. The most common examples for this kind of amino acid include Ornithine, citrulline, Gamma-aminobutyric acid, etc.
What is the Difference Between Proteinogenic and Non-proteinogenic Amino Acids?
There are various amino acids that we can classify into various different groups according to their properties. Proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids are two such classes of amino acids. The key difference between proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids is that proteinogenic amino acids are involved in the generation of proteins, whereas non-proteinogenic amino acids are not involved in the synthesis of amino acids. Therefore, proteinogenic amino acids are incorporated into proteins during translation, whereas non-proteinogenic amino acids are not incorporated into proteins during translation.
The following table presents the difference between proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids in more detail.
Summary – Proteinogenic vs Non-proteinogenic Amino Acids
We can classify amino acids into various different groups according to their properties. The key difference between proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids is that proteinogenic amino acids are involved in the generation of proteins, whereas non-proteinogenic amino acids are not involved in the synthesis of amino acids.
Reference:
1. “What Are Proteinogenic Amino Acids?” Amino Acid Studies, 7 Apr. 2017.
2. “Proteinogenic Amino Acids.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Molecular structures of the 21 proteinogenic amino acids” By Dan Cojocari ✉·✍· – Own work This W3C-unspecified vector image was created with Adobe Illustrator. (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Amino acid catabolism revised” By Mikael Häggström – (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoypqaislZ67sLPEp6CcZZGjsW66zqdkqaqfqbKqus6gnKehk2KurrXNqGSam5mZwHA%3D