What is the Difference Between Thrombin and Prothrombin
The key difference between thrombin and prothrombin is that thrombin is an enzyme that facilitates blood clotting by converting fibrinogen to fibrin, while prothrombin is a glycoprotein that is converted into thrombin during bleeding and subsequent clotting.
Coagulation is the process that forms a blood clot in order to stop bleeding. In this process, blood changes from a liquid state to a gel, preventing blood loss while bleeding. This process is responsible for the cessation of blood loss from a damaged blood vessel, followed by subsequent repair. The coagulation cascade ultimately leads to fibrin formation that triggers blood clotting. Different coagulation factors participate in this process. Thrombin and prothrombin are two important constituents among them.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Thrombin
3. What is Prothrombin
4. Similarities – Thrombin and Prothrombin
5. Thrombin vs Prothrombin in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Thrombin vs Prothrombin
What is Thrombin?
Thrombin is an enzyme present in the blood that facilitates blood clotting. Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin. It is a serine protease, and in humans, it is encoded by the F2 gene. The prothrombin or coagulation factor II is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the blood clotting process. Subsequently, thrombin acts as a serine protease that converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin. Thrombin also catalyzes many other coagulation-related reactions. Initially, Alexander Schmidt hypothesized the existence of an enzyme that converts fibrinogen into fibrin in 1872.
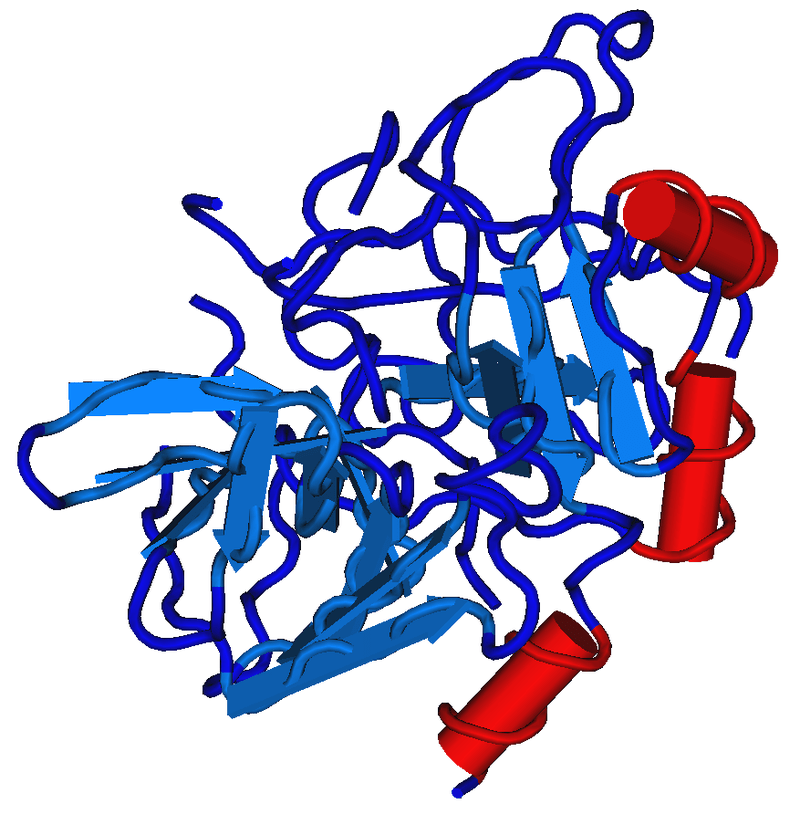
Figure 01: Thrombin
In the blood coagulation cascade, thrombin helps convert factor XI to Xia, VIII to VIIIa, V to Va, fibrinogen to fibrin, and XIII to XIIIa. Factor XIIIa is a transglutaminase that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between lysine and glutamine residues in fibrin. Covalent bonds increase the stability of fibrin clots. Thrombin also interacts with thrombomodulin. Moreover, thrombin promotes platelet activation and aggregation via the activation of protease-activated receptors on the cell membrane of the platelet. Thrombin plays a major role in many diseases. It is implicated as a major factor in vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. It also plays a role in cerebral ischemia and infarction and influences the onset and the progression of atherosclerosis. Furthermore, thrombin is a valuable research tool or biochemical tool due to its high proteolytic specificity. In addition, it is used in the food industry by combining with fibrinogen as a binding agent for meat.
What is Prothrombin?
Prothrombin is a glycoprotein that is converted into thrombin during bleeding and subsequent clotting. Its molecular weight is 72,000 Da. It is an alpha globulin and is present in the plasma at a concentration of 15 μg/ml. It is converted to an active enzyme by the action of tissue thromboplastins. Prothrombin is synthesized by the liver and has a half-life short as 10-12 hours and long as 60 hours. Both the biosynthesis and release of prothrombin require the action of vitamin K. Warfarin blocks prothrombin synthesis at an intermediate step, which can be overcome by the administration of vitamin K. Vitamin K is also required for three other clotting factors, including factors Vii, IX, and X. Moreover, the entire amino acid sequence of prothrombin has already been defined.
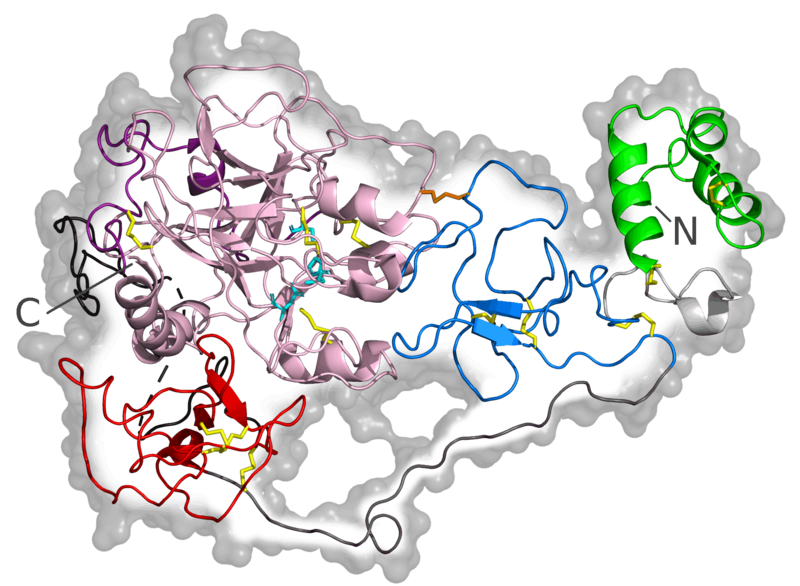
Figure 02: Prothrombin
Prothrombin is composed of four domains: N terminal Gla domain, two kringle domains, and a C-terminal trypsin-like serine protease domain. Hypoprothrombinemia, hyperprothrombinemia, and antiphospholipid syndrome are among a few rare diseases involving prothrombin. Furthermore, medically prothrombin complex concentrate and fresh frozen plasma can be used to correct deficiencies of prothrombin and intractable bleeding due to warfarin.
What are the Similarities Between Thrombin and Prothrombin?
- Thrombin and prothrombin are two important constituents of the coagulation cascade.
- They are proteins present in blood plasma.
- Both molecules are encoded by the F2 gene in chromosome 11.
- These molecules play major roles in various diseases.
What is the Difference Between Thrombin and Prothrombin?
Thrombin is an enzyme that facilitates blood clotting by converting fibrinogen to fibrin, while prothrombin is a glycoprotein that is converted into thrombin during bleeding and subsequent clotting. Thus, this is the key difference between thrombin and prothrombin. Furthermore, thrombin contains only the C-terminal trypsin-like serine protease domain, while prothrombin contains four domains, including the N terminal Gla domain, two kringle domains, and a C-terminal trypsin-like serine protease domain.
The below infographic presents the differences between thrombin and prothrombin in tabular form for side-by-side comparison.
Summary – Thrombin vs Prothrombin
Thrombin and prothrombin are two important constituents of the coagulation cascade. Thrombin is an enzyme that facilitates blood clotting by converting fibrinogen to fibrin, while prothrombin is a glycoprotein that is converted into thrombin during bleeding and subsequent clotting. So, this is the key difference between thrombin and prothrombin.
Reference:
1. “Thrombin.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
2. “Prothrombin.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
Image Courtesy:
1. “2HNT Gamma-Thrombin” By Nevit Dilmen – Self created from PDB entry with Cn3D Data Source: (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Human prothrombin mutant 6C2W closed structure” By 5-HT2AR – Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoytn6unnZe2r3nAp5tmqKKkwam%2BzqaZoqZf